|
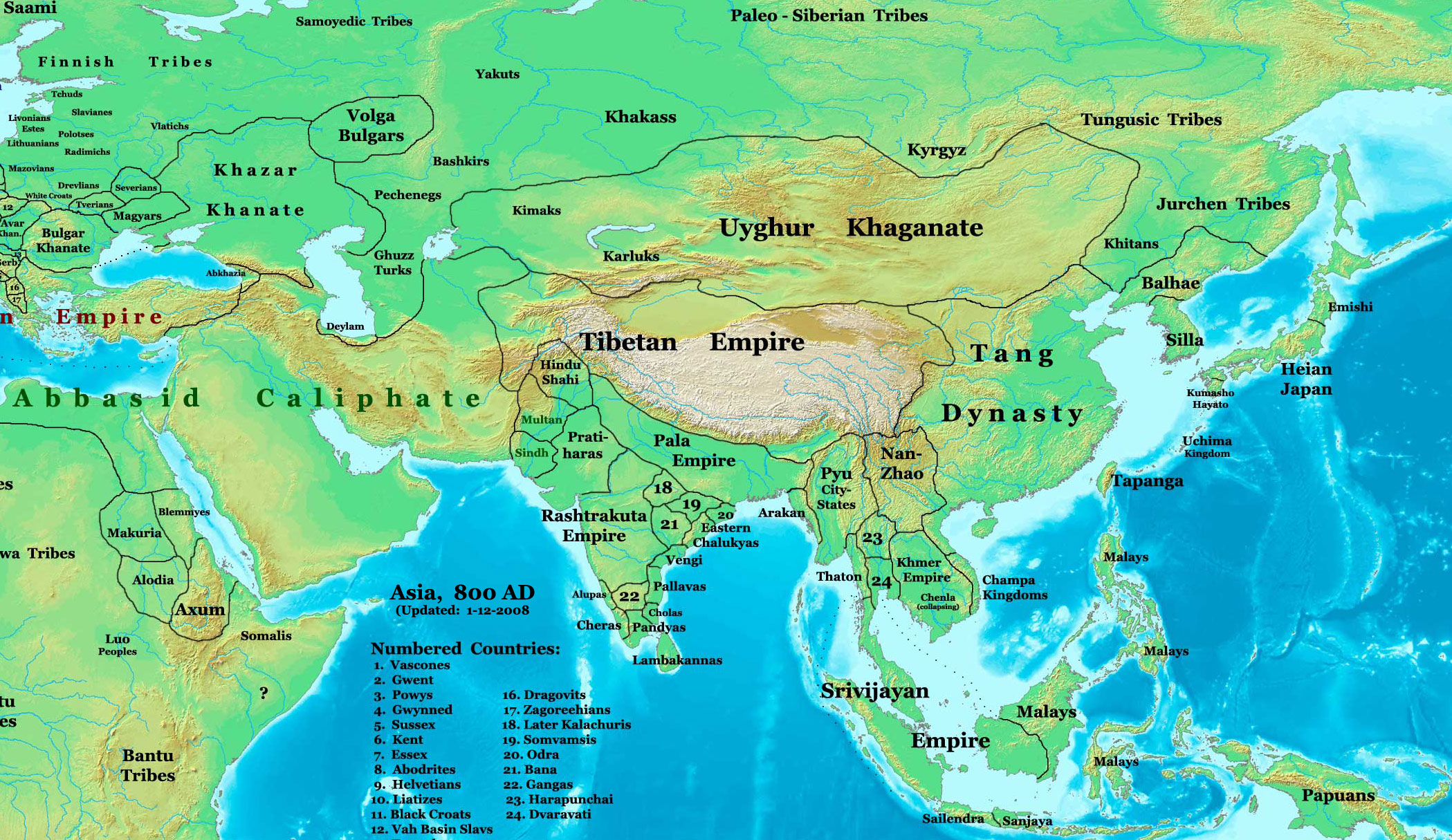
Magadha Empire (other)
The Magadha period refers to the era in the history of Indian subcontinent when several Magadha based empires or Magadha Empires asserted dominance over the region. A table of its rulers is shown below. For a general view of the history and culture of the Magadha region, see Magadha. Magadha empire may refer to: See also * Magadha * Magadha-Vajji war * Magadha-Anga war * Avanti-Magadhan Wars * List of Indian monarchs The following list of Indian monarchs is one of several lists of incumbents. It includes those said to have ruled a portion of the Indian subcontinent, including Sri Lanka. The earliest Indian rulers are known from epigraphical sources fo ... References {{reflist Magadha History of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka."Indian subcontinent". ''Oxford Dictionary of English, New Oxford Dictionary of English'' () New York: Oxford University Press, 2001; p. 929: "the part of Asia south of the Himalayas which forms a peninsula extending into the Indian Ocean, between the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Historically forming the whole territory of Greater India, the region is now divided into three countries named Bangladesh, India and Pakistan." The terms ''Indian subcontinent'' and ''South Asia'' are often used interchangeably to denote the region, although the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an empire that reached its peak under the reign of his grandson, Ashoka, Asoka, from 268 BCE to 231 BCE. The nature of the political formation that existed in Chandragupta's time is not certain. The Mauryan empire was a loose-knit empire. Quote: "The geography of the Mauryan Empire resembled a spider with a small dense body and long spindly legs. The highest echelons of imperial society lived in the inner circle composed of the ruler, his immediate family, other relatives, and close allies, who formed a dynastic core. Outside the core, empire travelled stringy routes dotted with armed cities. Outside the palace, in the capital cities, the highest ranks in the imperial elite were held by military commanders whose active loyalty and success in war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauḍa (city)
Gauḍa (also known as Gaur, Gour, Lakhnauti, and Jannatabad) is a historic city of Bengal in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, and one of the most prominent capitals of classical and medieval India, being the capital city of Bengal under several kingdoms. The Gauḍa region was also a province of several pan-Indian empires. During the seventh century, the Gauda Kingdom was founded by King Shashanka, whose reign corresponds with the beginning of the Bengali calendar. Gauda gradually became synonymous with Bengal and Bengalis. It was conquered by Bakhtiyar Khalji, a lieutenant of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor in 1203. For a period of 112 years, between 1453 and 1565, Gauda was the capital of the Bengal Sultanate. In 1500, Gauda was the fifth-most populous city in the world, with a population of 200,000, as well as one of the most densely populated cities in the Indian subcontinent. The Portuguese left detailed accounts of the city. The Sultans built a citadel, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bikrampur
Bikrampur ("City of Courage") was a pargana situated south of Dhaka, the modern capital city of Bangladesh. In the present day, it is known as Munshiganj District of Bangladesh. It is a historic region in Bengal and was a part of the Bhawal Estate. History Early history Ashoka, the emperor of the Maurya Dynasty, ruled all of major parts of Bengal from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. Being a devotee of Gautama Buddha, he propagated Buddhism across his kingdom which included Bikrampur to the east. Following the high ideals of this religion, Pala Kings came to Bikrampur to rule the region. Pala Era The second ruler of Pala Empire, Dharmapal, built a Buddhist monastery in Bikrampur during his reign in 770–810. After his death, his son, Devapala ruled this area until 850 CE. Then the region is successively ruled by Vigrahapala I, Narayanapala, Rajyapala, Gopala II, Vigrahapala II, Mahipala, Naya Pala, Vigrahapala III, Mahipala II, Shurapala II, Ramapala, Kumarapala, Gopala III and Mada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharmapala (emperor)
Dharmapala (Siddhamātṛikā Script: , Dha-rmma-pā-la; Bangla: ধর্মপাল)(ruled between 770s-810s AD) was the second ruler of the Pala Empire of Bengal and Bihar regions in the Indian subcontinent. He was the son and successor of Gopala, the founder of the Pala Dynasty. He greatly expanded the boundaries of the empire, and made the Palas a dominant power in the northern and eastern India. Dharmapala directly ruled over the present-day Bengal and Bihar, and installed a nominee at Kannauj. The Pala chronicles also claim that several other rulers of North India acknowledged his suzerainty, but these claims seem to be exaggerated. Dharmapala was defeated twice by the Gurjara-Pratiharas, but each time the Rashtrakutas subsequently defeated the Pratiharas, leaving Palas as the dominant power in North India. Dharmapala was succeeded by his son Devapala who further expanded the empire. Reign Based on the different interpretations of the various epigraphs and historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire (r. 750-1161 CE) was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix ''Pāla'' ("protector" in Prakrit). The empire was founded with the election of Gopāla as the emperor of Gauda in late eighth century AD. The Pala stronghold was located in Bengal and eastern Bihar, which included the major cities of Gauḍa, Vikramapura, Pāṭaliputra, Monghyr, Somapura, Ramavati (Varendra), Tāmralipta and Jaggadala. The Pālas were astute diplomats and military conquerors. Their army was noted for its vast war elephant corps. Their navy performed both mercantile and defensive roles in the Bay of Bengal. At its zenith under emperors Dharmapala and Devapala in the early ninth century, the Pala empire extended their dominance into the northern Indian region, with its territory stretching across the Gangetic pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishna-gupta
The Later Gupta dynasty ruled the Magadha region in eastern India between the 6th and 8th centuries CE. The Later Guptas succeeded the imperial Guptas as the rulers of Magadha, but there is no evidence connecting the two dynasties; these appear to be two distinct families. The Later Guptas are so-called because the names of their rulers ended with the suffix "-gupta" ( Late Brahmi: ''gu-pta''), which they might have adopted to portray themselves as the successors of the imperial Guptas. History After the decline of the Gupta Empire, the Later Guptas succeeded them as the rulers of Magadha. The daughter of the dynasty's founder Krishnagupta is said to have married prince Adityavarman of the Maukhari dynasty. According to the Aphsad inscription of Ādityasena, Krishnagupta's grandson Jivitagupta carried out military expeditions in the Himalayan region and southwestern Bengal. During the reign of Jivitagupta's son Kumaragupta, the dynasty developed a rivalry with the Maukharis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Gupta Dynasty
The Later Gupta dynasty ruled the Magadha region in eastern India between the 6th and 8th centuries CE. The Later Guptas succeeded the imperial Guptas as the rulers of Magadha, but there is no evidence connecting the two dynasties; these appear to be two distinct families. The Later Guptas are so-called because the names of their rulers ended with the suffix "-gupta" ( Late Brahmi: ''gu-pta''), which they might have adopted to portray themselves as the successors of the imperial Guptas. History After the decline of the Gupta Empire, the Later Guptas succeeded them as the rulers of Magadha. The daughter of the dynasty's founder Krishnagupta is said to have married prince Adityavarman of the Maukhari dynasty. According to the Aphsad inscription of Ādityasena, Krishnagupta's grandson Jivitagupta carried out military expeditions in the Himalayan region and southwestern Bengal. During the reign of Jivitagupta's son Kumaragupta, the dynasty developed a rivalry with the Maukharis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta (king)
Gupta (Gupta script: ''Gu-pta'', fl. late 3rd century CE) was the founder of the Gupta dynasty of northern India. He is identified with king Che-li-ki-to (believed to be the Chinese transcription of "''Shri''-Gupta"), who, according to the 7th century Chinese Buddhist monk Yijing, built a temple near Mi-li-kia-si-kia-po-no ( Mṛgaśikhāvana) for Chinese pilgrims. Name Gupta is not attested by his own inscriptions or coins, although some seals and coins have been wrongly attributed to him. The earliest description of him occurs in his great-grandson Samudragupta's Allahabad Pillar inscription, and is repeated verbatim in several later records of the dynasty: The Allahabad Pillar inscription names Samudragupta's ancestors as ''Shrī'' Gupta ( ''shri gu-pta''), ''Shrī'' Ghatotkacha, and ''Shrī'' Chandragupta. Some earlier scholars believed that the name of the dynasty's founder was "Shri-gupta" (IAST: Śrigupta), as Gupta does not appear to be a given name. However, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Golden Age of India by historians. The ruling dynasty of the empire was founded by the king Sri Gupta; the most notable rulers of the dynasty were Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Skandagupta. The 5th-century CE Sanskrit poet Kalidasa credits the Guptas with having conquered about twenty-one kingdoms, both in and outside India, including the kingdoms of Parasikas, the Hunas, the Kambojas, tribes located in the west and east Oxus valleys, the Kinnaras, Kiratas, and others.Raghu Vamsa v 4.60–75 The high points of this period are the great cultural developments which took place primarily during the reigns of Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Kumaragupta I. Many Hindu epics and literary sources, such as Mahabharata and Ramay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
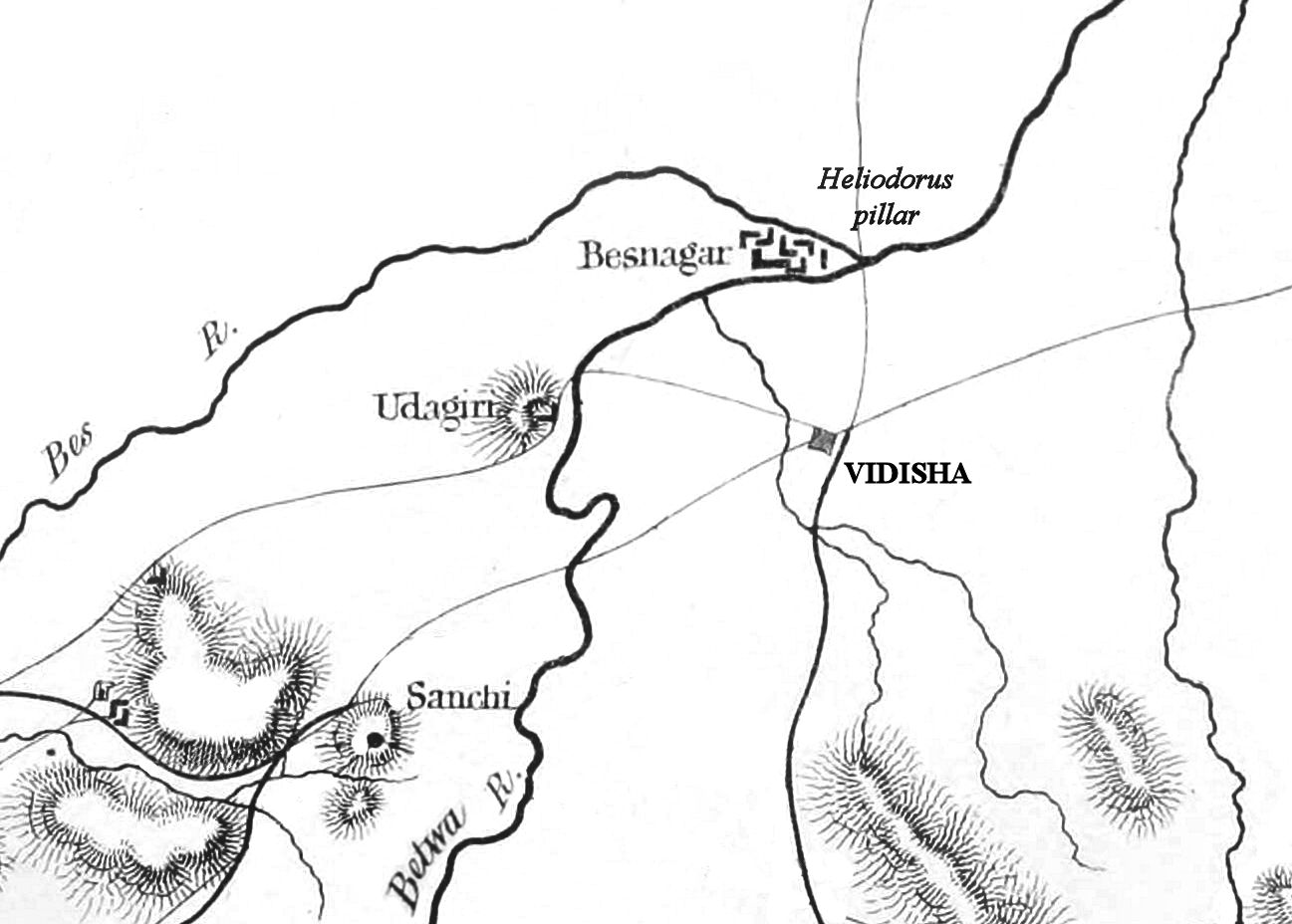
Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas. The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat state, which was formed in 1948. Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018. Demographics As of the 2011 Census of India, Vidisha had a population of 155,959. Males constitute 53.21% of the population and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasudeva Kanva
Vasudeva Kanva () was the founder of the Kanva dynasty. He was originally an Amatya (minister) of last Shunga ruler Devabhuti. Vasudeva killed the last Shunga ruler and established Kanva dynasty. Bana's Harshacharita informs us that he came to power after the death of Devabhuti by a daughter of his slave woman disguised as his queen. He was succeeded by his son Bhumimitra. Ascension to power He was originally an Amatya (minister) of last Shunga ruler Devabhuti. Vasudeva killed the last Shunga ruler and established Kanva dynasty. Bana's Harshacharita informs us that he came to power after the death of Devabhuti by a daughter of his slave woman disguised as his queen. Reign He was a Vaishnavite (worhsipper of Lord Vishnu). Most of the taxes collected during his reign were used for temples. He was one of the famous patrons of arts. During his reign, the Indo-Greeks invaded, but he managed to keep his throne. He was succeeded by his son Bhumimitra.- See also * Dushyanta * Shakunt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |