|
Maddale
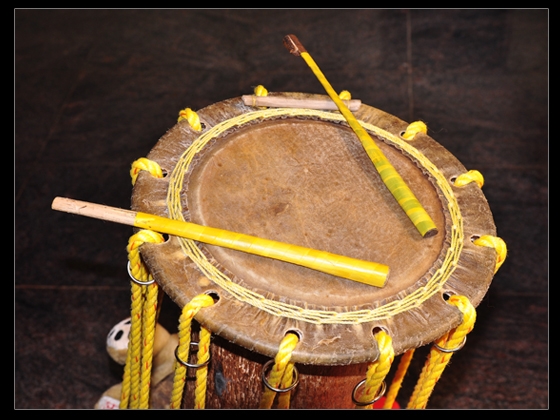
The Maddale ( kn, ಮದ್ದಲೆ) also called Mrudanga(ಮೃದಂಗ) in North Canara region is a percussion instrument from Karnataka, India. It is the primary rhythmic accompaniment in a Yakshagana ensemble along with Chande. Maddale also represents a remarkable progress in percussive instruments as it produces the perfectly hormonic tonic (shruti swara) when played anywhere on the surface compared to Mrudangam, Pakawaj or Tabla that can not produce the tonic (shruti) on all parts of the drum surface. The traditional variety of Maddale was 30 cm long, had 8 inch drum head for right and produced the louder sound. These days 6 - 6.5 inch wide right side maddale is used with only a few using 7 inch wide. Left bass side is about an inch (few hairs less) bigger than right. Maddale is available in more than three different variations. Maddale used in Yakshagana looks similar to mridangam but is markedly different in structure, acoustics, playing techniques and the rhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tala-Maddale
Tala-Maddale is an ancient form of performance dialogue or debate performance in Southern India in the Karavali and Malnad regions of Karnataka and Kerala. The plot and content of the conversation is drawn from popular mythology but the performance mainly consists of an impromptu debate between characters involving sarcasm, puns, philosophy positions and humour. The main plot is sung from the same oral texts used for the Yakshgana form of dance- drama. Performers claim that this was a more intellectual rendition of the dance during the monsoon season. The art form is popular in Uttara Kannada, Dakshina Kannada, Udupi and Shimoga districts of Karnataka and Kasaragod district of Kerala. It is a derived form of Yakshagana—a classical dance or musical form of art from the same region. Performances A typical Tala-Maddale show consists of veteran artists sitting in a circular fashion along with a Bhagavata (the singer, with "Tala" or pair of small hand cymbals) and "Maddale" (a typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maddale
The Maddale ( kn, ಮದ್ದಲೆ) also called Mrudanga(ಮೃದಂಗ) in North Canara region is a percussion instrument from Karnataka, India. It is the primary rhythmic accompaniment in a Yakshagana ensemble along with Chande. Maddale also represents a remarkable progress in percussive instruments as it produces the perfectly hormonic tonic (shruti swara) when played anywhere on the surface compared to Mrudangam, Pakawaj or Tabla that can not produce the tonic (shruti) on all parts of the drum surface. The traditional variety of Maddale was 30 cm long, had 8 inch drum head for right and produced the louder sound. These days 6 - 6.5 inch wide right side maddale is used with only a few using 7 inch wide. Left bass side is about an inch (few hairs less) bigger than right. Maddale is available in more than three different variations. Maddale used in Yakshagana looks similar to mridangam but is markedly different in structure, acoustics, playing techniques and the rhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakshagana
Yakshagaana is a traditional theatre, developed in Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, Uttara Kannada, Shimoga and western parts of Chikmagalur districts, in the state of Karnataka and in Kasaragod district in Kerala that combines dance, music, dialogue, costume, make-up, and stage techniques with a unique style and form. It is believed to have evolved from pre-classical music and theatre during the period of the Bhakti movement.Prof. Sridhara Uppura; 1998; ''Yakshagana and Nataka Diganta''; publications. It is sometimes simply called "Aata" or ''āṭa'' (meaning "the play"). This theatre style is mainly found in coastal regions of Karnataka in various forms. Towards the south from Dakshina Kannada to Kasaragod of Tulu Nadu region, the form of Yakshagana is called ' and towards the north from Udupi up to Uttara Kannada it is called '. Both of these forms are equally played all over the region.(Not sure about this one but) Yakshagana is traditionally presented from dusk to dawn. Its stories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chande
The ''chande'' is a drum used in the traditional and classical music of South India and particularly in Yakshagana theatre art of Karnataka. It follows the Yakshagana Tala system. The rhythms are based on pre-classical music forms that Karnataka Sangeta and Hindustani Sangeetha are based on.''Prof. Sridhara Uppura, Yakshagana and Nataka, Diganta Sahitya Publications, 1998, Managalore. There are different varieties of this instrument; two major varieties being the ''Badagu Thittu Chande'' (Northern School) and the ''Thenku Thittu Chande'' (Southern School). The latter can also be spelled ''chenda'' and is used exclusively in the art forms of southern coastal Karnataka and Kerala. This article deals with ''Badagu Thittu Chande'', used exclusively in Yakshagana of Karnataka. The chande used in ''Badagu Thittu'' is structurally and acoustically different from the ''chenda'' used in Kerala. History In ancient Hindu sculpture, painting, and mythology, the ''chande'' is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
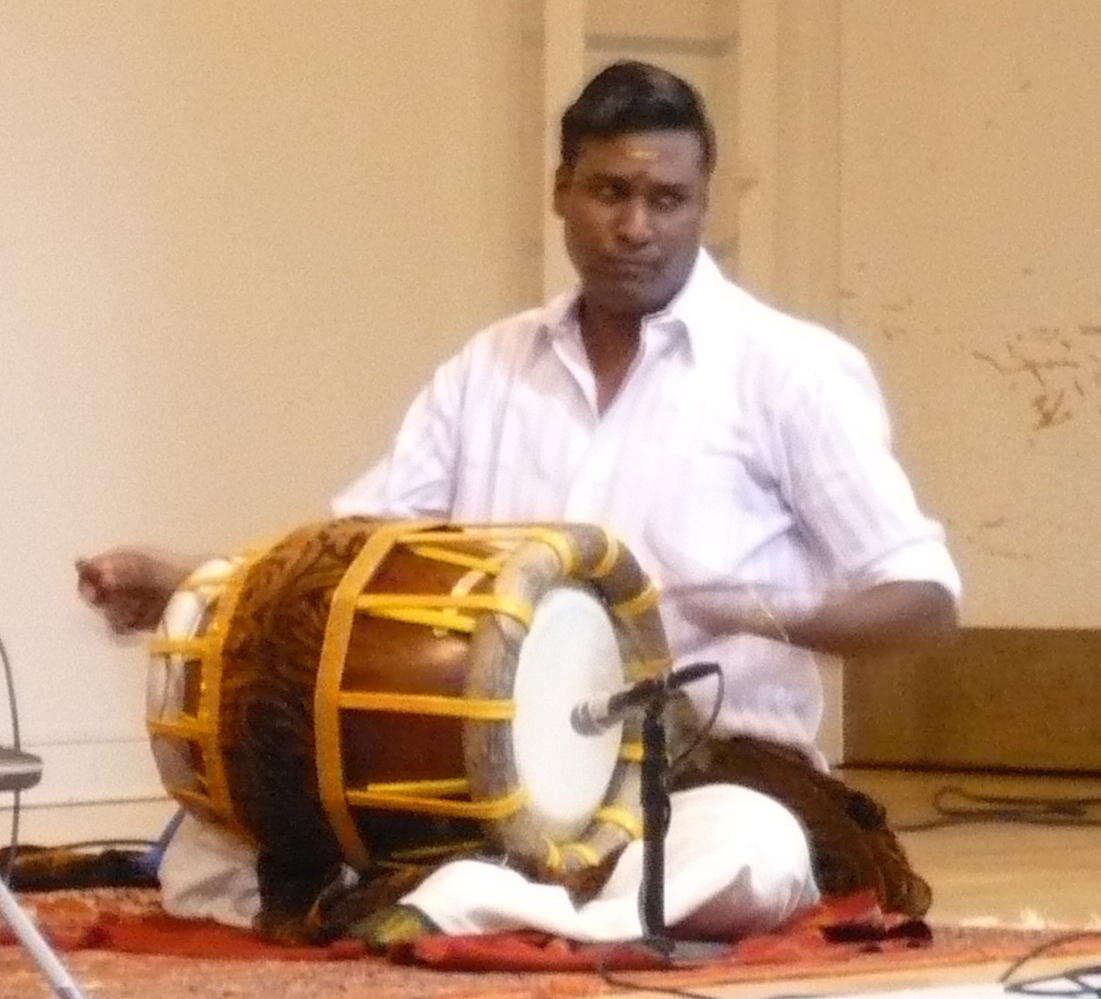
Mridanga
The khol is a terracotta two-sided drum used in northern and eastern India for accompaniment with devotional music (''bhakti''). It is also known as a mridanga (< + , ), not to be confused with ''''. It originates from the Indian states of , and . The drum is played with palms and fingers of both hands. Description The khol is regarded as resembling to the ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakshagana Tala
Yakshagana Tala (Kannada:ಯಕ್ಷಗಾನ ತಾಳ, pronounced as ''yaksha-gaana taala''), is a rhythmical pattern in Yakshagana that is determined by a composition called Yakshagana Padya. Tala also decides how a composition is enacted by dancers. It is similar to Tala in other forms of Indian music, but is structurally different from them. Each composition is set to one or more talas, and as a composition is rendered by Himmela, the percussion artist(s) play supporting the dance performance.Prof. Sridhara Uppara. 1998.Yakshagana and Nataka Diganta publications Tala is maintained by the singer using a pair of finger bells. The instrument for rhythm in Yakshagana are the Chande, Maddale and a Yakshagana Tala (bell) is also used along with chande. Yakshagana has a complete and complex system for rhythms. The most common Talas in Yakshagana are Matte, Eaka,Udaape, Jampe, Rupaka, Trivde, Atta, KorE and Aadi. Each tala has a cycle of N beats divided in M bars. Some talas are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
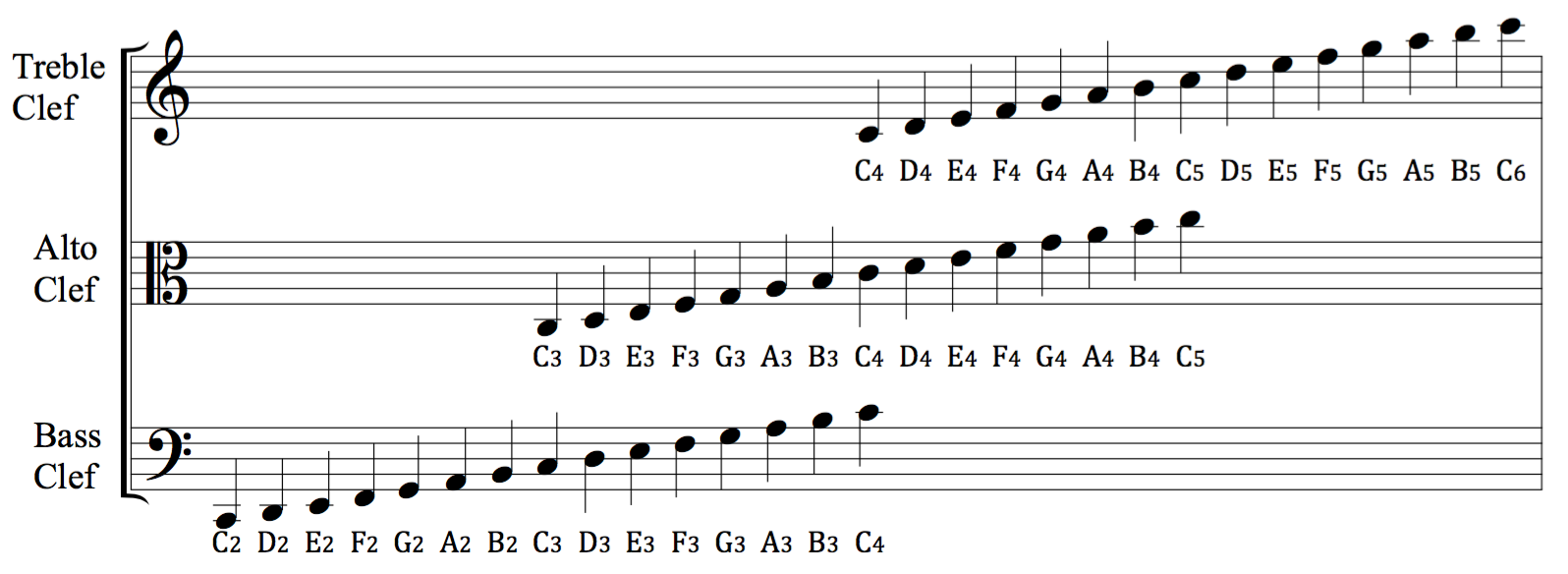
Clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces. The three clef symbols used in modern music notation are the G-clef, F-clef, and C-clef. Placing these clefs on a line fixes a reference note to that line—an F-clef fixes the F below middle C, a C-clef fixes middle C, and a G-clef fixes the G above middle C. In modern music notation, the G-clef is most frequently seen as treble clef (placing G4 on the second line of the stave), and the F-clef as bass clef (placing F3 on the fourth line). The C-clef is mostly encountered as alto clef (placing middle C on the third line) or tenor clef (middle C on the fourth line). A clef may be placed on a space instead of a line, but this is rare. The use of different clefs makes it possible to write music for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand Drums
A hand drum is any type of drum that is typically played with the bare hand rather than a stick, mallet, hammer, or other type of beater. Types The following descriptions allude to traditional versions of the drums. Modern synthetic versions are available for most if not all of the drums listed through various manufacturers. Middle and Near East *The tar is a frame drum common in Middle Eastern music. *The tambourine is a frame drum with jingles attached to the shell. *The daf and the dayereh are Iranian frame drums. *The ghaval is the Azerbaijani frame drum. *The tonbak is the Persian goblet drum. *The doumbek is a goblet shaped drum used in Arabic, Jewish, Assyrian, Persian, Balkan, Greek, Armenian, Azeri and Turkish music. * Mirwas Africa *The most common African drum known to westerners is the djembe, a large, single-headed drum with a goblet shape. *The Ashiko is another African drum in the shape of a truncated cone. Similar to the Djembe it is rope strung. This drum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnatic Music Instruments
Carnatic most often refers to: *Carnatic region, Southern India *Carnatic music, the classical music of Southern India Carnatic may also refer to: *Carnatic Wars, a series of military conflicts in India during the 18th century *, a ''Bangor''-class minesweeper of the Royal Indian Navy, that served in World War II *, a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Deptford in 1783 *, a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Portsmouth Dockyard in 1823 * – one of several vessels of that name *Carnatic Hall Carnatic Hall was an 18th-century mansion that was located in Mossley Hill, Liverpool, England. The house was built in 1779 for slave trader Peter Baker, who served as Mayor of Liverpool in 1795. Originally on the site of Mossley Hall (home o ..., built by slave trader, now closed university residence {{disambiguation, ship ca:Carnàtic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karatalas
The taal, manjira (also spelled manjīrā or manjeera), jalra, karatala, kartal or gini is a pair of clash cymbals, originating in the Indian subcontinent, which make high-pitched percussion sounds. In its simplest form, it consists of a pair of small hand cymbals. The word taal comes from the Sanskrit word ''Tālà'', which literally means a clap. It is a part of Indian music and culture, used in various traditional customs e.g. Bihu music, Harinaam etc. It is a type of Ghana vadya. In Hindu religious contexts it is known as karatalas (; ''kara'' "hand", "arm" and ''tāla'' "rhythm", "beat"), typically used to accompany devotional music such as bhajan and kirtan. They are commonly used by Hare Krishna devotees when performing harinam, but are ubiquitous to all Hindu devotional music. It is also called karatala or kartal (pronounced as “kartel”) in some contexts. Types There are many types of Taal, categorised by size, weight and appearance. * Bortaal is the big size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thavil
A ''thavil'' (Tamil:தவில்) or ''tavil'' is a barrel-shaped percussion instrument from Tamil Nadu. It is also widely used in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamilnadu and Telangana States of South India. It is used in temple, folk and Carnatic music, often accompanying the '' nadaswaram''. The ''thavil'' and the ''nadaswaram'' are essential components of traditional festivals and ceremonies in South India. In folk music contexts, a pair of wider, slimmer sticks are sometimes used. Thanjavur is famous for ''thavil'', so called ''Thanjavur Thavil''. In Kollywood Filmi songs thavils are mostly used, Notable movies: " Thillaanaa Mohanambal", "Paruthiveeran", " Karagattakaran", "Sarvam Thaala Mayam". History Thavil is a traditional musical instrument of the ancient city of Thanjavur in Tamil Nadu. It is an integral part of the Carnatic music in Thanjavur. It is mostly made in Thanjavur and Valayapatti. Physical components The ''thavil'' consists of a cylindric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabla
A tabla, bn, তবলা, prs, طبلا, gu, તબલા, hi, तबला, kn, ತಬಲಾ, ml, തബല, mr, तबला, ne, तबला, or, ତବଲା, ps, طبله, pa, ਤਬਲਾ, ta, தபலா, te, తబలా, ur, , group="nb", name="nb" is a pair of twin hand drums from the Indian subcontinent, that are somewhat similar in shape to the bongos. Since the 18th century, it has been the principal percussion instrument in Hindustani classical music, where it may be played solo, as accompaniment with other instruments and vocals, and as a part of larger ensembles. It is frequently played in popular and folk music performances in India, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nepal and Sri Lanka.Tabla Encyclopædia Britannica The tabla is an essential instrument in the bhakti devotional traditions of Hinduism and Sikhism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |