|
MOVIE Index
The MOtion-tuned Video Integrity Evaluation (MOVIE) index is a model and set of algorithms for predicting the perceived quality of digital television and cinematic pictures, as well as other kinds of digital images and videos. It was developed by Kalpana Seshadrinathan and Alan Bovik in the Laboratory for Image and Video Engineering (LIVE) at The University of Texas at Austin. It was described in print in the 2010 technical paper "Motion Tuned Spatio-Temporal Quality Assessment of Natural Videos". The original MOVIE paper was accorded an IEEE Signal Processing Society Best Journal Paper Award in 2013. Model overview The MOVIE index is a neuroscience-based model for predicting the perceptual quality of a (possibly compressed or otherwise distorted) motion picture or video against a pristine reference video. Thus, the MOVIE index is a full-reference metric. The MOVIE model is quite different from many other models since it uses neuroscience-based models of how the human brain proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Bovik
Alan Conrad Bovik (born June 25, 1958) is an American engineer, vision scientist, and educator. He is a professor at the University of Texas at Austin (UT-Austin), where he holds the Cockrell Family Regents Endowed Chair in the Cockrell School of Engineering and is Director of the Laboratory for Image and Video Engineering (LIVE). He is a faculty member in the UT-Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, the Machine Learning Laboratory, the Institute for Neuroscience, and the Wireless Networking and Communications Group. Bovik received a Primetime Emmy Award in 2015 for his development of perception-based video quality measurement tools that are now standards in television production. He also received a Technology and Engineering Emmy Award in 2021 for the “development of perceptual metrics for video encoding optimization.” Work Al Bovik was educated at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign (PhD 1984). He has made numerous fundamental contributions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
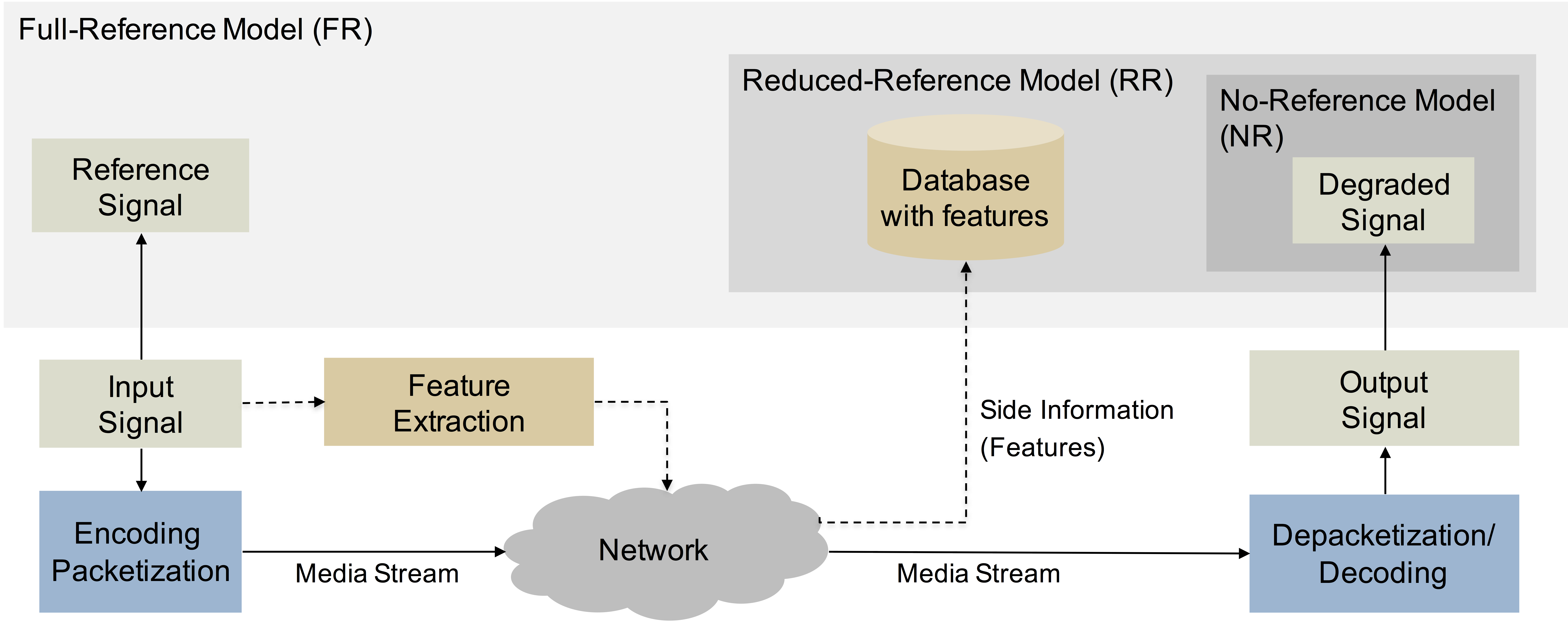
Video Quality
Video quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation (typically, compared to the original video). Video processing systems may introduce some amount of distortion or artifacts in the video signal that negatively impacts the user's perception of a system. For many stakeholders in video production and distribution, assurance of video quality is an important task. Video quality evaluation is performed to describe the quality of a set of video sequences under study. Video quality can be evaluated objectively (by mathematical models) or subjectively (by asking users for their rating). Also, the quality of a system can be determined offline (i.e., in a laboratory setting for developing new codecs or services), or in-service (to monitor and ensure a certain level of quality). From analog to digital video Since the world's first video sequence was recorded and transmitted, many video processing sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, ventral projection of the thalamus where the thalamus connects with the optic nerve. There are two LGNs, one on the left and another on the right side of the thalamus. In humans, both LGNs have six layers of neurons (grey matter) alternating with optic fibers (white matter). The LGN receives information directly from the ascending retinal ganglion cells via the optic tract and from the reticular activating system. Neurons of the LGN send their axons through the optic radiation, a direct pathway to the primary visual cortex. In addition, the LGN receives many strong feedback connections from the primary visual cortex. In humans as well as other mammals, the two strongest pathways linking the eye to the brain are those projecting to the dorsal part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Visual Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each hemisphere's V1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrastriate Cortex
The extrastriate cortex is the region of the occipital cortex of the mammalian brain located next to the primary visual cortex. Primary visual cortex (V1) is also named striate cortex because of its striped appearance in the microscope. The extrastriate cortex encompasses multiple functional areas, including V3, V4, V5/MT, which is sensitive to motion,Guy A. Orban. Higher Order Visual Processing in Macaque Extrastriate Cortex. ''Physiol Rev'' January 1, 2008 88:(1) 59-89; or the extrastriate body area (EBA) used in the perception of human bodies. Anatomy In terms of Brodmann areas, the extrastriate cortex comprises Brodmann area 18 and Brodmann area 19, while the striate cortex comprises Brodmann area 17. In primates, the extrastriate cortex includes visual area V3, visual area V4, and visual area MT (sometimes called V5), while V1 corresponds to the striate cortex, and V2 to the prestriate cortex. See also *List of regions in the human brain The human brain anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Quality
Video quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation (typically, compared to the original video). Video processing systems may introduce some amount of distortion or artifacts in the video signal that negatively impacts the user's perception of a system. For many stakeholders in video production and distribution, assurance of video quality is an important task. Video quality evaluation is performed to describe the quality of a set of video sequences under study. Video quality can be evaluated objectively (by mathematical models) or subjectively (by asking users for their rating). Also, the quality of a system can be determined offline (i.e., in a laboratory setting for developing new codecs or services), or in-service (to monitor and ensure a certain level of quality). From analog to digital video Since the world's first video sequence was recorded and transmitted, many video processing sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSIM
The structural similarity index measure (SSIM) is a method for predicting the perceived quality of digital television and cinematic pictures, as well as other kinds of digital images and videos. SSIM is used for measuring the similarity between two images. The SSIM index is a full reference metric; in other words, the measurement or prediction of image quality is based on an initial uncompressed or distortion-free image as reference. SSIM is a perception-based model that considers image degradation as ''perceived change in structural information'', while also incorporating important perceptual phenomena, including both luminance masking and contrast masking terms. The difference with other techniques such as MSE or PSNR is that these approaches estimate ''absolute errors''. Structural information is the idea that the pixels have strong inter-dependencies especially when they are spatially close. These dependencies carry important information about the structure of the objects i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |