|
MIRVs
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with intercontinental ballistic missiles carrying thermonuclear warheads, even if not strictly being limited to them. By contrast, a unitary warhead is a single warhead on a single missile. An intermediate case is the multiple reentry vehicle (MRV) missile which carries several warheads which are dispersed but not individually aimed. Only the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Russia, China and India are currently confirmed to have deployed MIRV missile systems. Pakistan is developing MIRV missile systems. Israel is suspected to possess or be in the process of developing MIRVs. The first true MIRV design was the Minuteman III, first successfully tested in 1968 and introduced into actual use in 1970. The Minuteman III held three small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Assured Destruction
Mutual assured destruction (MAD) is a doctrine of military strategy and national security policy which posits that a full-scale use of nuclear weapons by an attacker on a nuclear-armed defender with second-strike capabilities would cause the complete annihilation of both the attacker and the defender. It is based on the theory of rational deterrence, which holds that the threat of using strong weapons against the enemy prevents the enemy's use of those same weapons. The strategy is a form of Nash equilibrium in which, once armed, neither side has any incentive to initiate a conflict or to disarm. The term "mutual assured destruction", commonly abbreviated "MAD", was coined by Donald Brennan, a strategist working in Herman Kahn's Hudson Institute in 1962. However, Brennan came up with this acronym ironically, spelling out the English word " mad" to argue that holding weapons capable of destroying society was irrational. Theory Under MAD, each side has enough nuclear weapon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
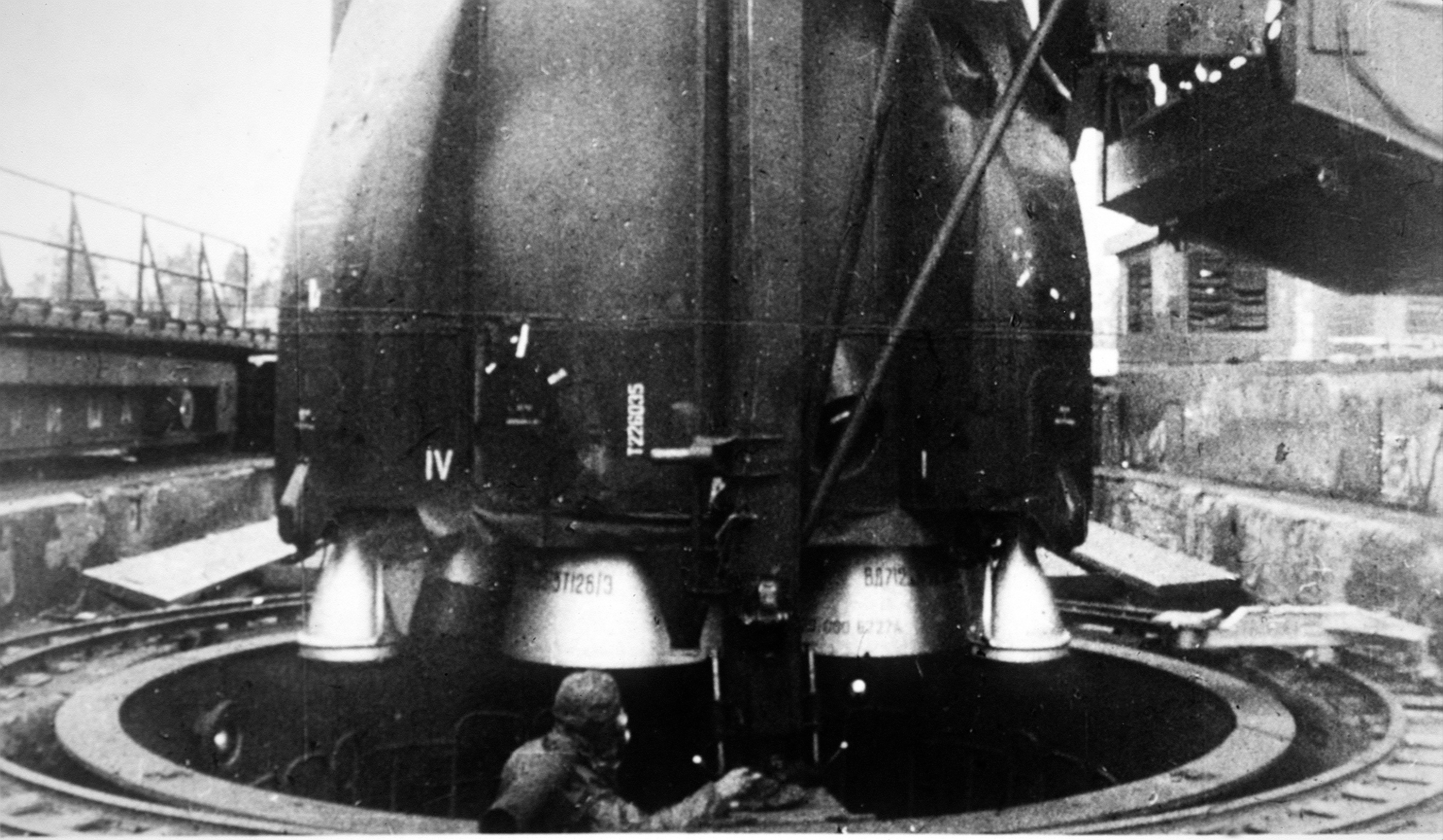
R-36 (missile)
The R-36 (russian: Р-36) is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MRV (multiple re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high throw-weight made it theoretically capable of carrying more warheads or penetration aids. Contemporary U.S. miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
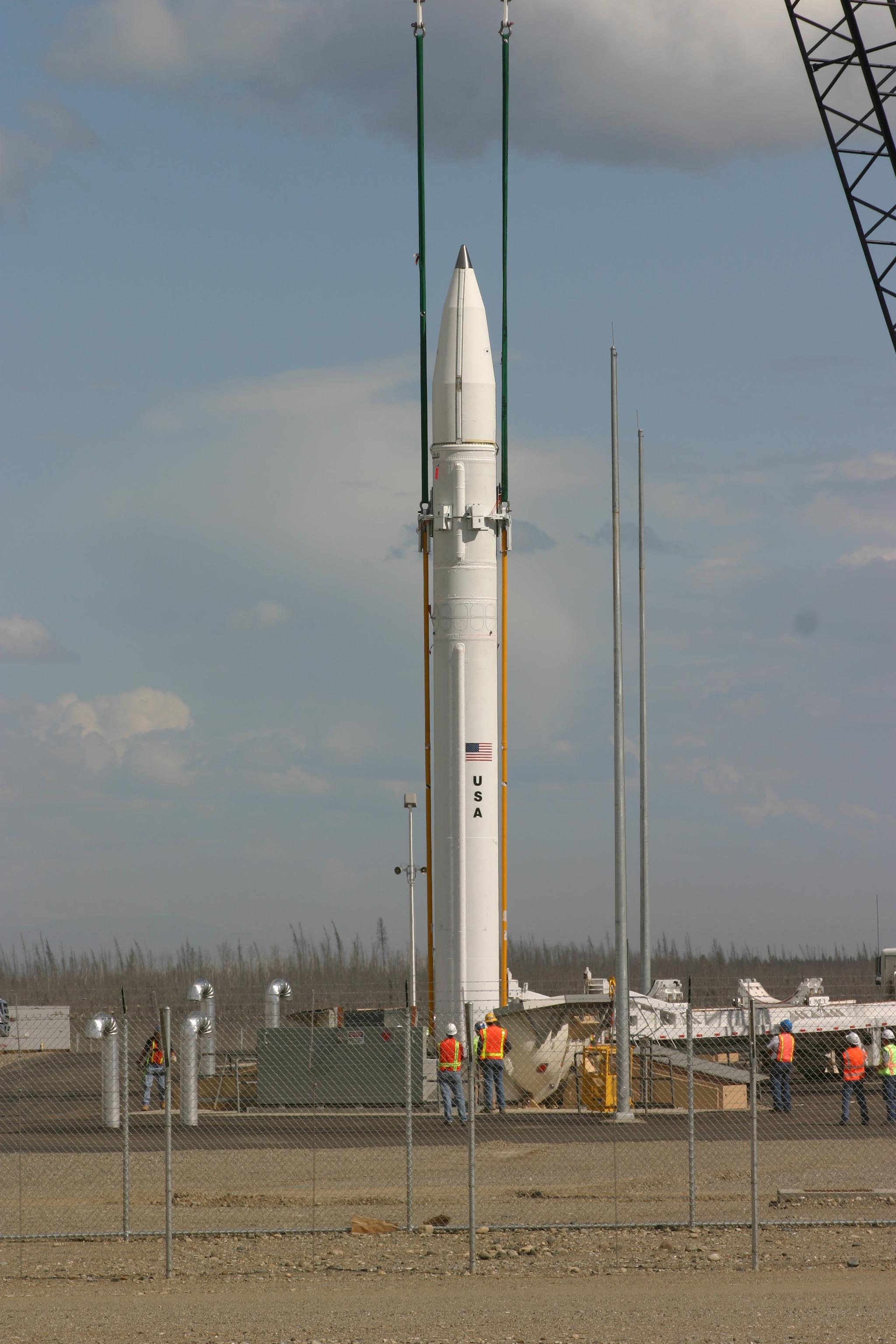
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
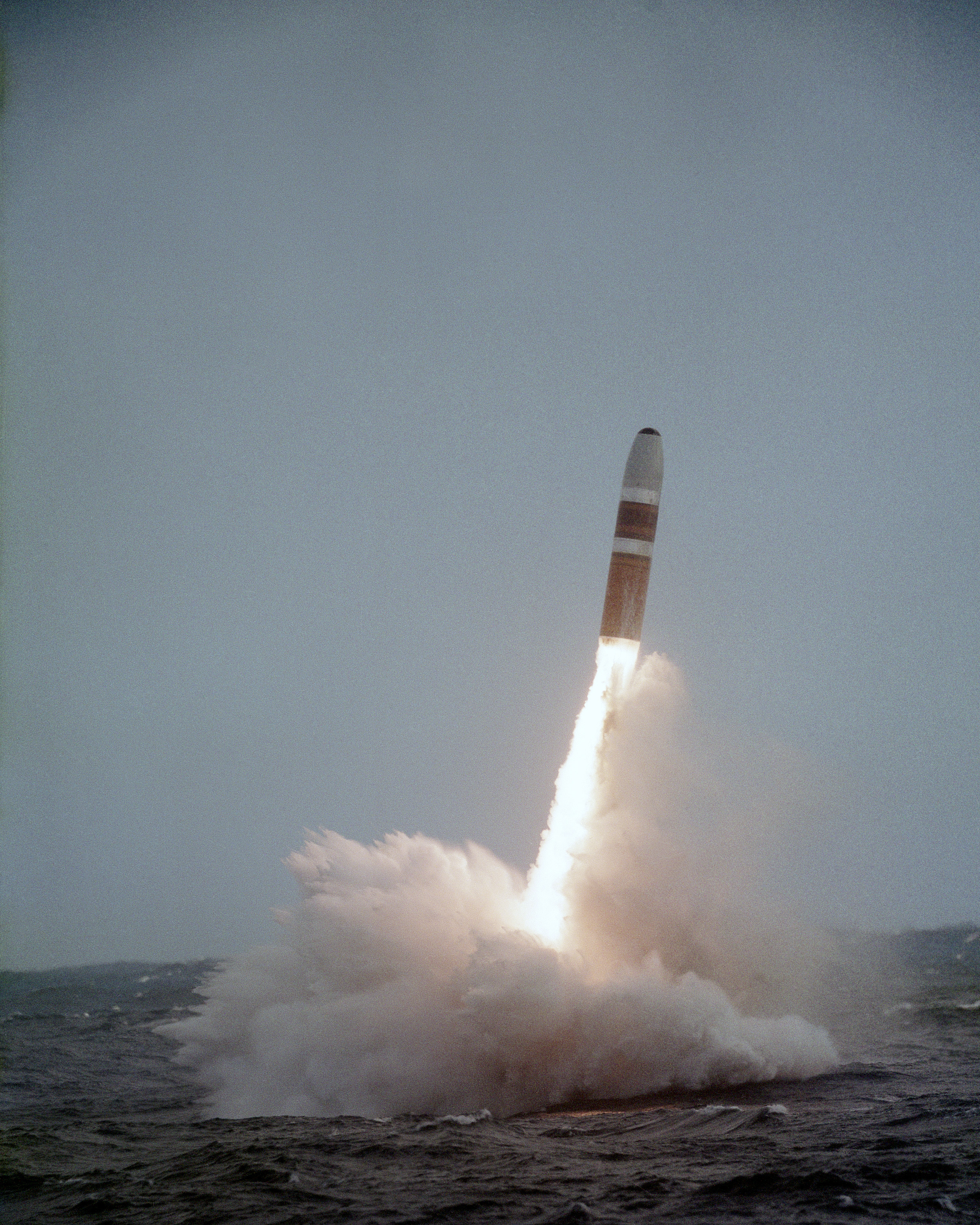
Submarine-launched Ballistic Missile
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which carries a nuclear warhead and allows a single launched missile to strike several targets. Submarine-launched ballistic missiles operate in a different way from submarine-launched cruise missiles. Modern submarine-launched ballistic missiles are closely related to intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), with ranges of over , and in many cases SLBMs and ICBMs may be part of the same family of weapons. History Origins The first practical design of a submarine-based launch platform was developed by the Germans near the end of World War II involving a launch tube which contained a V-2 ballistic missile variant and was towed behind a submarine, known by the code-name ''Prüfstand XII''. The war ended before it could be tested, but the engineers who had worked o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-ballistic Missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear weapon, nuclear, Chemical weapon, chemical, Bioagent, biological, or conventional weapon, conventional warheads in a ballistics, ballistic flight trajectory. The term "anti-ballistic missile" is a generic term conveying a system designed to intercept and destroy any type of ballistic threat; however, it is commonly used for systems specifically designed to counter intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Current counter-ICBM systems There are a limited number of systems worldwide that can intercept intercontinental ballistic missiles: * The Russian A-135 anti-ballistic missile system (renamed in 2017 to A-235) is used for the defense of Moscow. It became operational in 1995 and was preceded by the A-35 anti-ballistic missile system. The system uses ABM-4 Gorgon, Gorgon and Gazelle (missile), Gazelle missiles pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile components of the United States military's strategic nuclear forces from 1946 to 1992. SAC was also responsible for the operation of strategic reconnaissance aircraft and airborne command post aircraft as well as most of the USAF's aerial refueling fleet, including aircraft from the Air Force Reserve (AFRES) and Air National Guard (ANG). SAC primarily consisted of the Second Air Force (2AF), Eighth Air Force (8AF) and the Fifteenth Air Force (15AF), while SAC headquarters (HQ SAC) included Directorates for Operations & Plans, Intelligence, Command & Control, Maintenance, Training, Communications, and Personnel. At a lower echelon, SAC headquarters divisions included Aircraft Engineering, Missile Concept, and Strategic Communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost-exchange Ratio
In anti-ballistic missile (ABM) defence the cost-exchange ratio is the ratio of the incremental cost to the aggressor of getting one additional warhead through the defence screen, divided by the incremental cost to the defender of offsetting the additional missile. For instance, a single new ICBM might require a single new ABM to counter it, and if they both cost the same, the cost-exchange ratio would be 1:1. Throughout the Cold War, the cost-exchange ratio was almost always strongly in favor of the offense. Some of this has to do with the fact that an ICBM can be aimed at any target, which the defender cannot know in advance. To shoot that warhead down, the defender has to wait until it appears on radar, which typically happens only a few hundred miles from the target. This means a single defensive missile cannot be used to counter a single warhead; ABMs have to be deployed in a spread-out fashion so that one can respond no matter where the warhead appears. Even if a single ABM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Munition
A cluster munition is a form of air-dropped or ground-launched explosive weapon that releases or ejects smaller submunitions. Commonly, this is a cluster bomb that ejects explosive bomblets that are designed to kill personnel and destroy vehicles. Other cluster munitions are designed to destroy runways or electric power transmission lines, disperse chemical or biological weapons, or to scatter land mines. Some submunition-based weapons can disperse non-munitions, such as leaflets. Because cluster bombs release many small bomblets over a wide area, they pose risks to civilians both during attacks and afterwards. Unexploded bomblets can kill or maim civilians and/or unintended targets long after a conflict has ended, and are costly to locate and remove. Cluster munitions are prohibited for those nations that ratified the Convention on Cluster Munitions, adopted in Dublin, Ireland, in May 2008. The Convention entered into force and became binding international law upon ratifyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuck Hansen
Chuck Hansen (May 13, 1947 - March 26, 2003) was the compiler, over a period of 30 years, of the world's largest private collection of unclassified documents on how America developed atomic and thermonuclear weapons. Research Hansen's documents were obtained through the U.S. Freedom of Information Act and since his death have been housed at the National Security Archive at George Washington University.Christopher Reed.Chuck Hansen: Obsessive collector whose files told America's A-bomb secrets''The Guardian'', 25 April 2003.William J. Broad''The New York Times'', December 12, 1989. In 1988, Hansen wrote the book ''U.S. Nuclear Weapons: The Secret History'',Jeffrey G. BarlowU. S. Nuclear Weapons: The Secret History (Review)''The Journal of Military History'', Vol. 53, No. 1 (Jan., 1989), pp. 105-106. which, along with great detail about the process of developing, testing and administering atomic weapons was critical of the U.S. Defense Department, the Atomic Energy Commission, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national security and the United States Armed Forces. The DoD is the largest employer in the world, with over 1.34 million active-duty service members (soldiers, marines, sailors, airmen, and guardians) as of June 2022. The DoD also maintains over 778,000 National Guard and reservists, and over 747,000 civilians bringing the total to over 2.87 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the DoD's stated mission is to provide "the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security". The Department of Defense is headed by the secretary of defense, a cabinet-level head who reports directly to the president of the United States. Beneath the Department of Defense are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federal research facility in Livermore, California, United States. The lab was originally established as the University of California Radiation Laboratory, Livermore Branch in 1952 in response to the detonation of the first atomic bomb by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It later became autonomous in 1971 and was designated a national laboratory in 1981. A federally funded research and development center, Lawrence Livermore Lab is primarily funded by the U.S. Department of Energy and it is managed privately and operated by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC (a partnership of the University of California), Bechtel, BWX Technologies, AECOM, and Battelle Memorial Institute in affiliation with the Texas A&M University System. In 2012, the laboratory had the synthetic chemical element livermorium (element 116) named after it. Overview LLNL is self-described as a "premier research and development institution for sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |