|
MG132
MG132 is a potent, reversible, and cell-permeable proteasome inhibitor ( Ki = 4 nM). It belongs to the class of synthetic peptide aldehydes. It reduces the degradation of ubiquitin-conjugated proteins in mammalian cells and permeable strains of yeast by the 26S complex without affecting its ATPase or isopeptidase activities. MG132 activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1), which initiates apoptosis. MG132 also inhibits NF-κB activation with an IC50 of 3 μM and prevents β-secretase cleavage. Molecular mechanism There are several inhibitors that can readily enter cell and selectively inhibit degradative pathway. It includes peptide aldehydes, such as Cbz-leu-leu-leucinal (MG132), Cbz-leu-leu-norvalinal ( MG115) and acetyl-leu-leu-norleucinal ( ALLN). These are substrate analogues and potent transition-state inhibitors of chymotrypsin like activity of proteasome machinery. The peptide aldehydes are also known to inhibit certain lysosomal cysteine proteases and the calpa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
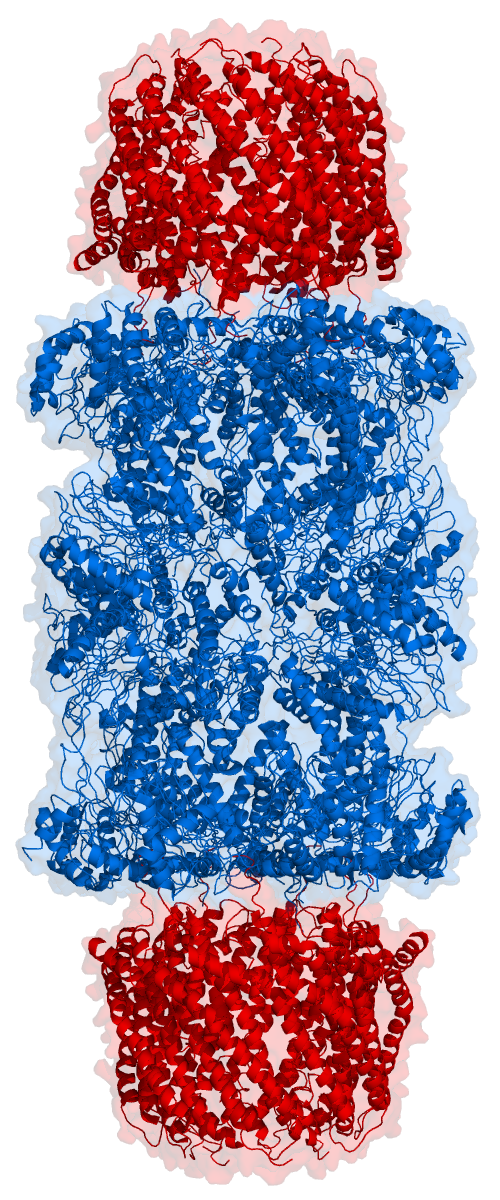
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome Inhibitors
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome Inhibitor
Proteasome inhibitors are drugs that block the action of proteasomes, cellular complexes that break down proteins. They are being studied in the treatment of cancer; and three are approved for use in treating multiple myeloma. Mechanism Multiple mechanisms are likely to be involved, but proteasome inhibition may prevent degradation of pro-apoptotic factors such as the p53 protein, permitting activation of programmed cell death in neoplastic cells dependent upon suppression of pro-apoptotic pathways. For example, bortezomib causes a rapid and dramatic change in the levels of intracellular peptides. Examples * The first non-peptidic proteasome inhibitor discovered was the natural product lactacystin. * Disulfiram has been proposed as another proteasome inhibitor. * Epigallocatechin-3-gallate has also been proposed. * Marizomib (salinosporamide A) has started clinical trials for multiple myeloma. * Oprozomib (ONX-0912), delanzomib (CEP-18770) have also started clinical trials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calpain
A calpain (; , ) is a protein belonging to the family of calcium-dependent, non-lysosomal cysteine proteases (protease, proteolytic enzymes) expressed ubiquitously in mammals and many other organisms. Calpains constitute the C2 family of protease clan CA in the MEROPS database. The calpain proteolytic system includes the calpain proteases, the small regulatory subunit CAPNS1, also known as CAPN4, and the endogenous calpain-specific inhibitor, calpastatin. Discovery The history of calpain's discovery originates in 1964, when calcium-dependent proteolytic activities caused by a "calcium-activated neutral protease" (CANP) were detected in brain, lens of the eye and other tissue (biology), tissues. In the late 1960s the enzymes were isolated and characterised independently in both rat brain and skeletal muscle. These activities were caused by an intracellular cysteine protease not associated with the lysosome and having an optimum activity at neutral pH, which clearly distinguishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine Protease
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad. Discovered by Gopal Chunder Roy in 1873, the first cysteine protease to be isolated and characterized was papain, obtained from ''Carica papaya''. Cysteine proteases are commonly encountered in fruits including the papaya, pineapple, fig and kiwifruit. The proportion of protease tends to be higher when the fruit is unripe. In fact, the latex of dozens of different plant families are known to contain cysteine proteases. Cysteine proteases are used as an ingredient in meat tenderizers. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 14 superfamilies plus several currently unassigned families (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent convergent evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin (, chymotrypsins A and B, alpha-chymar ophth, avazyme, chymar, chymotest, enzeon, quimar, quimotrase, alpha-chymar, alpha-chymotrypsin A, alpha-chymotrypsin) is a digestive enzyme component of pancreatic juice acting in the duodenum, where it performs proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins and polypeptides. Chymotrypsin preferentially cleaves peptide amide bonds where the side chain of the amino acid N-terminal to the scissile amide bond (the P1 position) is a large hydrophobic amino acid (tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine). These amino acids contain an aromatic ring in their side chain that fits into a hydrophobic pocket (the S1 position) of the enzyme. It is activated in the presence of trypsin. The hydrophobic and shape complementarity between the peptide substrate P1 side chain and the enzyme S1 binding cavity accounts for the substrate specificity of this enzyme. Chymotrypsin also hydrolyzes other amide bonds in peptides at slower rates, particularly tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |