|
MESI
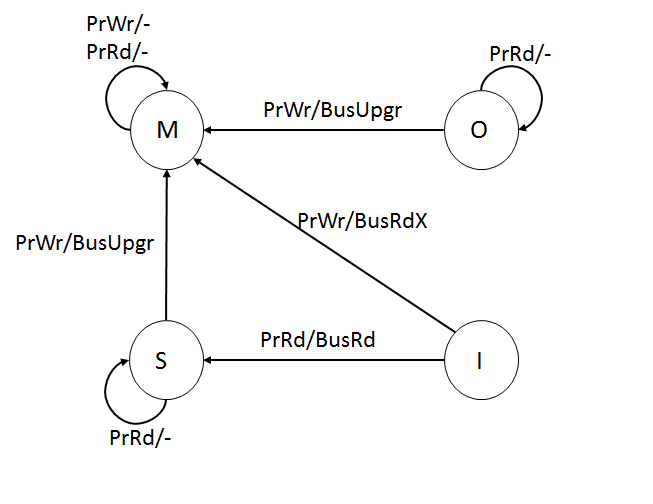
The MESI protocol is an Invalidate-based cache coherence protocol, and is one of the most common protocols that support write-back caches. It is also known as the Illinois protocol (due to its development at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign). Write back caches can save a lot of bandwidth that is generally wasted on a write through cache. There is always a dirty state present in write back caches that indicates that the data in the cache is different from that in main memory. The Illinois Protocol requires a cache to cache transfer on a miss if the block resides in another cache. This protocol reduces the number of main memory transactions with respect to the MSI protocol. This marks a significant improvement in performance. States The letters in the acronym MESI represent four exclusive states that a cache line can be marked with (encoded using two additional bits): ;Modified (M): The cache line is present only in the current cache, and is ''dirty'' - it has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MESIF Protocol
The MESIF protocol is a cache coherency and memory coherence protocol developed by Intel Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ... for cache coherent non-uniform memory architectures. The protocol consists of five states, Modified (M), Exclusive (E), Shared (S), Invalid (I) and Forward (F). The M, E, S and I states are the same as in the MESI protocol. The F state is a specialized form of the S state, and indicates that a cache should act as a designated responder for any requests for the given line. The protocol ensures that, if any cache holds a line in the S state, at most one (other) cache holds it in the F state. In a system of caches employing the MESI protocol, a cache line request that is received by multiple caches holding a line in the S state will be serviced i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSI Protocol
The MOSI protocol is an extension of the basic MSI cache coherency protocol. It adds the Owned state, which indicates that the current processor owns this block, and will service requests from other processors for the block. Overview of States Following are the permitted states of a given cache line: Modified (M) - Only one cache has a valid copy of the block and the value is likely to be different from the one in main memory. It has almost the same meaning as a dirty state in a write back cache except for the difference that modified state also implies exclusive ownership of that block. Dirty state just means that the value of the block is different from the one in main memory, whereas, modified implies that the value is different than that of the main memory and that it is cached in only one location. Owned (O) - Multiple caches may hold the most recent and correct value of a block and the value in main memory may or may not be correct. At a time, only one cache can have th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOESI Protocol
(For a detailed description see Cache coherency protocols (examples)) In computing, MOESI is a full cache coherency protocol that encompasses all of the possible states commonly used in other protocols. In addition to the four common MESI protocol states, there is a fifth "Owned" state representing data that is both modified and shared. This avoids the need to write modified data back to main memory before sharing it. While the data must still be written back eventually, the write-back may be deferred. In order for this to be possible, direct cache-to-cache transfers of data must be possible, so a cache with the data in the modified state can supply that data to another reader without transferring it to memory. As discussed in AMD64 Architecture Programmer's Manual Vol. 2 System Programming''', each cache line is in one of five states: ;Modified: This cache has the only valid copy of the cache line, and has made changes to that copy. ;Owned:This cache is one of several wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Coherence
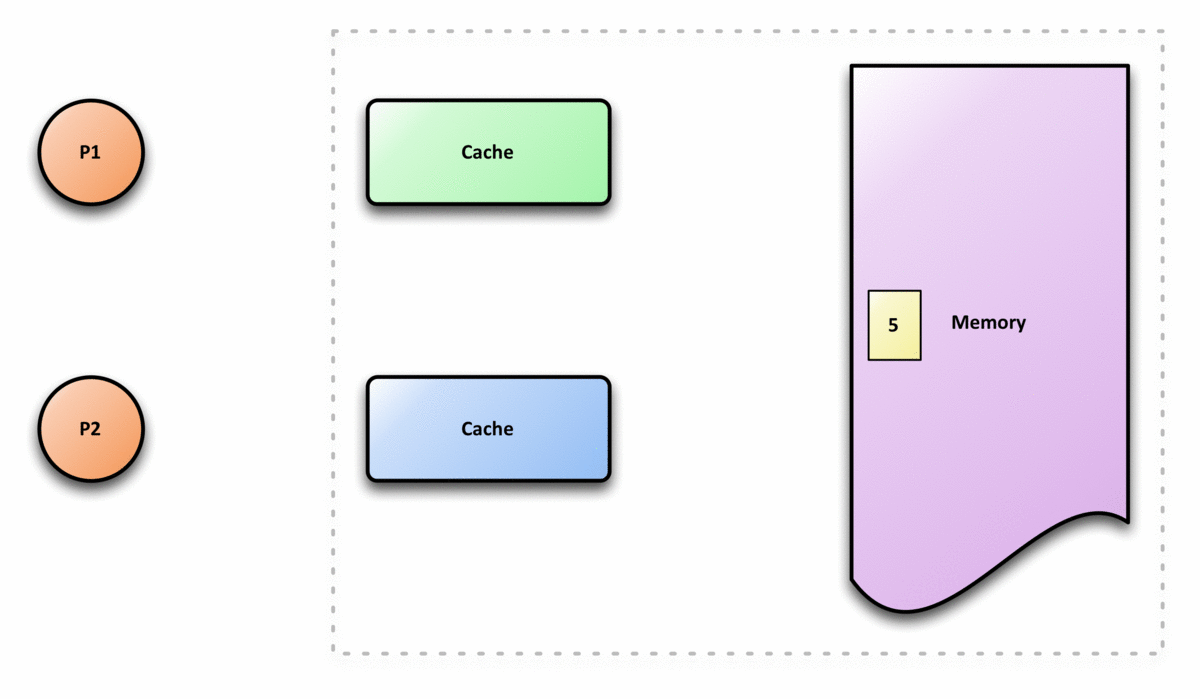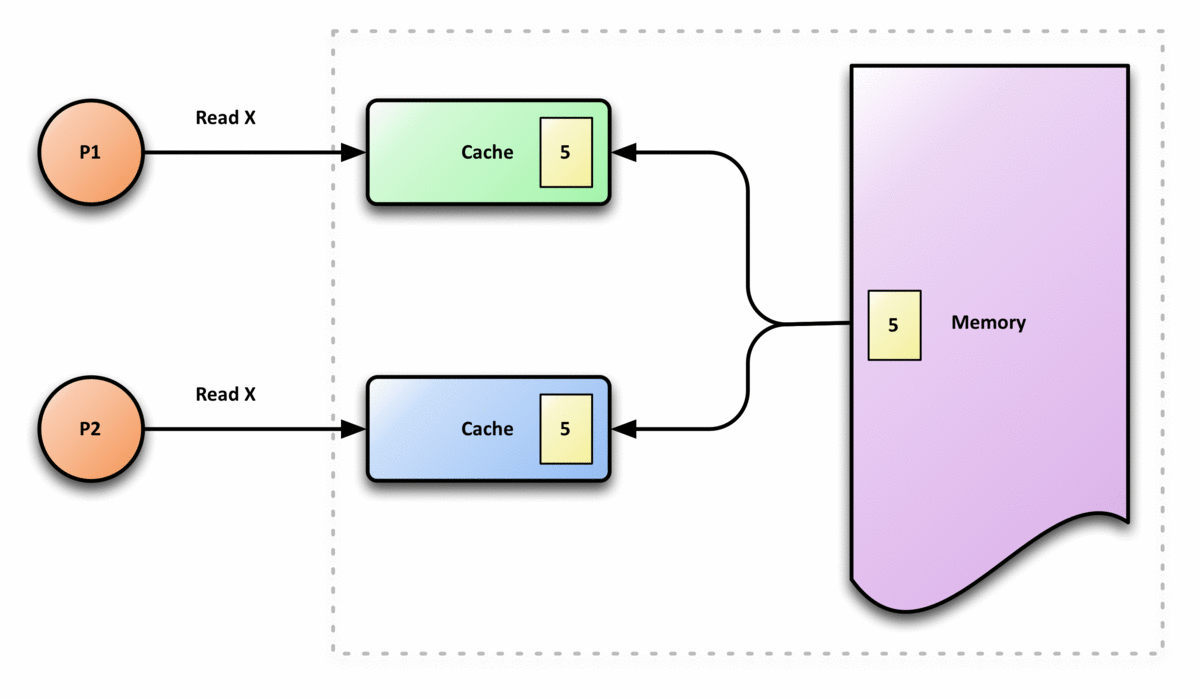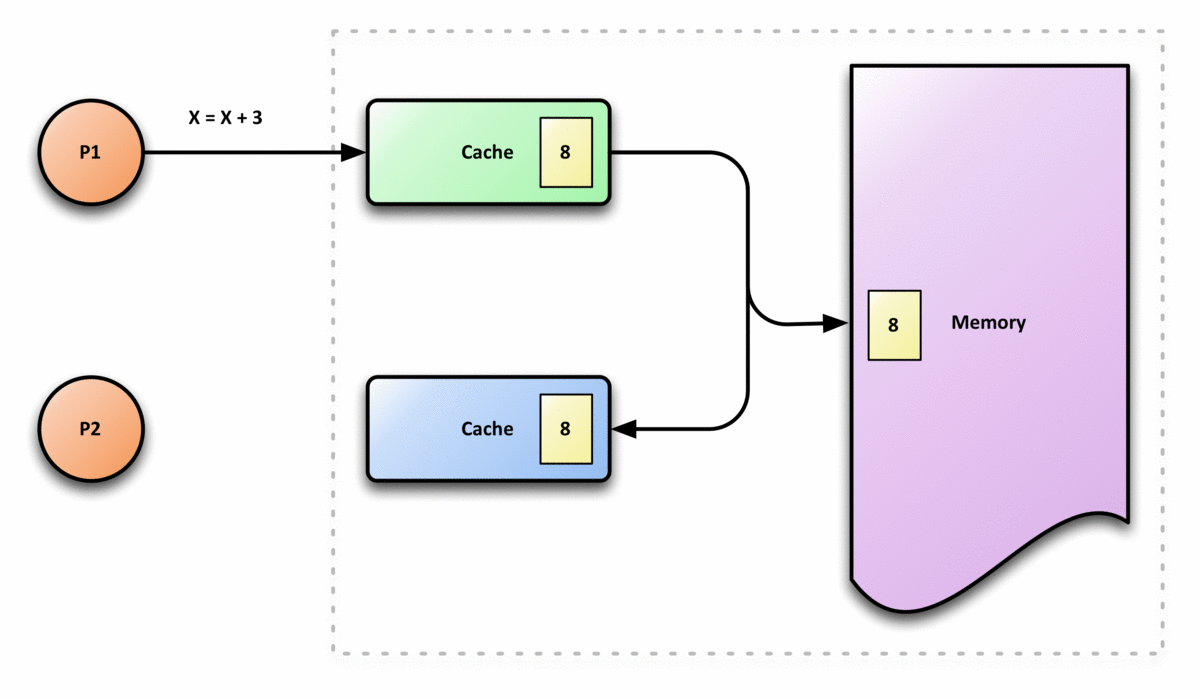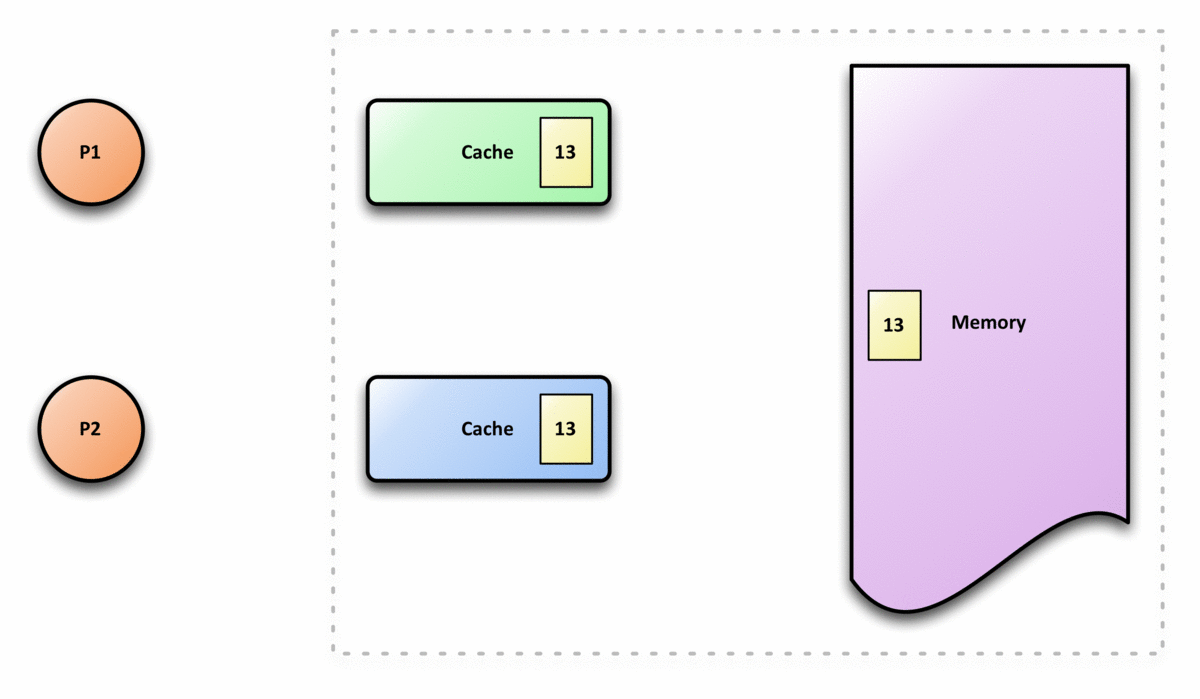
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that ends up stored in multiple local caches. When clients in a system maintain caches of a common memory resource, problems may arise with incoherent data, which is particularly the case with CPUs in a multiprocessing system. In the illustration on the right, consider both the clients have a cached copy of a particular memory block from a previous read. Suppose the client on the bottom updates/changes that memory block, the client on the top could be left with an invalid cache of memory without any notification of the change. Cache coherence is intended to manage such conflicts by maintaining a coherent view of the data values in multiple caches. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Coherency
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that ends up stored in multiple local caches. When clients in a system maintain caches of a common memory resource, problems may arise with incoherent data, which is particularly the case with CPUs in a multiprocessing system. In the illustration on the right, consider both the clients have a cached copy of a particular memory block from a previous read. Suppose the client on the bottom updates/changes that memory block, the client on the top could be left with an invalid cache of memory without any notification of the change. Cache coherence is intended to manage such conflicts by maintaining a coherent view of the data values in multiple caches. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence Protocol
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that ends up stored in multiple local caches. When clients in a system maintain caches of a common memory resource, problems may arise with incoherent data, which is particularly the case with CPUs in a multiprocessing system. In the illustration on the right, consider both the clients have a cached copy of a particular memory block from a previous read. Suppose the client on the bottom updates/changes that memory block, the client on the top could be left with an invalid cache of memory without any notification of the change. Cache coherence is intended to manage such conflicts by maintaining a coherent view of the data values in multiple caches. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefly (cache Coherence Protocol)
The Firefly cache coherence protocol is the schema used in the DEC Firefly multiprocessor workstation, developed by DEC Systems Research Center. This protocol is a 3 State Write Update Cache Coherence Protocol. Unlike the Dragon protocol, the Firefly protocol updates the Main Memory as well as the Local caches on Write Update Bus Transition. Thus the Shared Clean and Shared Modified States present in case of Dragon Protocol, are not distinguished between in case of Firefly Protocol. States In this protocol, the following states can be assigned to each block: * Valid-Exclusive(V): The cache block is valid, clean and only resides in one cache. * Shared(S): The cache block is valid, clean and may reside in multiple caches. * Dirty(D): The block is the only copy of the memory and it is dirty i.e. its value has been modified since being brought from the memory. This is the only state that generates a write-back when the block is replaced in the cache. These states correspond to the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus Snooping
Bus snooping or bus sniffing is a scheme by which a coherency controller (snooper) in a cache (a snoopy cache) monitors or snoops the bus transactions, and its goal is to maintain a cache coherency in distributed shared memory systems. A cache containing a coherency controller (snooper) is called a snoopy cache. This scheme was introduced by Ravishankar and Goodman in 1983. How it works When specific data is shared by several caches and a processor modifies the value of the shared data, the change must be propagated to all the other caches which have a copy of the data. This change propagation prevents the system from violating cache coherency. The notification of data change can be done by bus snooping. All the snoopers monitor every transaction on a bus. If a transaction modifying a shared cache block appears on a bus, all the snoopers check whether their caches have the same copy of the shared block. If a cache has a copy of the shared block, the corresponding snooper performs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSI Protocol
In computing, the MSI protocol - a basic cache-coherence protocol - operates in multiprocessor systems. As with other cache coherency protocols, the letters of the protocol name identify the possible states in which a cache line can be. Overview In MSI, each block contained inside a cache can have one of three possible states: *Modified: The block has been modified in the cache. The data in the cache is then inconsistent with the backing store (e.g. memory). A cache with a block in the "M" state has the responsibility to write the block to the backing store when it is evicted. *Shared: This block is unmodified and exists in read-only state in at least one cache. The cache can evict the data without writing it to the backing store. *Invalid: This block is either not present in the current cache or has been invalidated by a bus request, and must be fetched from memory or another cache if the block is to be stored in this cache. These coherency states are maintained through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Write-once (cache Coherency)
In cache coherency protocol literature, Write-Once was the first MESI protocol defined. It has the optimization of executing write-through on the first write and a write-back on all subsequent writes, reducing the overall bus traffic in consecutive writes to the computer memory. It was first described by James R. Goodman in (1983). Cache coherence protocols are an important issue in Symmetric multiprocessing systems, where each CPU maintains a cache of the memory. States In this protocol, each block in the local cache is in one of these four states: * Invalid: This block has an incoherent copy of the memory. * Valid: This block has a coherent copy of the memory. The data may be possibly shared, but its content is not modified. * Reserved: The block is the only copy of the memory, but it is still coherent. No write-back is needed if the block is replaced. * Dirty: The block is the only copy of the memory and it is incoherent. This copy was written one or more times. This is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MERSI Protocol
The MERSI protocol is a cache coherency and memory coherence protocol used by the PowerPC G4. The protocol consists of five states, Modified (M), Exclusive (E), Read Only or Recent (R), Shared (S) and Invalid (I). The M, E, S and I states are the same as in the MESI protocol The MESI protocol is an Invalidate-based cache coherence protocol, and is one of the most common protocols that support write-back caches. It is also known as the Illinois protocol (due to its development at the University of Illinois at Urbana-C .... The R state is similar to the E state in that it is constrained to be the only clean, valid, copy of that data in the computer system. Unlike the E state, the processor is required to initially request ownership of the cache line in the R state before the processor may modify the cache line and transition to the M state. In both the MESI and MERSI protocols, the transition from the E to M is silent. For any given pair of caches, the permitted states of a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
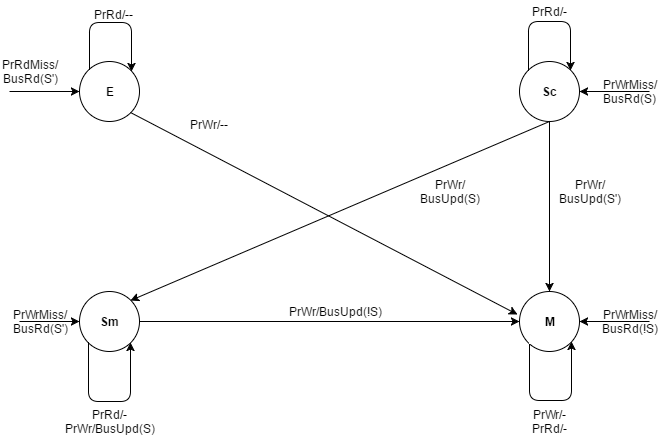
Dragon Protocol
The Dragon Protocol is an update based cache coherence protocol used in multi-processor systems. Write propagation is performed by directly updating all the cached values across multiple processors. Update based protocols such as the Dragon protocol perform efficiently when a write to a cache block is followed by several reads made by other processors, since the updated cache block is readily available across caches associated with all the processors. States Each cache block resides in one of the four states: exclusive-clean, shared-clean, shared-modified and modify. * Exclusive-clean (E): This means that the cache block was first fetched by the current processor and has not been accessed by any other processor since. * Shared clean (Sc): This means that the cache block definitely exists in multiple processor’s caches, and that the current processor is not the last one to write the block. States E and Sc are maintained separately by the protocol to prevent read-write operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |