|
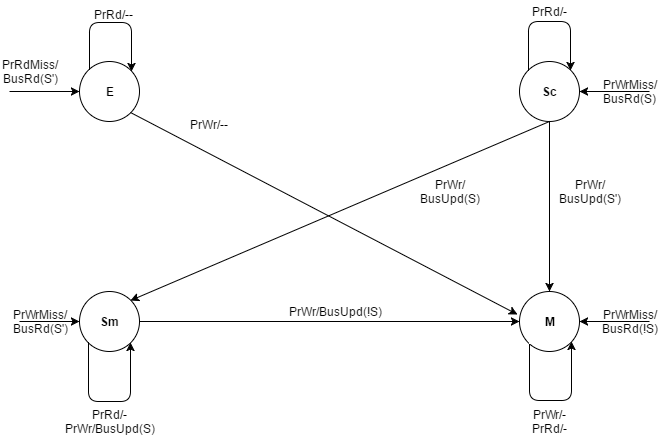
Dragon Protocol
The Dragon Protocol is an update based cache coherence protocol used in multi-processor systems. Write propagation is performed by directly updating all the cached values across multiple processors. Update based protocols such as the Dragon protocol perform efficiently when a write to a cache block is followed by several reads made by other processors, since the updated cache block is readily available across caches associated with all the processors. States Each cache block resides in one of the four states: exclusive-clean, shared-clean, shared-modified and modify. * Exclusive-clean (E): This means that the cache block was first fetched by the current processor and has not been accessed by any other processor since. * Shared clean (Sc): This means that the cache block definitely exists in multiple processor’s caches, and that the current processor is not the last one to write the block. States E and Sc are maintained separately by the protocol to prevent read-write operations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Coherence
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that ends up stored in multiple local caches. When clients in a system maintain caches of a common memory resource, problems may arise with incoherent data, which is particularly the case with CPUs in a multiprocessing system. In the illustration on the right, consider both the clients have a cached copy of a particular memory block from a previous read. Suppose the client on the bottom updates/changes that memory block, the client on the top could be left with an invalid cache of memory without any notification of the change. Cache coherence is intended to manage such conflicts by maintaining a coherent view of the data values in multiple caches. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-processor
Multiprocessing is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. There are many variations on this basic theme, and the definition of multiprocessing can vary with context, mostly as a function of how CPUs are defined ( multiple cores on one die, multiple dies in one package, multiple packages in one system unit, etc.). According to some on-line dictionaries, a multiprocessor is a computer system having two or more processing units (multiple processors) each sharing main memory and peripherals, in order to simultaneously process programs. A 2009 textbook defined multiprocessor system similarly, but noting that the processors may share "some or all of the system’s memory and I/O facilities"; it also gave tightly coupled system as a synonymous term. At the operating system level, ''multiprocessing'' is some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache (computing)
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere. A ''cache hit'' occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a ''cache miss'' occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs. To be cost-effective and to enable efficient use of data, caches must be relatively small. Nevertheless, caches have proven themselves in many areas of computing, because typical computer applications access data with a high degree of locality of reference. Such access patterns exhibit temporal locality, where data is requested that has been recently requested already, and spatial locality, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Consistency
Sequential consistency is a consistency model used in the domain of concurrent computing Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed '' concurrently''—during overlapping time periods—instead of ''sequentially—''with one completing before the next starts. This is a property of a syst ... (e.g. in distributed shared memory, distributed transactions, etc.). It is the property that "... the result of any execution is the same as if the operations of all the processors were executed in some sequential order, and the operations of each individual processor appear in this sequence in the order specified by its program." That is, the execution order of a program in the same processor (or thread) is the same as the program order, while the execution order of a program on different processors (or threads) is undefined. In an example like this: execution order between A1, B1 and C1 is preserved, that is, A1 runs before B1, and B1 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefly (cache Coherence Protocol)
The Firefly cache coherence protocol is the schema used in the DEC Firefly multiprocessor workstation, developed by DEC Systems Research Center. This protocol is a 3 State Write Update Cache Coherence Protocol. Unlike the Dragon protocol, the Firefly protocol updates the Main Memory as well as the Local caches on Write Update Bus Transition. Thus the Shared Clean and Shared Modified States present in case of Dragon Protocol, are not distinguished between in case of Firefly Protocol. States In this protocol, the following states can be assigned to each block: * Valid-Exclusive(V): The cache block is valid, clean and only resides in one cache. * Shared(S): The cache block is valid, clean and may reside in multiple caches. * Dirty(D): The block is the only copy of the memory and it is dirty i.e. its value has been modified since being brought from the memory. This is the only state that generates a write-back when the block is replaced in the cache. These states correspond to the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Futurebus
Futurebus, or IEEE 896, is a computer bus standard, intended to replace all local bus connections in a computer, including the CPU, memory, plug-in cards and even, to some extent, LAN links between machines. The effort started in 1979 and didn't complete until 1987, and then immediately went into a redesign that lasted until 1994. By this point, implementation of a chip-set based on the standard lacked industry leadership. It has seen little real-world use, although custom implementations continue to be designed and used throughout industry. History In the late 1970s, VMEbus was faster than the parts plugged into it. It was quite reasonable to connect a CPU and RAM to VME on separate cards to build a computer. However, as the speed of the CPUs and RAM rapidly increased, VME was quickly overwhelmed. Increasing the speed of VME was not easy, because all of the parts plugged into it would have to be able to support these faster speeds as well. Futurebus looked to fix these problems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon Protocol Processor Initiated Transactions
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as winged, horned, and capable of breathing fire. Dragons in eastern cultures are usually depicted as wingless, four-legged, serpentine creatures with above-average intelligence. Commonalities between dragons' traits are often a hybridization of feline, reptilian and avian features. Scholars believe huge extinct or migrating crocodiles bear the closest resemblance, especially when encountered in forested or swampy areas, and are most likely the template of modern Oriental dragon imagery. Etymology The word ''dragon'' entered the English language in the early 13th century from Old French ''dragon'', which in turn comes from la, draconem (nominative ) meaning "huge serpent, dragon", from Ancient Greek , (genitive , ) "serpent, giant se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Performance Measurement And Metric
A CPU cache is a piece of hardware that reduces access time to data in memory by keeping some part of the frequently used data of the main memory in a 'cache' of smaller and faster memory. The performance of a computer system depends on the performance of all individual units—which include execution units like integer, branch and floating point, I/O units, bus, caches and memory systems. The gap between processor speed and main memory speed has grown exponentially. Until 2001–05, CPU speed, as measured by clock frequency, grew annually by 55%, whereas memory speed only grew by 7%. This problem is known as the memory wall. The motivation for a cache and its hierarchy is to bridge this speed gap and overcome the memory wall. The critical component in most high-performance computers is the cache. Since the cache exists to bridge the speed gap, its performance measurement and metrics are important in designing and choosing various parameters like cache size, associativity, replacem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence Protocol
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that ends up stored in multiple local caches. When clients in a system maintain caches of a common memory resource, problems may arise with incoherent data, which is particularly the case with CPUs in a multiprocessing system. In the illustration on the right, consider both the clients have a cached copy of a particular memory block from a previous read. Suppose the client on the bottom updates/changes that memory block, the client on the top could be left with an invalid cache of memory without any notification of the change. Cache coherence is intended to manage such conflicts by maintaining a coherent view of the data values in multiple caches. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MESI Protocol
The MESI protocol is an Invalidate-based cache coherence protocol, and is one of the most common protocols that support write-back caches. It is also known as the Illinois protocol (due to its development at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign). Write back caches can save a lot of bandwidth that is generally wasted on a write through cache. There is always a dirty state present in write back caches that indicates that the data in the cache is different from that in main memory. The Illinois Protocol requires a cache to cache transfer on a miss if the block resides in another cache. This protocol reduces the number of main memory transactions with respect to the MSI protocol. This marks a significant improvement in performance. States The letters in the acronym MESI represent four exclusive states that a cache line can be marked with (encoded using two additional bits): ;Modified (M): The cache line is present only in the current cache, and is ''dirty'' - it has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
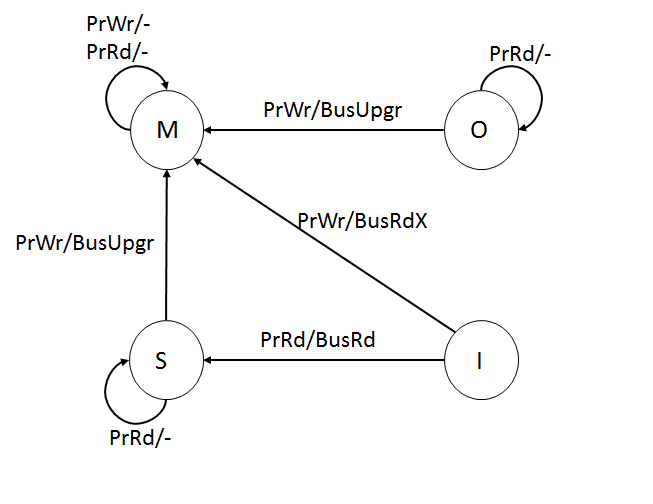
MOSI Protocol
The MOSI protocol is an extension of the basic MSI cache coherency In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that ends up stored in multiple local caches. When clients in a system maintain caches of a common memory resource, problems may arise with incoherent data, whi ... protocol. It adds the Owned state, which indicates that the current processor owns this block, and will service requests from other processors for the block. Overview of States Following are the permitted states of a given cache line: Modified (M) - Only one cache has a valid copy of the block and the value is likely to be different from the one in main memory. It has almost the same meaning as a dirty state in a write back cache except for the difference that modified state also implies exclusive ownership of that block. Dirty state just means that the value of the block is different from the one in main memory, whereas, modified implies that the value is diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |