|
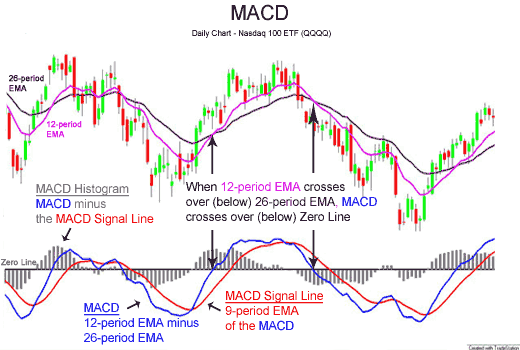
MACD
MACD, short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of securities prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s. It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price. The MACD indicator (or "oscillator") is a collection of three time series calculated from historical price data, most often the closing price. These three series are: the MACD series proper, the "signal" or "average" series, and the "divergence" series which is the difference between the two. The MACD series is the difference between a "fast" (short period) exponential moving average (EMA), and a "slow" (longer period) EMA of the price series. The average series is an EMA of the MACD series itself. The MACD indicator thus depends on three time parameters, namely the time constants of the three EMAs. The notation "MACD(''a'',''b'',''c'')" usually denotes the indicator where the MACD series is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macd Indicator
MACD, short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a technical indicator, trading indicator used in technical analysis of securities prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s. It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum (finance), momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price. The MACD indicator (or "oscillator") is a collection of three time series calculated from historical price data, most often the share price, closing price. These three series are: the MACD series proper, the "signal" or "average" series, and the "divergence" series which is the difference between the two. The MACD series is the difference between a "fast" (short period) moving average#Exponential moving average, exponential moving average (EMA), and a "slow" (longer period) EMA of the price series. The average series is an EMA of the MACD series itself. The MACD indicator thus depends on three time parameters, namely the time constants of the three EMAs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Analysis
In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis use many of the same tools of technical analysis, which, being an aspect of active management, stands in contradiction to much of modern portfolio theory. The efficacy of both technical and fundamental analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable, and research on whether technical analysis offers any benefit has produced mixed results. History The principles of technical analysis are derived from hundreds of years of financial market data. Some aspects of technical analysis began to appear in Amsterdam-based merchant Joseph de la Vega's accounts of the Dutch financial markets in the 17th century. In Asia, technical analysis is said to be a method developed by Homma Munehisa duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Analysis
In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis use many of the same tools of technical analysis, which, being an aspect of active management, stands in contradiction to much of modern portfolio theory. The efficacy of both technical and fundamental analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable, and research on whether technical analysis offers any benefit has produced mixed results. History The principles of technical analysis are derived from hundreds of years of financial market data. Some aspects of technical analysis began to appear in Amsterdam-based merchant Joseph de la Vega's accounts of the Dutch financial markets in the 17th century. In Asia, technical analysis is said to be a method developed by Homma Munehisa duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detrended Price Oscillator
The detrended price oscillator (DPO) is an indicator in technical analysis that attempts to eliminate the long-term trends in prices by using a displaced moving average so it does not react to the most current price action. This allows the indicator to show intermediate overbought and oversold levels effectively. The detrended price oscillator is a form of price oscillator, like the "percentage price oscillator" (PPO) and the "absolute price oscillator" (APO) both of which are forms of Gerald Appel's moving average convergence/divergence indicator (MACD). The APO is an equivalent to the MACD indicator while the PPO is an improved alternative to the APO or the MACD for use when a stock's price change has been large, or when comparing the oscillator behavior for different stocks which have significantly different prices. Although these are not so commonly used with the DPO, for the other price oscillators, as for the MACD, a signal line is frequently generated for the price oscillat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Strength Index
The relative strength index (RSI) is a technical indicator used in the analysis of financial markets. It is intended to chart the current and historical strength or weakness of a stock or market based on the closing prices of a recent trading period. The indicator should not be confused with relative strength. The RSI is classified as a momentum oscillator, measuring the velocity and magnitude of price movements. Momentum is the rate of the rise or fall in price. The relative strength RS is given as the ratio of higher closes to lower closes, with closes here meaning averages of absolute values of price changes. The RSI computes momentum as the ratio of higher closes to overall closes: stocks which have had more or stronger positive changes have a higher RSI than stocks which have had more or stronger negative changes. The RSI is most typically used on a 14-day timeframe, measured on a scale from 0 to 100, with high and low levels marked at 70 and 30, respectively. Short or longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Oscillator
In technical analysis of securities trading, the stochastic oscillator is a momentum indicator that uses support and resistance levels. George Lane developed this indicator in the late 1950s. The term '' stochastic'' refers to the point of a current price in relation to its price range over a period of time. This method attempts to predict price turning points by comparing the closing price of a security to its price range. The 5-period stochastic oscillator in a daily timeframe is defined as follows: :\%K = 100\times\frac \%D_N = \frac where \mathrm_5 and \mathrm_5 are the highest and lowest prices in the last 5 days respectively, while %''D'' is the ''N''-day moving average of %''K'' (the last ''N'' values of %''K''). Usually this is a simple moving average, but can be an exponential moving average for a less standardized weighting for more recent values. There is only one valid signal in working with %''D'' alone — a divergence between %''D'' and the analyzed sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Average
In statistics, a moving average (rolling average or running average) is a calculation to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set. It is also called a moving mean (MM) or rolling mean and is a type of finite impulse response filter. Variations include: simple, cumulative, or weighted forms (described below). Given a series of numbers and a fixed subset size, the first element of the moving average is obtained by taking the average of the initial fixed subset of the number series. Then the subset is modified by "shifting forward"; that is, excluding the first number of the series and including the next value in the subset. A moving average is commonly used with time series data to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends or cycles. The threshold between short-term and long-term depends on the application, and the parameters of the moving average will be set accordingly. It is also used in economics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Price Oscillator (APO)
Absolute may refer to: Companies * Absolute Entertainment, a video game publisher * Absolute Radio, (formerly Virgin Radio), independent national radio station in the UK * Absolute Software Corporation, specializes in security and data risk management * Absolut Vodka, a brand of Swedish vodka Mathematics and science * Absolute (geometry), the quadric at infinity * Absolute (perfumery), a fragrance substance produced by solvent extraction * Absolute magnitude, the brightness of a star * Absolute value, a notion in mathematics, commonly a number's numerical value without regard to its sign *Absolute temperature, a temperature on the thermodynamic temperature scale * Absolute zero, the lower limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, -273.15 °C * Absoluteness in mathematical logic Music * Absolute (production team), a British music writing and production team * Absolute (record compilation), a brand of compilation albums from EVA Records * ''Absolute'' (Aion album), 1994 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams %R
Williams %R, or just %R, is a technical analysis oscillator showing the current closing price in relation to the high and low of the past days (for a given ). It was developed by a publisher and promoter of trading materials, Larry Williams Larry Williams (born Lawrence Eugene Williams, a.k.a. Lawrence Edward Williams; May 10, 1935 – January 7, 1980) was an American rhythm and blues and rock and roll singer, songwriter, producer, and pianist from New Orleans, Louisiana. Williams .... Its purpose is to tell whether a stock or commodity market is trading near the high or the low, or somewhere in between, of its recent trading range. : \%R = \times -100 The oscillator is on a negative scale, from −100 (lowest) up to 0 (highest), obverse of the more common 0 to 100 scale found in many technical analysis oscillators. A value of −100 means the close today was the lowest low of the past days, and 0 means today's close was the highest high of the past days. (Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
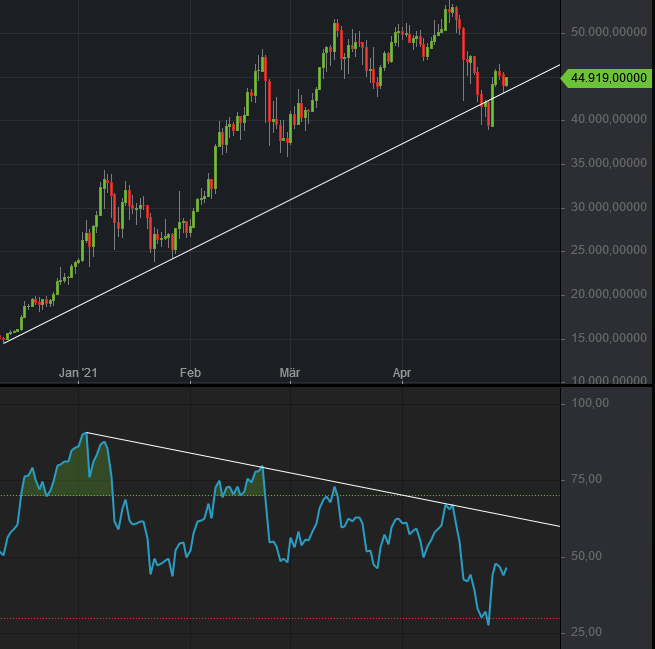
Ultimate Oscillator
The ultimate oscillator is a theoretical concept in finance developed by Larry Williams as a way to account for the problems experienced in most oscillators when used over different lengths of time. The oscillator is a technical analysis indicator based on a notion of buying or selling "pressure" represented by where a day's closing price falls within the day's true range. The calculation starts with "buying pressure", which is the amount by which the close is above the "true low" on a given day. The true low is the lesser of the given day's trading low and the previous close. : bp = close - \min (low, prev\,close) The true range (the same as used in average true range) is the difference between the "true high" and the true low above. The true high is the greater of the given day's trading high and the previous close. : tr = \max (high, prev\,close) - \min (low, prev\,close) The total buying pressure over the past 7 days is expressed as a fraction of the total true range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prentice Hall Press
Prentice Hall was an American major educational publisher owned by Savvas Learning Company. Prentice Hall publishes print and digital content for the 6–12 and higher-education market, and distributes its technical titles through the Safari Books Online e-reference service. History On October 13, 1913, law professor Charles Gerstenberg and his student Richard Ettinger founded Prentice Hall. Gerstenberg and Ettinger took their mothers' maiden names, Prentice and Hall, to name their new company. Prentice Hall became known as a publisher of trade books by authors such as Norman Vincent Peale; elementary, secondary, and college textbooks; loose-leaf information services; and professional books. Prentice Hall acquired the training provider Deltak in 1979. Prentice Hall was acquired by Gulf+Western in 1984, and became part of that company's publishing division Simon & Schuster. S&S sold several Prentice Hall subsidiaries: Deltak and Resource Systems were sold to National Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentage Price Oscillator (PPO)
In mathematics, a percentage (from la, per centum, "by a hundred") is a number or ratio expressed as a fraction of 100. It is often denoted using the percent sign, "%", although the abbreviations "pct.", "pct" and sometimes "pc" are also used. A percentage is a dimensionless number (pure number); it has no unit of measurement. Examples For example, 45% (read as "forty-five per cent") is equal to the fraction , the ratio 45:55 (or 45:100 when comparing to the total rather than the other portion), or 0.45. Percentages are often used to express a proportionate part of a total. (Similarly, one can also express a number as a fraction of 1,000, using the term "per mille" or the symbol "".) Example 1 If 50% of the total number of students in the class are male, that means that 50 out of every 100 students are male. If there are 500 students, then 250 of them are male. Example 2 An increase of $0.15 on a price of $2.50 is an increase by a fraction of = 0.06. Expressed as a pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |