|
M15-class Monitor
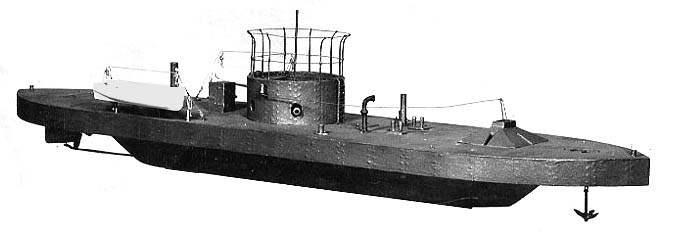
The ''M15'' class comprised fourteen monitors of the Royal Navy, all built and launched during 1915. Design The ships of this class were ordered in March, 1915, as part of the Emergency War Programme of ship construction. They were designed to use the 9.2 inch Mk VI gun turrets removed from the and the Mk X turrets held in stock for the and s. This resulted in the first four of the class, which were built by William Gray & Company of Hartlepool, receiving the Mk X mounting. The remaining ten ships, all built by Sir Raylton Dixon & Co., Middlesbrough, all received the Mk VI mounting. During September 1915, the 9.2 inch guns of HMS ''M24'', ''M25'', ''M26'' and ''M27'' were removed for use as artillery. These were replaced by 7.5-inch guns. ''M24'' and ''M25'' received the spare guns reserved for the recently sunk pre-dreadnought battleship , ''M26'' received one of ''Swiftsure''s spare guns. ''M27'' received 6-inch (M27) guns. ''M21'' and ''M23'' also had their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor (warship)
A monitor is a relatively small warship which is neither fast nor strongly armored but carries disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s, during the First World War and with limited use in the Second World War. The original monitor was designed in 1861 by John Ericsson, who named it . They were designed for shallow waters and served as coastal ships. The term also encompassed more flexible breastwork monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship. In the early 20th century, the term was revived for shallow-draught armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the s carried guns firing heavier shells than any other warship ever has, seeing action (albeit briefly) against German targets during World War I. The ''Lord Clive'' vessels were scrapped in the 1920s. The term "monitor" also encompasses the strongest of riverine warcraft, known as river monitors. During the Vietnam War these much sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Warfare In The Mediterranean During World War I
The First battle of the Mediterranean During WW1 was between the Central Powers' navies of Austria-Hungary, Germany and the Ottoman Empire and the Allied navies of Italy, France, Greece, Japan, America and the British Empire. Austro-Hungarian Imperial and Royal Navy Austria-Hungary was a medium-sized naval power in 1914. It had a coastline from Trieste (in present-day Italy) to below Cattaro in Montenegro. The Austro-Hungarian Navy had nine pre-dreadnought and four brand new dreadnought s, armoured cruisers, protected cruisers, light cruisers, destroyers, large numbers of fast torpedo-boats and a number of submarines. In addition, the Germans managed to send some further U-boats to the Mediterranean which operated from Austrian naval bases, initially under the Austrian navy flag, later under the German navy flag. Italian ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) The Kingdom of Italy during World War I had six dreadnought battleships ( as a prototype, , and of the , and of the ). Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M22
HMS ''M22'' was a First World War Royal Navy monitor. Later converted to a minelayer and renamed HMS ''Medea'' , she was wrecked whilst being towed for breaking up on 2 January 1939. Design Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M22''s primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk VI gun removed from the HMS ''Gibraltar''. In addition to her 9.2 inch gun she also possessed one 12 pounder and one six pound anti-aircraft gun. Due to the shortage of Bolinder diesel engines that equipped her sisters, she was fitted with 2 shaft triple expansion steam engines that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M22'' ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the Sir Raylton Dixon & Co. Ltd shipyard at Govan in March 1915, launched on 10 June 1915, and completed in August 1915. World War 1 ''M22'' served within the Mediterranean from Septembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M21
HMS ''M21'' was a First World War Royal Navy ''M15''-class monitor. After service in the Mediterranean and the Dover Patrol, she struck a mine off Ostend in January 1918 and sank off Dover. Design Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M21''s primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk VI gun removed from the HMS ''Theseus''. In addition to her 9.2 inch gun, she also possessed one 12 pounder and one six pound anti-aircraft gun. Due to the shortage of Bolinder diesel engines that equipped her sisters, she was fitted with 2 shaft triple expansion steam engines that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M21'' ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the Sir Raylton Dixon & Co. Ltd shipyard at Govan in March 1915, launched on 27 May 1915, and completed in July 1915. World War I ''M21'' served initially in the Mediterranean from Sept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M20
HMS ''M20'' was a First World War Royal Navy ''M15''-class monitor. Design Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M20''s primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk VI gun removed from the HMS ''Gibraltar''. In addition to her 9.2-inch gun she also possessed one 12 pounder and one six-pound anti-aircraft gun. She was equipped with a four-shaft Bolinder two-cylinder semi-diesel engine with 640 horsepower that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty-nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M20'' ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the Sir Raylton Dixon & Co. Ltd shipyard at Govan in March 1915, launched on 11 May 1915, and completed in July 1915. World War 1 ''M20'' served within the Mediterranean from August 1915 to December 1918. She did not return to Home Waters, paying off at Malta Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M19
HMS ''M19'' was a First World War Royal Navy ''M15''-class monitor. Design Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M19''s primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk VI gun removed from the HMS ''Edgar''. In addition to her 9.2-inch gun she also possessed one 12 pounder and one six pound anti-aircraft gun. She was equipped with a four shaft Bolinder two-cylinder semi-diesel engine with 640 horsepower that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M19'' ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the Sir Raylton Dixon & Co. Ltd shipyard at Govan in March 1915, launched on 4 May 1915, and completed in June 1915. World War 1 ''M19'' served within the Mediterranean from July 1915 to December 1915. On 4 December 1915, she was badly damaged by a gun explosion. She did not return to Home Waters, paying off at Mudros Moudros ( el, Μούδρ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M18
HMS ''M18'' was a ''M15''-class monitor built for the Royal Navy during the First World War. Design Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M18''s primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk X gun which had been held as a spare for the and . In addition to her 9.2-inch gun, she also possessed one 12 pounder and one six pound anti-aircraft gun. She was equipped with a four-shaft Bolinder two-cylinder semi-diesel engine with 640 horsepower that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty-nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M18'' ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the William Gray shipyard at Hartlepool in March 1915, launched on 15 May 1915, and completed in July 1915. World War 1 ''M18'' served in the Mediterranean The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M17
HMS ''M17'' was a First World War Royal Navy ''M15''-class monitor. Design Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M17''s primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk X gun which had been held as a spare for the and . In addition to her 9.2 inch gun, she also possessed one 12 pounder and one six pound anti-aircraft gun. She was equipped with Triple Expansion steam engines rated to 800 horse power that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M17'' was ordered in March 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the William Gray shipyard at Hartlepool in March 1915, launched on 12 May 1915, and completed in July 1915. World War 1 ''M17'' served in the Mediterranean The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M16
HMS ''M16'' was a First World War Royal Navy monitor. Design Originally intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M16''s primary armament was a single 9.2 inch Mk X gun which had been held as a spare for the and . In addition to her 9.2 inch gun, she also possessed one 12 pounder and one six pound anti-aircraft gun. She was equipped with Triple Expansion steam engines rated to 800 horse power that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M16'' was ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the William Gray shipyard at Hartlepool in March 1915, launched on 3 May 1915, and completed in June 1915. World War 1 ''M16'' served in the Mediterranean The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS M15
HMS ''M15'' was a World War I, First World War Royal Navy Monitor (ship), monitor. She was sunk off Gaza City, Gaza by on 11 November 1917. Design Intended as a shore bombardment vessel, ''M15''s primary armament was a single BL 9.2 inch gun Mk IX–X, 9.2 inch Mk X gun which had been held as a spare for the and . In addition to her 9.2-inch gun, she also possessed one QF 12 pounder 12 cwt naval gun, 12-pounder and one QF 6 pounder Hotchkiss, six pound anti-aircraft gun. She was equipped with Triple Expansion steam engines rated to 800 horse power that allowed a top speed of eleven knots. The monitor's crew consisted of sixty nine officers and men. Construction HMS ''M15'' was ordered in March, 1915, as part of the War Emergency Programme destroyers, War Emergency Programme of ship construction. She was laid down at the William Gray shipyard at Hartlepool in March 1915, launched on 28 April 1915, and completed in June 1915. First World War ''M15'' was towed to Malta in July, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Training Ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house classrooms. The hands-on aspect provided by sail training has also been used as a platform for everything from semesters at sea for undergraduate oceanography and biology students, marine science and physical science for high school students, to character building for at-risk youths. Notable training ships Royal Navy * * * * * * * ''Cornwall'' * * * * * * '' Indefatigable'' * , including adjacent * * * * ''Mount Edgcumbe'' * * * '' Warspite'' (1877) * '' Warspite'' (1922) * * '' Wellesley'' * Other navies * Algerian Navy ** '' El-Mellah'' * Argentine Navy ** ** * Bangladesh Navy ** BNS ''Shaheed Ruhul Amin'' * Brazilian Navy ** ''Cisne Branco'' * Bulgarian Navy ** * Royal Canadian Navy ** (sail training) ** HMCS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minelayer
A minelayer is any warship, submarine or military aircraft deploying explosive mines. Since World War I the term "minelayer" refers specifically to a naval ship used for deploying naval mines. "Mine planting" was the term for installing controlled mines at predetermined positions in connection with coastal fortifications or harbor approaches that would be detonated by shore control when a ship was fixed as being within the mine's effective range. Before World War I, mine ships were termed mine planters generally. For example, in an address to the United States Navy ships of Mine Squadron One at Portland, England, Admiral Sims used the term “mine layer” while the introduction speaks of the men assembled from the “mine planters”. During and after that war the term "mine planter" became particularly associated with defensive coastal fortifications. The term "minelayer" was applied to vessels deploying both defensive- and offensive mine barrages and large scale sea mining. " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
