|
Māui Dolphin
Māui dolphin, Maui's dolphin, or ''Popoto'' (''Cephalorhynchus hectori maui'') is a subspecies of the Hector's dolphin (''Cephalorhynchus hectori'')—New Zealand's only endemic cetacean. It is one of the rarest and smallest dolphins in the world. Māui dolphins are only found off the west coast of New Zealand's North Island, and are now one of the rarest and smallest dolphin subspecies globally. A 2021 report issued by the New Zealand government suggests the population rests at 54 individuals, but when taking into account recent mortalities, the population could sit at fewer than 40 individuals. Both the Māui dolphin and South Island Hector's dolphin are threatened by commercial fisheries, including set-netting and trawling, recreational netting, and disease including toxoplasmosis and brucellosis. Low food availability may also be an issue for Māui dolphins, which may increase their susceptibility to climate change. Etymology The word "Māui" in the dolphin's name comes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated as subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific name, infraspecific ranks, such as variety (botany), variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes, bacterial nomenclature and virus clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahuru
The ahuru (''Auchenoceros punctatus'') is a species of morid cod found in waters off the eastern coast of New Zealand and to the south as well as in the Cook Strait. It is found at depths from . This species grows to in total length. It is the only known species of its genus Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino .... References * * *Tony Ayling & Geoffrey Cox, ''Collins Guide to the Sea Fishes of New Zealand'', (William Collins Publishers Ltd, Auckland, New Zealand 1982) Moridae Endemic marine fish of New Zealand Fish described in 1873 {{Gadiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
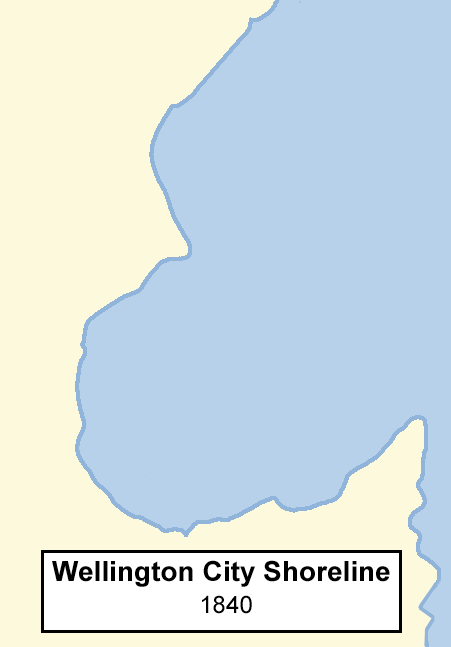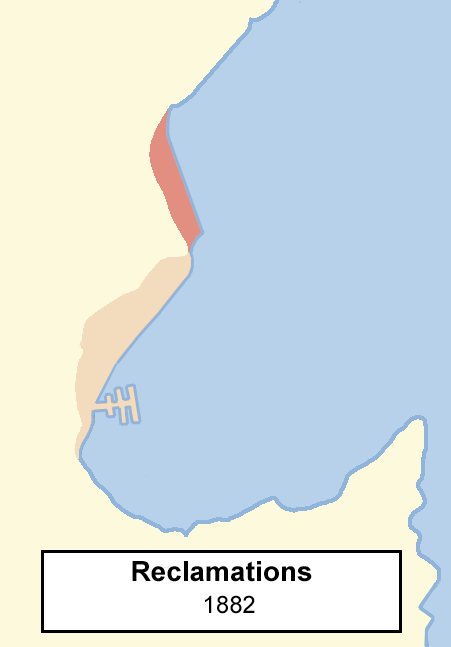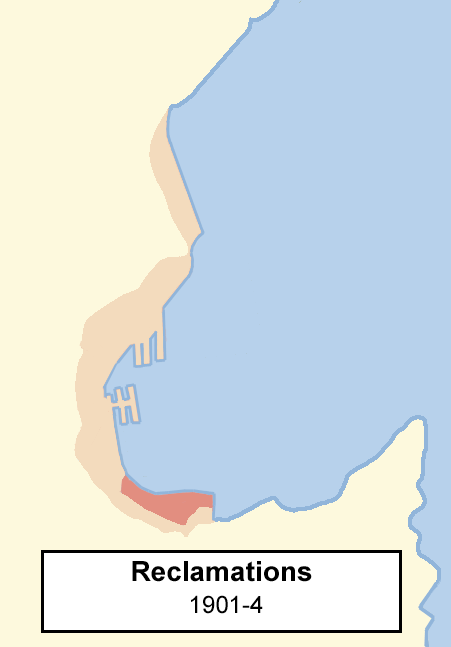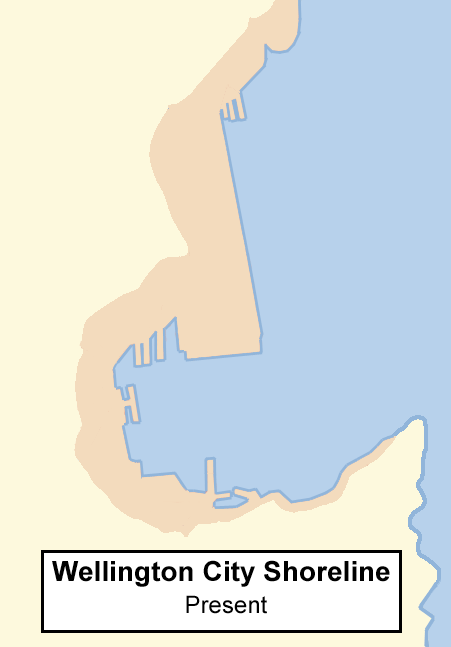
Wellington Harbour
Wellington Harbour ( ), officially called Wellington Harbour / Port Nicholson, is a large natural harbour on the southern tip of New Zealand's North Island. The harbour entrance is from Cook Strait. Central Wellington is located on parts of the western and southern sides of the harbour, and the suburban area of Lower Hutt is to the north and east. The harbour area bounded by a line between Pencarrow Head to Petone foreshore, was officially named Port Nicholson until it assumed its current dual name in 1984. Toponymy The earliest known Māori name for the area, ''Te Upoko-o-te-Ika-a-Māui'', is derived from Māori legend and translates literally as "the head of Māui's fish". ''Te Whanganui-a-Tara'', another Māori name for the area, translates literally as "the great harbour of Tara". It is believed to refer to Tara, a son of the Polynesian explorer Whātonga, who was sent down from the Māhia Peninsula by his father to explore southern lands for their people to se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whanganui
Whanganui, also spelt Wanganui, is a city in the Manawatū-Whanganui region of New Zealand. The city is located on the west coast of the North Island at the mouth of the Whanganui River, New Zealand's longest navigable waterway. Whanganui is the 19th most-populous urban area in New Zealand and the second-most-populous in Manawatū-Whanganui, with a population of as of . Whanganui is the ancestral home of Te Āti Haunui-a-Pāpārangi and other Whanganui Māori tribes. The New Zealand Company began to settle the area in 1840, establishing its second settlement after Wellington. In the early years, most European settlers came via Wellington. Whanganui greatly expanded in the 1870s, and freezing works, woollen mills, phosphate works and wool stores were established in the town. Today, much of Whanganui's economy relates directly to the fertile and prosperous farming hinterland. Like several New Zealand urban areas, it was officially designated a city until an administrative r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maunganui Bluff
Maunganui Bluff is a prominent coastal bluff located on the west coast of New Zealand's North Island, in the Northland region. Known locally as ''The Bluff'', it is set in a scenic reserve and rises above sea level. Maunganui Bluff marks the northern extent of long Ripiro Beach (the longest unbroken beach in New Zealand). Etymology ''Maunganui'' in Māori means ''big mountain''. Geology Studies using remote sensing indicate these basalt layers form part of an eroded basalt shield volcano, originally centered about 10 kilometers west of Maunganui Bluff, with an estimated width of 50 kilometers. Comparatively, other Miocene basalt shield volcanoes, such as those at Banks Peninsula, Dunedin, and the Auckland Islands, each spanned roughly 20 to 30 kilometers. Maunganui Bluff and the Waipoua Forest region are primarily composed of Early Miocene basalt flows that include pyroclastic deposits, volcanic breccia, dikes Dyke or dike may refer to: General uses * Dyke (sla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Threat Classification System
The New Zealand Threat Classification System is used by the Department of Conservation to assess conservation priorities of species in New Zealand. The system was developed because the IUCN Red List, a similar conservation status system, had some shortcomings for the unique requirements of conservation ranking in New Zealand. plants, animals, and fungi are evaluated, though the lattermost has yet to be published. Algae were assessed in 2005 but not reassessed since. Other protist A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...s have not been evaluated. Categories Species that are ranked are assigned categories: ;Threatened :This category has three major divisions: :*Nationally Critical - equivalent to the IUCN category of Critically endangered :*Nationally Endangered - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), '' Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as kelps provide essential nursery habitat for fisheries and other marine species and thus protect food sources; other species, such as planktonic algae, play a vital role in capturing carbon and producing at least 50% of Earth's oxygen. Natural seaweed ecosystems are sometimes under threat from human activity. For example, mechanical dredging of kelp destroys the resource and dependent fisheries. Other forces also threaten some seaweed ecosystems; for example, a wasting disease in predators of purple urchins has led to an urchin population surge which has destroyed large kelp forest regions off the coast of California. Humans have a long history of cultivating seaweeds for their uses. In recent years, seaweed farming has become a global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply to any frequency range, including ultrasound. Ultrasonic devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on the mathematical properties of String instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Echolocation
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological active sonar used by several animal groups, both in the air and underwater. Echolocating animals emit calls and listen to the Echo (phenomenon) , echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for animal navigation , navigation, foraging, and predation, hunting prey. Echolocation calls can be Frequency modulation, frequency modulated (FM, varying in pitch during the call) or constant frequency (CF). FM offers precise range discrimination to localize the prey, at the cost of reduced operational range. CF allows both the prey's velocity and its movements to be detected by means of the Doppler effect. FM may be best for close, cluttered environments, while CF may be better in open environments or for hunting while perched. Echolocating animals include mammals, especially odontocetes (toothed whales) and some bat species, and, using s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Shark
The blue shark (''Prionace glauca''), also known as the great blue shark, is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae and the only member of its genus which inhabits deep waters in the world's temperate and tropical oceans. Averaging around and preferring cooler waters, the blue shark migrates long distances, such as from New England to South America. It is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN. Although generally lethargic, they can move very quickly. Blue sharks are viviparous and are noted for large litters of 25 to over 100 pups. They feed primarily on small fish and squid, although they can take larger prey. Some of the blue shark’s predators include the killer whale and larger sharks like tiger sharks and the great white shark. Their maximum lifespan is still unknown, but it is believed that they can live up to 20 years. They are one of the most abundant pelagic sharks, with large numbers being caught by fisheries as bycatch on longlines and nets. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great White Shark
The great white shark (''Carcharodon carcharias''), also known as the white shark, white pointer, or simply great white, is a species of large Lamniformes, mackerel shark which can be found in the coastal surface waters of all the major oceans. It is the only known surviving species of its genus ''Carcharodon''. The great white shark is notable for its size, with the largest preserved female specimen measuring in length and around in weight at maturity. However, most are smaller; males measure , and females measure on average. According to a 2014 study, the lifespan of great white sharks is estimated to be as long as 70 years or more, well above previous estimates, making it one of the longest lived Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fishes currently known. According to the same study, male great white sharks take 26 years to reach sexual maturity, while the females take 33 years to be ready to produce offspring. Great white sharks can swim at speeds of 25 km/h (16 mph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |