|
Myxozoan
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. Over 2,180 species have been described and some estimates have suggested at least 30,000 undiscovered species. Many have a two-host lifecycle, involving a fish and an annelid worm or a bryozoan. The average size of a myxosporean spore usually ranges from 10 μm to 20 μm, whereas that of a malacosporean (a subclade of the Myxozoa) spore can be up to 2 mm. Myxozoans can live in both freshwater and marine habitats. Myxozoans are highly derived cnidarians that have undergone dramatic evolution from a free swimming, self-sufficient jellyfish-like creature into their current form of obligate parasites composed of very few cells – sometimes only a single cell. As myxozoans evolved into microscopic parasites, they lost many g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxozoans Life Cycle
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek language, Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. Over 2,180 species have been described and some estimates have suggested at least 30,000 undiscovered species. Many have a two-host lifecycle, involving a fish and an annelid worm or a bryozoan. The average size of a myxosporean spore usually ranges from 10 μm to 20 μm, whereas that of a malacosporean (a subclade of the Myxozoa) spore can be up to 2 mm. Myxozoans can live in both freshwater and marine habitats. Myxozoans are highly derived cnidarians that have undergone dramatic evolution from a free swimming, self-sufficient jellyfish-like creature into their current form of obligate parasites composed of very few cells – sometimes only a single cell. As myxozoans evolved into microscopic parasites, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration. Many cnidarian species produce colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both (hence they are trimorphic). Cnidarians' activities are coordinated by a decentralized nerve net and simple receptors. Several free-swimming species of Cubozoa and Scyphozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxobolus Cerebralis
''Myxobolus cerebralis'' is a myxosporean parasite of salmonids (salmon and trout species) that causes whirling disease in farmed salmon and trout and also in wild fish populations. It was first described in rainbow trout in Germany in 1893, but its range has spread and it has appeared in most of Europe (including Russia), the United States, South Africa, Canada and other countries due to the aid of humans of shipments of cultured and wild fish. In the 1980s, ''M. cerebralis'' was found to require a tubificid oligochaete (a kind of segmented worm) to complete its life cycle. The parasite infects its hosts with its cells after piercing them with polar filaments ejected from nematocyst-like capsules. This infects the cartilage and possibly the nervous tissue of salmonids, causing a potentially lethal infection. Causing the host to develop a black tail, spinal deformities, and possible more deformities in the anterior part of the fish. Whirling disease affects juvenile fish (fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
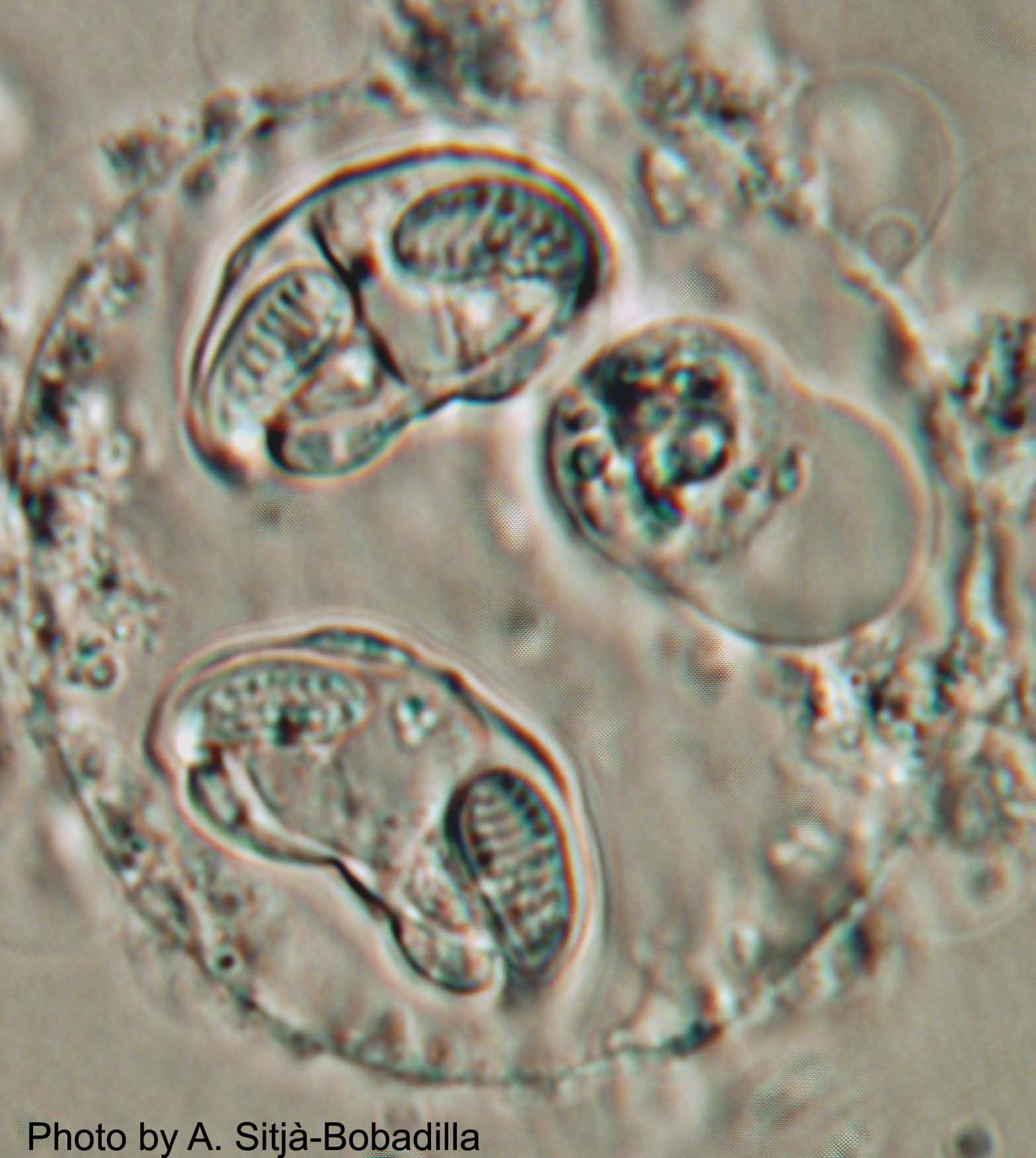
Enteromyxum Leei
''Enteromyxum leei'' is a species of myxozoan, histozoic parasite that infects the intestinal tract and sometimes associated organs, like gall bladder and liver, of several teleostean fish species. Myxozoans are microscopic metazoans, with an obligate parasitic life-style. The parasite stages of this species live in the paracelullar space between fish enterocytes. It is the causative agent of enteromyxosis, or emaciative disease, also known as "razor blade syndrome" in sparid fish. ''E. leei'' has a wide host and geographical range within marine fish (at least 60 species from 22 different families, mainly Perciforms), and even freshwater fish have been infected experimentally. ''E. leei'' initially emerged in the Mediterranean in the late 1980s and it is believed to have been unintentionally introduced into the Red Sea.Diamant, A. (1997). Fish-to-fish transmission of a marine myxosporean. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 30, 99-105. Its pathogenicity and economic impact depend on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whirling Disease
''Myxobolus cerebralis'' is a myxosporean parasite of salmonids (salmon and trout species) that causes whirling disease in farmed salmon and trout and also in wild fish populations. It was first described in rainbow trout in Germany in 1893, but its range has spread and it has appeared in most of Europe (including Russia), the United States, South Africa, Canada and other countries due to the aid of humans of shipments of cultured and wild fish. In the 1980s, ''M. cerebralis'' was found to require a tubificid oligochaete (a kind of segmented worm) to complete its life cycle. The parasite infects its hosts with its cells after piercing them with polar filaments ejected from nematocyst-like capsules. This infects the cartilage and possibly the nervous tissue of salmonids, causing a potentially lethal infection. Causing the host to develop a black tail, spinal deformities, and possible more deformities in the anterior part of the fish. Whirling disease affects juvenile fish (fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetracapsuloides Bryosalmonae
''Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae'' is a myxozoan parasite of salmonid fish. It is the only species currently recognized in the monotypic genus ''Tetracapsuloides''. It is the cause of proliferative kidney disease (PKD), one of the most serious parasitic diseases of salmonid populations in Europe and North America that can result in losses of up to 90% in infected populations. Taxonomy Until the late 1990s, the organism which caused PKD was enigmatic, thus called PKX organism. The causative agent of PKD was recognized as a form of Malacosporean, but the absence of mature spores in salmonid hosts, the lack of fish to fish transmission, and seasonality of the disease suggested that the life cycle of PKX was completed in another host and that infection of salmonids could be accidental. Korotneff observed a myxozoan in the bryozoan, '' Plumatella fungosa'', in 1892, which he described as ''Myxosporidium bryozoides.'' Myxozoan infection of bryozoans was not reported again until 1996. Eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proliferative Kidney Disease
''Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae'' is a myxozoan parasite of salmonid fish. It is the only species currently recognized in the monotypic genus ''Tetracapsuloides''. It is the cause of proliferative kidney disease (PKD), one of the most serious parasitic diseases of salmonid populations in Europe and North America that can result in losses of up to 90% in infected populations. Taxonomy Until the late 1990s, the organism which caused PKD was enigmatic, thus called PKX organism. The causative agent of PKD was recognized as a form of Malacosporean, but the absence of mature spores in salmonid hosts, the lack of fish to fish transmission, and seasonality of the disease suggested that the life cycle of PKX was completed in another host and that infection of salmonids could be accidental. Korotneff observed a myxozoan in the bryozoan, '' Plumatella fungosa'', in 1892, which he described as ''Myxosporidium bryozoides.'' Myxozoan infection of bryozoans was not reported again until 1996. Eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectoproct
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a lophophore, a "crown" of tentacles used for filter feeding. Most marine bryozoans live in tropical waters, but a few are found in oceanic trenches and polar waters. The bryozoans are classified as the marine bryozoans (Stenolaemata), freshwater bryozoans (Phylactolaemata), and mostly-marine bryozoans (Gymnolaemata), a few members of which prefer brackish water. 5,869living species are known. At least two genera are solitary (''Aethozooides'' and ''Monobryozoon''); the rest are colonial. The terms Polyzoa and Bryozoa were introduced in 1830 and 1831, respectively. Soon after it was named, another group of animals was discovered whose filtering mechanism looked similar, so it was included in Bryozoa until 1869, when the two groups were no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proliferative Gill Disease
Proliferation may refer to: Weapons *Nuclear proliferation, the spread of nuclear weapons, material, and technology *Chemical weapon proliferation, the spread of chemical weapons, material, and technology *Small arms proliferation, the spread of small weapons *Counter-proliferation, efforts to stop weapon proliferation Computer science *License proliferation, a problem caused by incompatible software licenses *Data proliferation, the challenge of dealing with large amounts of data Medicine and biology *Cell proliferation, cell growth and division *Proliferation, a phase of wound healing *Atypical small acinar proliferation, a concept in urologic pathology * Intravenous atypical vascular proliferation, a skin condition * Massive periretinal proliferation, a disease of the eye Music * ''Proliferation'' (album), a 2008 album by Mike Reed's People, Places & Things Other uses * Conceptual proliferation, a concept in Buddhism *Product proliferation Product proliferation occurs when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparidae
The Sparidae are a family of fish in the order Perciformes, commonly called sea breams and porgies. The sheepshead, scup, and red seabream are species in this family. Most sparids are deep-bodied compressed fish with a small mouth separated by a broad space from the eye, a single dorsal fin with strong spines and soft rays, a short anal fin, long pointed pectoral fins and rather large firmly attached scales. They are found in shallow temperate and tropical waters and are bottom-dwelling carnivores. There are hermaphrodites in the Sparidae. Protogyny and protandry appear sporadically through this lineage of fish. Simultaneous hermaphrodites and bi-directional hermaphrodites do not appear as much since Sparidae are found in shallower waters. Species of fish that express a hermaphroditic condition usually "lack a genetic hardwire", therefore ecological factors play a role in sex determination. Most species possess grinding, molar-like teeth. Eating the head is known to cause hallu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |