|
Myxarium Simile
''Myxarium'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hyaloriaceae. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are gelatinous and effused or pustular. The genus is cosmopolitan. All species grow on dead wood or dead herbaceous stems. Taxonomy History The genus was originally described by Karl Friedrich Wilhelm Wallroth in 1833 based on the visible white inclusions in the basidiocarps of the type species, '' Myxarium nucleatum'', which he interpreted as spores (they are in fact crystals of calcium oxalate). The genus was synonymized with '' Exidia'' by subsequent authors, until revived by Dutch mycologist M.A. Donk in 1966. The revised concept of ''Myxarium'' emphasized the microscopic presence of septate basidia with enucleate stalk cells ("myxarioid" basidia), a feature absent in ''Exidia''. Additional species were added to the genus on this basis. Current status Molecular research, based on cladistic analysis of DNA sequences, indicates that ''Myxarium'' is distinct from ''Exidia'' and fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxarium Populinum
''Myxarium'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hyaloriaceae. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are gelatinous and effused or pustular. The genus is cosmopolitan. All species grow on dead wood or dead herbaceous stems. Taxonomy History The genus was originally described by Karl Friedrich Wilhelm Wallroth in 1833 based on the visible white inclusions in the basidiocarps of the type species, '' Myxarium nucleatum'', which he interpreted as spores (they are in fact crystals of calcium oxalate). The genus was synonymized with '' Exidia'' by subsequent authors, until revived by Dutch mycologist M.A. Donk in 1966. The revised concept of ''Myxarium'' emphasized the microscopic presence of septate basidia with enucleate stalk cells ("myxarioid" basidia), a feature absent in ''Exidia''. Additional species were added to the genus on this basis. Current status Molecular research, based on cladistic analysis of DNA sequences, indicates that ''Myxarium'' is distinct from ''Exidia'' and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exidia
''Exidia'' is a genus of fungi in the family Auriculariaceae. The species are saprotrophic, occurring in attached or recently fallen dead wood, and produce gelatinous basidiocarps (fruit bodies). The fruit bodies are diverse, pustular, lobed, button-shaped or cup-shaped. Several species, including the type species ''Exidia glandulosa'', have sterile pegs or pimples on their spore-bearing surface. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution and around 20 species are currently recognized worldwide. Initial molecular research indicates the genus is artificial. Taxonomy ''Exidia'' species were originally placed in the genus ''Tremella'' along with many other gelatinous fungi. The genus ''Exidia'' was separated from ''Tremella'' by Fries in 1822, based mainly on fruit body shape. Fries initially included species now assigned to ''Auricularia'' within the genus. Recent molecular research has indicated that ''Exidia'' as currently circumscribed is an artificial grouping, the species not b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
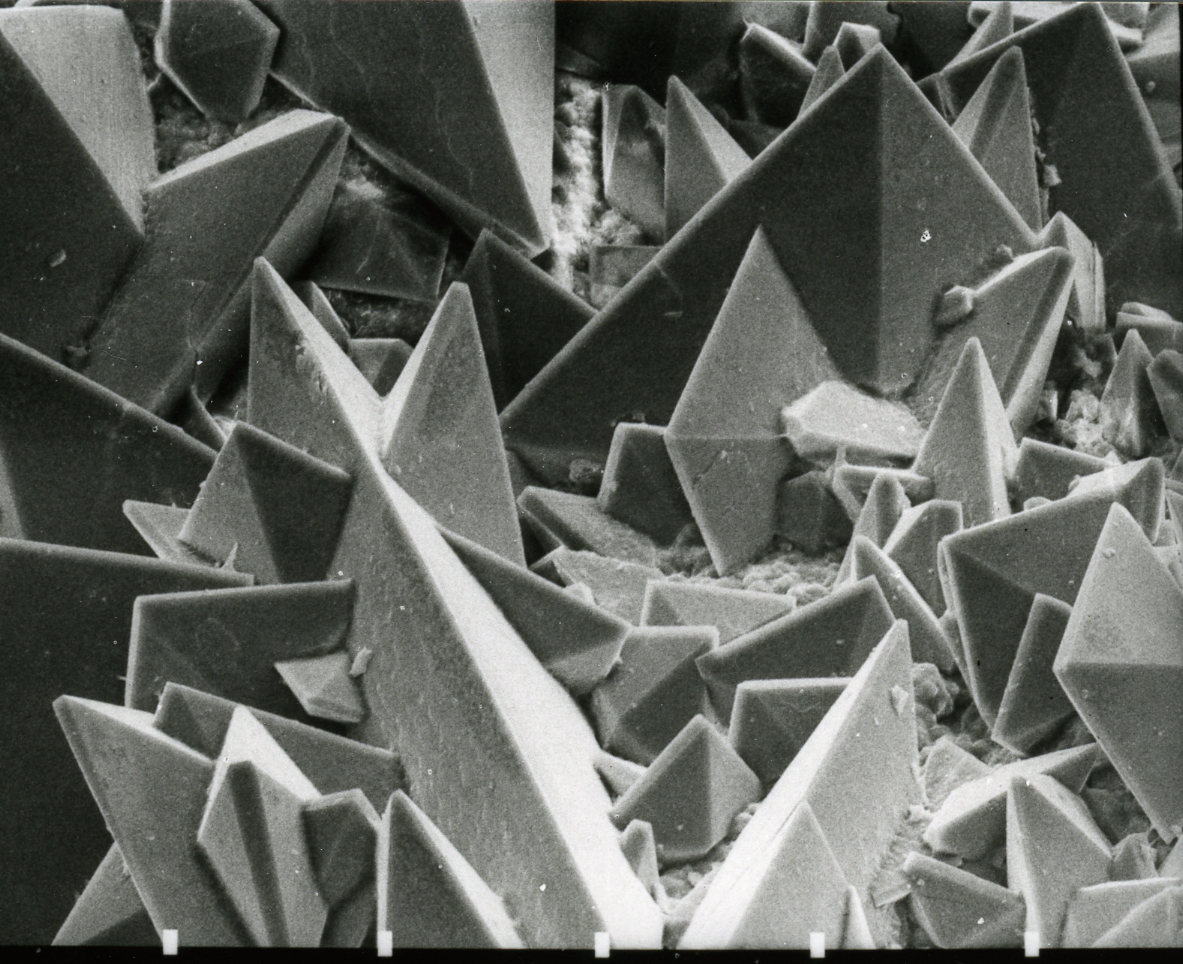
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Tribes with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence Many plants accumu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Friedrich Wilhelm Wallroth
Karl Friedrich Wilhelm Wallroth (13 March 1792 in Breitenstein, Saxony-Anhalt – 22 March 1857 in Nordhausen, Thuringia, Nordhausen) was a German botanist. His name is abbreviated Wallr. as a taxon authority. He attended classes in medicine and botany at the University of Halle, afterwards continuing his studies in Göttingen, where he was a pupil of botanist Heinrich Schrader (botanist), Heinrich Adolf Schrader (1767-1836). In 1816 he obtained his medical doctorate at the University of Göttingen. In 1822 he was appointed district physician to the city of Nordhausen, Thuringia, Nordhausen, where along with his duties as a doctor, he performed botanical research. Among his writings were a treatise on cryptogams native to Germany, ''Flora Cryptogamica Germaniae'' (1831–33), and a study on the biology of lichens, titled ''Naturgeschichte der Flechten'' (1825 and 1827). Wallroth is credited for introducing the terms "" and "" to explain two distinct forms of lichen thallus, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiocarps
In fungi, a basidiocarp, basidiome, or basidioma () is the sporocarp (fungi), sporocarp of a basidiomycota, basidiomycete, the Multicellular organism, multicellular structure on which the spore-producing hymenium is borne. Basidiocarps are characteristic of the hymenomycetes; Urediniomycetes, rusts and Ustilaginomycetes, smuts do not produce such structures. As with other sporocarps, epigeous (above-ground) basidiocarps that are visible to the naked eye (especially those with a more or less agaricoid morphology) are commonly referred to as mushrooms, while hypogeous (underground) basidiocarps are usually called false truffles. Structure All basidiocarps serve as the structure on which the hymenium is produced. Basidia are found on the surface of the hymenium, and the basidia ultimately produce spores. In its simplest form, a basidiocarp consists of an undifferentiated fruiting structure with a hymenium on the surface; such a structure is characteristic of many simple jelly fungi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaloriaceae
The Hyaloriaceae are a family of fungi in the order Auriculariales. Species within the family have gelatinous basidiocarps (fruit bodies) that produce spores on septate basidia and, as such, were formerly referred to the " heterobasidiomycetes" or "jelly fungi". All appear to be saprotrophic, growing on dead wood or plant remains. Less than 30 species are currently included within the Hyaloriaceae, but the family has not been extensively researched. Taxonomy History The family was established in 1900 by German mycologist Gustav Lindau to accommodate a single, neotropical species, '' Hyaloria pilacre''. Lindau considered his new family to be close to the Tremellaceae, but distinguished by the "angiocarpous" or gasteroid development of its fruit bodies (meaning that the spore-bearing hymenia were covered until maturity, rather than exposed). The Hyaloriaceae were placed within the order Tremellales by most subsequent authors, until 1984, when American mycologist Robert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

