|
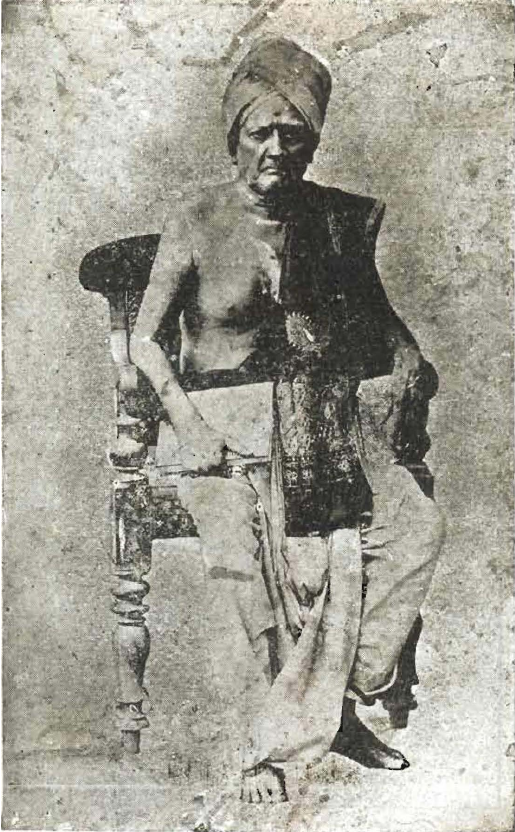
Mysore Vasudevacharya
Mysore Vasudevacharya (28 May 1865 – 17 May 1961) was an Indian musician and composer of Carnatic music compositions who belonged to the direct line of Thyagaraja's disciples. Vasudevachar's compositions (numbering over 200) were mostly in Telugu and Sanskrit. Some of his most popular kritis include '' Broche varevaru ra'' in Khamas raga, ''Devadideva'' in Sunadavinodini, ''Mamavatu Sri Saraswati'' in Hindolam, ''Shankari Ninne'' in Pantuvarali, ''Bhajare Re Manasa'' in Abheri and ''Ra Ra Rajeevalochana Rama'' in Mohanam. He was a recipient of the civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan. He is credited with two writings in Kannada, one of them an autobiography called ''Nenapugalu'' (memories) and ''Na Kanda Kalavidaru'' (the musicians I have met) in which he wrote the biographies of many well known musicians. Mysore Vasudevachar also taught in Rukmini Devi's Kalakshetra, (founded in 1936). He was already quite old by then, but thanks to Rukmini Devi he agreed to shift to Kalakshe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary alliance with British India. The British took Direct Control over the Princely State in 1831.Rajakaryaprasakta Rao Bahadur (1936), p383 It then became Mysore State (later enlarged and renamed to Karnataka) with its ruler remaining as Rajapramukh until 1956, when he became the first Governor of the reformed state. The kingdom, which was founded and ruled for most part by the Hindu Wodeyar family, initially served as feudatories under the Vijayanagara Empire. The 17th century saw a steady expansion of its territory and during the rule of Narasaraja Wodeyar I and Chikka Devaraja Wodeyar, the kingdom annexed large expanses of what is now southern Karnataka and parts of Tamil Nadu to become a powerful state in the southern Deccan. During a brief Muslim rule, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhwa Brahmin
Madhva Brahmins (also often referred as Madhvas or Sadh-Vaishnavas), are Hindu Brahmin communities in India, who follow Sadh Vaishnavism and Dvaita philosophy propounded by Madhvacharya. They are found mostly in the Indian states of Karnataka, Maharashtra, Goa, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. History The Madhwa community traces its philosophical origins to Madhvacharya, the first said Sadh Vaishnava acharya, who lived around 13th century. The Ashta Mathas of Udupi were established by Madhvacharya by his disciples. Other Acharyas who established mathas after Madhvacharya include Padmanabha Tirtha, Naraharitirtha, Akshobhya Tirtha, Jayatirtha, Sripadaraja, Vyasatirtha, Vadiraja Tirtha, Vijayendra Tirtha, Raghavendra Tirtha. The affiliations of the Madhwa philosophy extended in the form of temples and monasteries from Udupi in the South India to Dwaraka in West India to Gaya in the East India to Badrinath in the North India. The town of Udupi is famous f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tala (music)
A tala ( IAST ''tāla'') literally means a 'clap, tapping one's hand on one's arm, a musical measure'. It is the term used in Indian classical music similar to musical meter, that is any rhythmic beat or strike that measures musical time. The measure is typically established by hand clapping, waving, touching fingers on thigh or the other hand, verbally, striking of small cymbals, or a percussion instrument in the Indian subcontinental traditions. Along with '' raga'' which forms the fabric of a melodic structure, the ''tala'' forms the life cycle and thereby constitutes one of the two foundational elements of Indian music. ''Tala'' is an ancient music concept traceable to Vedic era texts of Hinduism, such as the '' Samaveda'' and methods for singing the Vedic hymns. The music traditions of the North and South India, particularly the ''raga'' and ''tala'' systems, were not considered as distinct till about the 16th century. There on, during the tumultuous period of Islamic ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raga
A ''raga'' or ''raag'' (; also ''raaga'' or ''ragam''; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a melodic mode. The ''rāga'' is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradition, and as a result has no direct translation to concepts in classical European music. Each ''rāga'' is an array of melodic structures with musical motifs, considered in the Indian tradition to have the ability to "colour the mind" and affect the emotions of the audience. Each ''rāga'' provides the musician with a musical framework within which to improvise. Improvisation by the musician involves creating sequences of notes allowed by the ''rāga'' in keeping with rules specific to the ''rāga''. ''Rāga''s range from small ''rāga''s like Bahar and Shahana that are not much more than songs to big ''rāga''s like Malkauns, Darbari and Yaman, which have great scope for improvisation and for which performances can last over an hour. ''Rāga''s may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shyama Sastri
Shyama Shastri (; 26 April 1762 – 1827) or Syama Sastri was a musician and composer of Carnatic music. He was the oldest among the Trinity of Carnatic music, Tyagaraja and Muthuswami Dikshitar being the other two. Early life and career Shyama Shastri, whose birth name was Venkata Subrahmanya, was born on 26 April 1762 in a Telugu Brahmin family. He was also known as one of the trinity of carnatic music. To later generations, he is better known by his adopted name Shyama Shastri or by his musical mudra (signature) Shyama Krishna. He was born in Tiruvarur, in what is now the state of Tamil Nadu. He received his instruction in the vedas, astrology, and other traditional subjects early on and learned music from his maternal uncle. He was later trained in music by Adiappayya, a noted durbar musician of Thanjavur. Although Śyāma Śastri did not compose as many ''kritis'' as his two prolific contemporaries, his compositions are still well known due to the literary, melodic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muthuswami Dikshitar
Muthuswami Dikshitar (Mudduswamy Dikshitar)(, 24 March 1776 – 21 October 1835), mononymously Dikshitar, was a South Indian poet, singer and veena player, and a legendary composer of Indian classical music, who is considered one of the musical trinity of Carnatic music. Muthuswami Dikshitar was born on 24 March 1775 in Tiruvarur near Thanjavur, in what is now the state of Tamil Nadu in India, to a family that is traditionally traced back to Virinichipuram in the northern boundaries of the state. His compositions, of which around 500 are commonly known, are noted for their elaborate and poetic descriptions of Hindu gods and temples and for capturing the essence of the raga forms through the vainika (veena) style that emphasises gamakas. They are typically in a slower speed (chowka kala). He is also known by his signature name of Guruguha which is also his mudra (and can be found in each of his songs). His compositions are widely sung and played in classical concerts of Carnatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
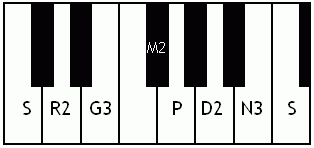
Kalyani (rāga)
Kalyani is a melakarta raga (parent musical scale) in the Carnatic music. It was called Kalyan but is now more popularly called Yaman in Hindustani Music. Its Western equivalent is the Lydian mode. Kalyani in Carnatic music In South Indian weddings it is a very prominently played raga. The word ''Kalyani'' means ''she who causes auspicious things''. It is the 65th melakarta raga under the Katapayadi sankhya. It is also called ''Mechakalyani''. The notes for Kalyani are S R2 G3 M2 P D2 N3. Kalyani is the first Prathi Madhyama raga that was ever discovered. It was obtained by the process of Graha Bhedam or modal shift of tonic of the ancient Shadja Grama. Specifics on this raga Kalyani has scope for elaborate alapana. One should not remain too long on panchamam (pa) or alternate between shadjamam and panchamam too frequently. Kalyani is prominently known among the public. It is often performed at the beginning of concerts because it is considered auspicious. Structure and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyagaraja
Thyagaraja (Telugu: త్యాగరాజ) (4 May 1767 – 6 January 1847), also known as Thyāgayya and in full as Kakarla Thyagabrahmam, was a composer and vocalist of Carnatic music, a form of Indian classical music. Tyagaraja and his contemporaries, Shyama Shastri and Muthuswami Dikshitar, are regarded as the Trinity of Carnatic music. Thyagaraja composed thousands of devotional compositions, most in Telugu and in praise of Lord Rama, many of which remain popular today, the most popular being "Nagumomu". Of special mention are five of his compositions called the '' Pancharatna Kritis'' ( "five gems"), which are often sung in programs in his honour, and ''Utsava Sampradaya Krithis'' ( Festive ritual compositions), which are often sung to accompany temple rituals. Tyagaraja lived through the reigns of four kings of the Maratha dynasty — Tulaja II (1763–1787), Amarasimha (1787–1798), Serfoji II (1798–1832) and Sivaji II (1832–1855), although he served none ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Śloka
Shloka or śloka ( sa, श्लोक , from the root , Macdonell, Arthur A., ''A Sanskrit Grammar for Students'', Appendix II, p. 232 (Oxford University Press, 3rd edition, 1927). in a broader sense, according to Monier-Williams's dictionary, is "any verse or stanza; a proverb, saying"; but in particular it refers to the 32-line verse, derived from the Vedic Sanskrit, Vedic ''anuṣṭubh'' metre, used in the ''Bhagavad Gita'' and many other works of classical Sanskrit literature. In its usual form it consists of four ''pādas'' or quarter-verses, of 8 syllables each, or (according to an alternative analysis) of two half-verses of 16 syllables each. The metre is similar to the Vedic Sanskrit, Vedic ''anuṣṭubh'' metre, but with stricter rules. The ''śloka'' is the basis for Indian epic poetry, and may be considered the Indian verse form ''par excellence'', occurring as it does far more frequently than any other metre in classical Sanskrit prosody, Sanskrit poetry. The ''ślok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thillana
A Tillana or thillana is a rhythmic piece in Carnatic music that is generally performed at the end of a concert and widely used in classical indian dance performances. It was popularised by Dr. M Balamuralikrishna and some other musicians A Tillana uses tala-like phrases in the pallavi and anupallavi, and lyrics in the charanam. The '' thillana'' is based on the tarana which was introduced by Amir Khusrau Abu'l Hasan Yamīn ud-Dīn Khusrau (1253–1325 AD), better known as Amīr Khusrau was an Indo-Persian Sufi singer, musician, poet and scholar who lived under the Delhi Sultanate. He is an iconic figure in the cultural history of the Indian sub ... (1253-1325 CE). Popular Compositions * Kadanakuthuhalam Thillana composed by Dr.M. Balamuralikrishna (Ragam: Kadanakuthuhalam) * Kadanakuthuhalam Thillana composed by Lalgudi Jayaraman (Ragam: Kadanakuthuhalam) * Kalinga Narthana Thillana composed by Sri Oothukkadu Venkata Ravi (Ragam: Gambhira Natta) * Mohanakalyani Thilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varnam
Varṇam is a type of composition in the Carnatic music system consisting of short metric pieces which encapsulate the main features (patterns of notes) of a '' raga''. Varnams capture the ''raga bhavam'', ''ranjaka prayogas'' ''visesha sancharas'', etc. ''Dhatu'' and ''janta prayogas'' (phrase usage) are usually part of a varnam. Understanding of these aspects is key to developing ''manodharma sangeetham'' (i.e., improvisation aspects of Carnatic music such as ''raga aalapana'', ''swara kalpana'', ''neraval'', etc.). Known for their complex structure, varnams are a fundamental form in Carnatic music. All varnams consist of lyrics, Bradnock (1992), p631 as well as ''swara'' passages, including a '' pallavi'', an '' anupallavi'', ''muktaayi swaras'', a '' charanam'', and '' chitta swaras''. There are different types of varnams, such as ''taana varnam'', ''pada varnam'', ''daru varnam'' and ''ragamalika varnam''. They also come in different ''taalams'' (beat cycles). Though the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriti (music)
''Kriti'' (Sanskrit: कृति, ''kṛti'') is a format of musical composition typical to Carnatic music Carnatic music, known as or in the South Indian languages, is a system of music commonly associated with South India, including the modern Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, and Sri Lanka. It is o .... ''Kritis'' form the mental backbone of any typical Carnatic music concert and is the longer format of Carnatic song. "Kriti" also means Creation. Structure Conventional ''Kritis'' typically contain three parts #'' Pallavi'', the equivalent of a refrain in Western music #'' Anupallavi'', the second verse, which is sometimes optional #'' Charanam'', the final (and longest) verse that wraps up the song The ''charanam'' usually borrows patterns from the ''anupallavi''. The ''charanam's'' last line usually contains the composer's signature, or '' mudra'', with which the composer leaves their mark. Variations Some Kritis have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)