|
Myriapora Truncata
''Myriapora truncata'', also known by its common name false coral is a species from the genus '' Myriapora''. The species was originally described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. Description ''Myriapora truncata'' is a common species on rocky environments from the water surface to a depth of 60 meter, where it forms calcareous colonies. It has a bright red colour which earned it its common name of "False coral". Ecology Studies suggest that ''M. truncata'' seem well able to withstand the levels of ocean acidification Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxid ... predicted in the next 200 years. Natural products ''Myriapora truncata'' is the source of 4 polyketide-derived metabolites: Myriaprones 1-4 References Taxa named by Peter Simon Pallas Cheilostomati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myriapora
''Myriapora'' is a genus of bryozoans belonging to the family Myriaporidae. The genus has almost cosmopolitan distribution. Species: *'' Myriapora beyrichi'' *'' Myriapora bugei'' *'' Myriapora fungiformis'' *'' Myriapora kuhni'' *'' Myriapora operculata'' *'' Myriapora orientalis'' *'' Myriapora sciutoi'' *'' Myriapora simplex'' *''Myriapora truncata ''Myriapora truncata'', also known by its common name false coral is a species from the genus '' Myriapora''. The species was originally described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. Description ''Myriapora truncata'' is a common species on rocky e ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q3869126 Bryozoan genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810. Life and work Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University of Göttingen. In 1760, he moved to the University of Leiden and passed his doctor's degree at the age of 19. Pallas travelled throughout the Netherlands and to London, improving his medical and surgical knowledge. He then settled at The Hague, and his new system of animal classification was praised by Georges Cuvier. Pallas wrote ''Miscellanea Zoologica'' (1766), which included descriptions of several vertebrates new to science which he had discovered in the Dutch museum collections. A planned voyage to southern Africa and the East Indies fell through when his father reca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1766
Events January–March * January 1 – Charles Edward Stuart ("Bonnie Prince Charlie") becomes the new Stuart claimant to the throne of Great Britain, as King Charles III, and figurehead for Jacobitism. * January 14 – Christian VII becomes King of Denmark. * January 20 – Outside of the walls of the Thailand capital of Ayutthaya, tens of thousands of invaders from Burma (under the command of General Ne Myo Thihapate and General Maha Nawatra) are confronted by Thai defenders led by General Phya Taksin. The defenders are overwhelmed and the survivors take refuge inside Ayutthaya. The siege continues for 15 months before the Burmese attackers collapse the walls by digging tunnels and setting fire to debris. The city falls on April 9, 1767, and King Ekkathat is killed. * February 5 – An observer in Wilmington, North Carolina reports to the Edinburgh newspaper ''Caledonian Mercury'' that three ships have been seized by British men-of-war, on the char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcareous
Calcareous () is an adjective meaning "mostly or partly composed of calcium carbonate", in other words, containing lime or being chalky. The term is used in a wide variety of scientific disciplines. In zoology ''Calcareous'' is used as an adjectival term applied to anatomical structures which are made primarily of calcium carbonate, in animals such as gastropods, i.e., snails, specifically about such structures as the operculum, the clausilium, and the love dart. The term also applies to the calcium carbonate tests of often more or less microscopic Foraminifera. Not all tests are calcareous; diatoms and radiolaria have siliceous tests. The molluscs are calcareous, as are calcareous sponges ( Porifera), that have spicules which are made of calcium carbonate. In botany ''Calcareous grassland'' is a form of grassland characteristic of soils containing much calcium carbonate from underlying chalk or limestone rock. In medicine The term is used in pathology, for example i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Acidification
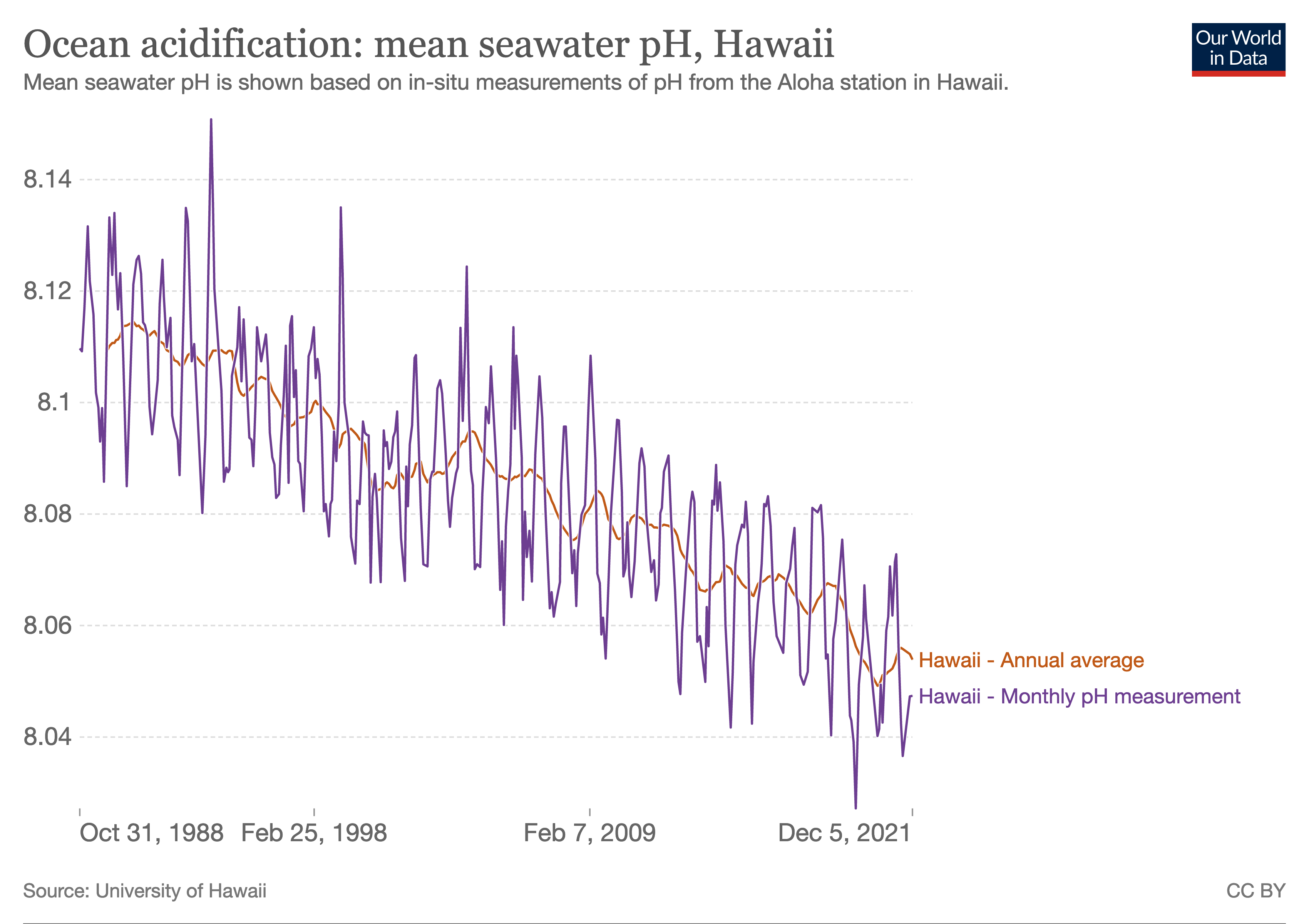
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxide emissions from human activities which have led to atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels of more than 410 ppm (in 2020). The oceans absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. This leads to the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (H+). The free hydrogen ions (H+) decrease the pH of the ocean, therefore increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). A decrease in pH corresponds to a decrease in the concentration of carbonate ions, which are the main building block for calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells and skeletons. Marine calcifying organisms, like mollusks, oysters and corals, are particularly affected by this as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Peter Simon Pallas
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |