|
Myriagram
The myriagram (french: myriagramme) is a former France, French and International System of Units, metric unit of mass equal to 10,000 grams (''myriad'' being the Greek word for ten thousand). Although never as widely used as the kilogram, the myriagram was employed during the 19th century as a replacement for the earlier American customary system quarter (unit), quarter, which was equal to . In 1975, the United States, having previously authorized use of the myriagram in 1866, declared the term no longer acceptable. See also * myria- * History of the International System of Units References Units of mass {{fr-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myria-
Myria- (symbol my) is a now obsolete decimal metric prefix denoting a factor of 104 (ten thousand). It originates from the Greek μύριοι (''mýrioi'') (myriad). The prefix was part of the original metric system adopted by France in 1795, but was not adopted when the SI prefixes were internationally adopted by the 11th CGPM conference in 1960. In 1685 John Wallis proposed the usage of myrio. Also, in 19th century English it was sometimes spelled myrio, in line with a puristic opinion by Thomas Young. The ''myriametre'' (10 km) is occasionally encountered in 19th-century train tariffs, or in some classifications of wavelengths as the adjective '' myriametric''. The French ''mesures usuelles'' (1812-1839) did not include any units of length greater than the ''toise'', but the ''myriametre'' remained in use throughout this period. (Website based on ''Alte Meß- und Währungssysteme aus dem deutschen Sprachgebiet'', .) In Sweden and Norway, the ''myriametre'' is stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International System Of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myriad
A myriad (from Ancient Greek grc, μυριάς, translit=myrias, label=none) is technically the number 10,000 (ten thousand); in that sense, the term is used in English almost exclusively for literal translations from Greek, Latin or Sinospheric languages (Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Vietnam), or when talking about ancient Greek numerals. More generally, a myriad may be used in colloquial vernaculars to imply an indefinitely large number. History The Aegean numerals of the Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations included a single unit to denote tens of thousands. It was written with a symbol composed of a circle with four dashes . In Classical Greek numerals, a myriad was written as a capital mu: Μ, as lower case letters did not exist in Ancient Greece. To distinguish this numeral from letters, it was sometimes given an overbar: . Multiples were written above this sign, so that for example would equal 4,582×10,000 or 45,820,000. The etymology of the word ''myriad'' itself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myriameter
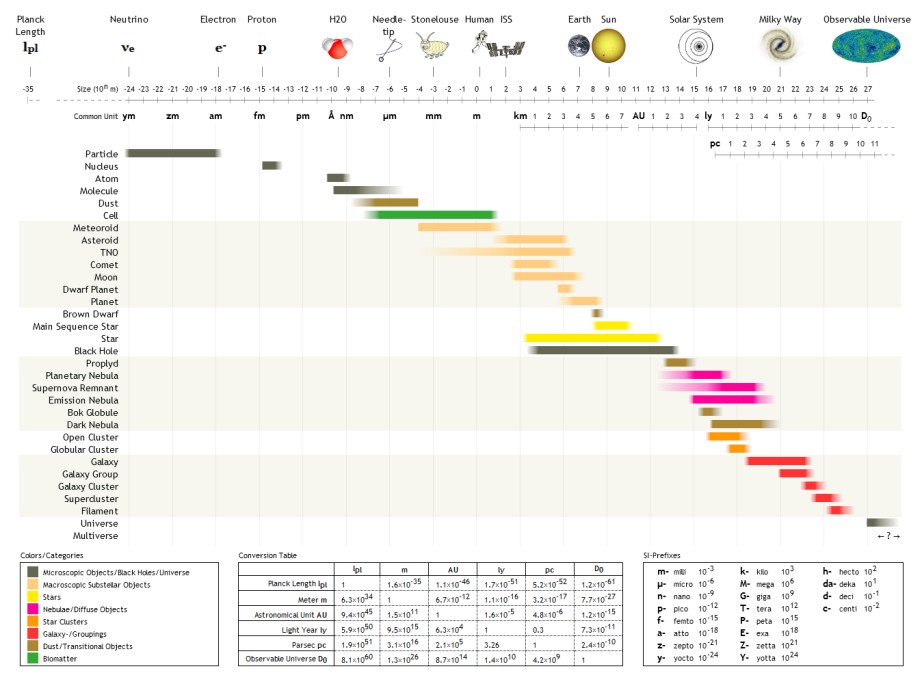
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths. __TOC__ Overview Detailed list To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^metres. Subatomic scale Atomic to cellular scale Cellular to human scale Human to astronomical scale Astronomical scale Less than 1 zeptometre The ' ( SI symbol: ') is a unit of length in the metric system equal to . To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths shorter than 10−21 m (1 zm). *1.6 × 10−5 quectometres (1.6 × 10−35 metres) – the Planck length (Measures of distance shorter than this do not make physical sense, according to current theories of physics.) *1 qm – 1 quectometre, the smallest named subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one nonillionth of a metre *1 rm – 1 rontometre, a subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one octilliont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The International System Of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |