|
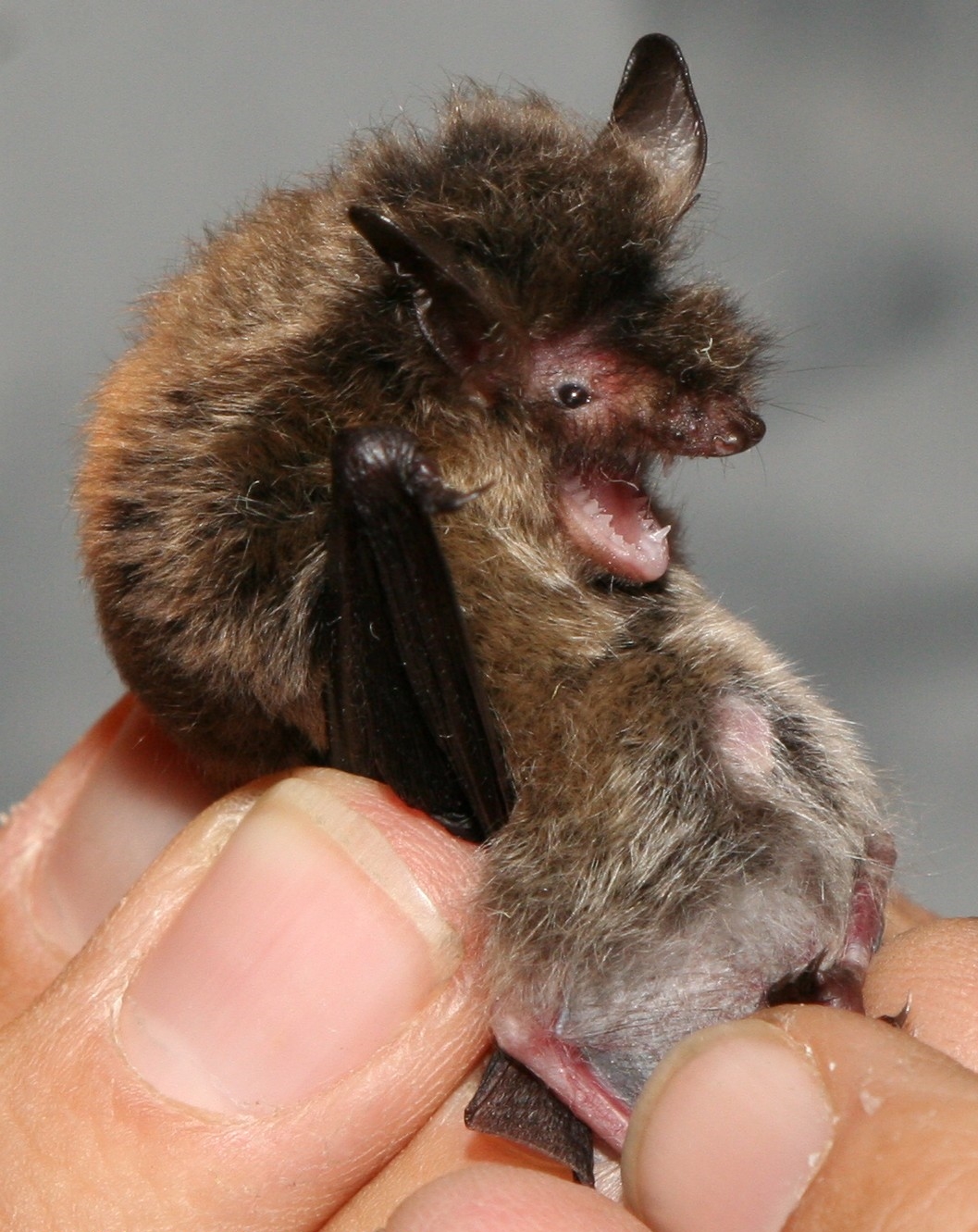
Myotis Alticraniatus
The mouse-eared bats or myotises are a diverse and widespread genus (''Myotis'') of bats within the family Vespertilionidae. The noun "''myotis''" itself is a New Latin construction, from the Greek "''muós'' (meaning "mouse") and "''oûs''" (meaning ear), literally translating to "mouse-eared". Relationships ''Myotis'' has historically been included in the subfamily Vespertilioninae, but was classified in its own subfamily, Myotinae, by Nancy Simmons in 1998. In her 2005 classification in ''Mammal Species of the World'', Simmons listed the genera ''Cistugo'' and ''Lasionycteris'' in the Myotinae in addition to ''Myotis'' itself.Simmons, 2005, p. 499 However, molecular data indicate that ''Cistugo'' is distantly related to all other Vespertilionidae, so it was reclassified into its own family, the Cistugidae, and that ''Lasionycteris'' belongs in the Vespertilioninae.Roehrs et al., 2010 The genus '' Submyotodon'' has since been added to the subfamily, making it and ''Myotis'' it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tortonian
The Tortonian is in the geologic time scale an age or stage of the late Miocene that spans the time between 11.608 ± 0.005 Ma and 7.246 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). It follows the Serravallian and is followed by the Messinian. The Tortonian roughly overlaps with the regional Pannonian Stage of the Paratethys timescale of Central Europe. It also overlaps the upper Astaracian, Vallesian and lower Turolian European land mammal ages, the upper Clarendonian and lower Hemphillian North American land mammal ages and the upper Chasicoan and lower Huayquerian South American land mammal ages. Definition The Tortonian was introduced by Swiss stratigrapher Karl Mayer-Eymar in 1858. It was named after the Italian city of Tortona in the region Piedmont. The base of the Tortonian Stage is at the last common appearance of calcareous nanoplankton '' Discoaster kugleri'' and planktonic foram '' Globigerinoides subquadratus''. It is also associated with the short normal polarized magneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesper Bat
Vespertilionidae is a family of microbats, of the order Chiroptera, flying, insect-eating mammals variously described as the common, vesper, or simple nosed bats. The vespertilionid family is the most diverse and widely distributed of bat families, specialised in many forms to occupy a range of habitats and ecological circumstances, and it is frequently observed or the subject of research. The facial features of the species are often simple, as they mainly rely on vocally emitted echolocation. The tails of the species are enclosed by the lower flight membranes between the legs. Over 300 species are distributed all over the world, on every continent except Antarctica. It owes its name to the genus ''Vespertilio'', which takes its name from a word for bat, ', derived from the Latin term ' meaning 'evening'; they are termed "evening bats" and were once referred to as "evening birds". (The term "evening bat" also often refers more specifically to one of the species, '' Nycticeius humer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy. The recurrent evolution of flight is a classic example, as flying insects, birds, pterosaurs, and bats have independently evolved the useful capacity of flight. Functionally similar features that have arisen through convergent evolution are ''analogous'', whereas '' homologous'' structures or traits have a common origin but can have dissimilar functions. Bird, bat, and pterosaur wings are analogous structures, but their forelimbs are homologous, sharing an ancestral state despite serving different functions. The opposite of convergence is divergent evolution, where related species evolve different traits. Convergent evolution is similar to parallel evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotropical
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone. Definition In biogeography, the Neotropic or Neotropical realm is one of the eight terrestrial realms. This realm includes South America, Central America, the Caribbean islands, and southern North America. In Mexico, the Yucatán Peninsula and southern lowlands, and most of the east and west coastlines, including the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula are Neotropical. In the United States southern Florida and coastal Central Florida are considered Neotropical. The realm also includes temperate southern South America. In contrast, the Neotropical Floristic Kingdom excludes southernmost South America, which instead is placed in the Antarctic kingdom. The Neotropic is delimited by similarities in fauna or flora. Its fauna and flora are distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotis Sibiricus
The Siberian bat or Siberian whiskered myotis (''Myotis sibiricus'') is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found throughout northeastern Asia, primarily in Siberia. It is known for its high life expectancy relative to its body size, approximately twice that of humans, and holds the record for the oldest bat; in 2005, one individual was discovered in a cave in Siberia that had been banded in 1964, making the bat at least 41 years old. Taxonomy It was previously classified within the Brandt's bat (''M. brandtii''), but more recent phylogenetic studies have found deep genetic divergence between both taxa, indicating that both are distinct species from one another, and they have thus been split by authorities including the American Society of Mammalogists, the IUCN Red List, and ITIS. Distribution and habitat It is found throughout much of the Palearctic east of the Ob River, from eastern Kazakhstan east throughout southern Siberia to the Kamchatka Pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotis Brandtii
Brandt's bat or Brandt's myotis (''Myotis brandtii'') is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is native throughout most of Europe and parts of western Asia. Taxonomy and etymology The species was described in 1845 by German zoologist Eduard Friedrich Eversmann, who placed it the genus ''Vespertilio''. For a time, the Brandt's bat was considered a subspecies of the whiskered bat, ''Myotis mystacinus''. In 1958, one author proposed that the two might be separate species, based on baculum differences; this idea gained traction in papers authored in 1970 and 1971. It is named for the German zoologist Johann Friedrich von Brandt. Formerly, populations in central and eastern Asia were classified in this species. However, more recent studies indicate that they form a distinct species, the Siberian bat (''Myotis sibiricus''). Range and habitat It is found throughout Europe and western Asia, and can be found in the following regions: Great Britain, Western Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nearctic
The Nearctic realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting the Earth's land surface. The Nearctic realm covers most of North America, including Greenland, Central Florida, and the highlands of Mexico. The parts of North America that are not in the Nearctic realm are Eastern Mexico, Southern Florida, coastal Central Florida, Central America, and the Caribbean islands, which, together with South America, are part of the Neotropical realm. Major ecological regions The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) divides the Nearctic into four bioregions, defined as "geographic clusters of ecoregions that may span several habitat types, but have strong biogeographic affinities, particularly at taxonomic levels higher than the species level (genus, family)." Canadian Shield The Canadian Shield bioregion extends across the northern portion of the continent, from the Aleutian Islands to Newfoundland. It includes the Nearctic's Arctic Tundra and Boreal forest ecoregions. In terms of flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotis
The mouse-eared bats or myotises are a diverse and widespread genus (''Myotis'') of bats within the family Vespertilionidae. The noun "''myotis''" itself is a New Latin construction, from the Greek "''muós'' (meaning "mouse") and "''oûs''" (meaning ear), literally translating to "mouse-eared". Relationships ''Myotis'' has historically been included in the subfamily Vespertilioninae, but was classified in its own subfamily, Myotinae, by Nancy Simmons in 1998. In her 2005 classification in ''Mammal Species of the World'', Simmons listed the genera ''Cistugo'' and ''Lasionycteris'' in the Myotinae in addition to ''Myotis'' itself.Simmons, 2005, p. 499 However, molecular data indicate that ''Cistugo'' is distantly related to all other Vespertilionidae, so it was reclassified into its own family, the Cistugidae, and that ''Lasionycteris'' belongs in the Vespertilioninae.Roehrs et al., 2010 The genus '' Submyotodon'' has since been added to the subfamily, making it and ''Myotis'' it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberian Bat
The Siberian bat or Siberian whiskered myotis (''Myotis sibiricus'') is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found throughout northeastern Asia, primarily in Siberia. It is known for its high life expectancy relative to its body size, approximately twice that of humans, and holds the record for the oldest bat; in 2005, one individual was discovered in a cave in Siberia that had been banded in 1964, making the bat at least 41 years old. Taxonomy It was previously classified within the Brandt's bat (''M. brandtii''), but more recent phylogenetic studies have found deep genetic divergence between both taxa, indicating that both are distinct species from one another, and they have thus been split by authorities including the American Society of Mammalogists, the IUCN Red List, and ITIS. Distribution and habitat It is found throughout much of the Palearctic east of the Ob River, from eastern Kazakhstan east throughout southern Siberia to the Kamchatka Pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice (magazine)
''Vice'' (stylized in all caps) is a Canadian-American magazine focused on lifestyle, arts, culture, and news/politics. Founded in 1994 in Montreal as an alternative punk magazine, the founders later launched the youth media company Vice Media, which consists of divisions including the printed magazine as well as a website, broadcast news unit, a film production company, a record label, and a publishing imprint. As of February 2015, the magazine's editor-in-chief is Ellis Jones. History Founded by Suroosh Alvi, Gavin McInnes, and Shane Smith (the latter two being childhood friends), the magazine was launched in 1994 as the ''Voice of Montreal'' with government funding. The intention of the founders was to provide work and a community service. When the editors later sought to dissolve their commitments with the original publisher, Alix Laurent, they bought him out and changed the name to ''Vice'' in 1996. Richard Szalwinski, a Canadian software millionaire, acquired the magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
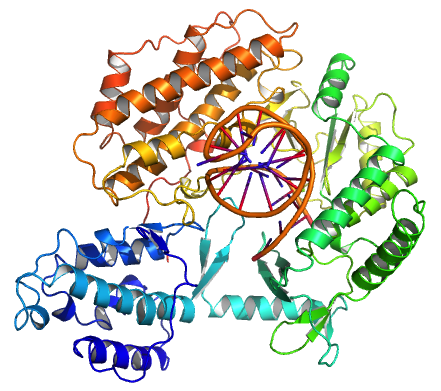
Telomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most eukaryotes. Telomeres protect the end of the chromosome from DNA damage or from fusion with neighbouring chromosomes. The fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' lacks telomerase, but instead uses retrotransposons to maintain telomeres. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase enzyme that carries its own RNA molecule (e.g., with the sequence 3′- CCC AA UCCC-5′ in ''Trypanosoma brucei'') which is used as a template when it elongates telomeres. Telomerase is active in gametes and most cancer cells, but is normally absent from, or at very low levels in, most somatic cells. History The existence of a compensatory mechanism for telomere shortening was first found by Soviet biologist Alexey Olovnikov in 1973, who also suggested the telomere hypothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
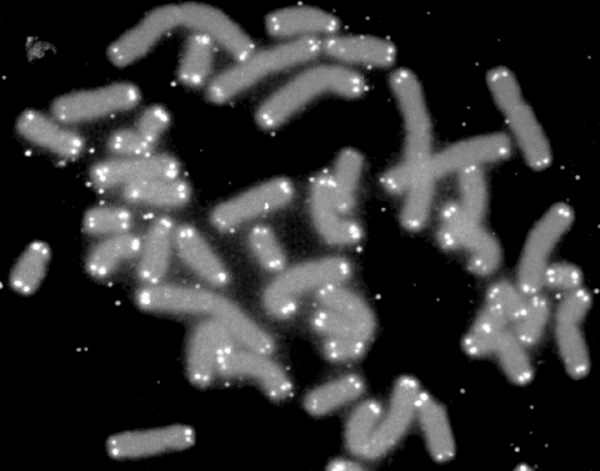
Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery In the early 1970s, Soviet theorist Alexei Olovnikov first recognized that chromosomes could not completely replicate their ends; this is known as the "end replication problem". Building on this, and accommodating Leonard Hayflick's idea of limited somatic cell division, Olovnikov suggested that DNA sequences are lost every time a cell replicates until the loss reaches a critical level, at which point cell division end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |