|
Mylar Punched Tape
BoPET (biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate) is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties, and electrical insulation. A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other polyester films under different brand names. In the UK and US, the best-known trade names are Mylar, Melinex, and Hostaphan. History BoPET film was developed in the mid-1950s,Izard, Emmette Farr"Production of polyethylene terephthalate" U.S. patent no. 2,534,028 (filed: 1948 May 13; issued: 1950 December 12). originally by DuPont, Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI), and Hoechst. In 1955 Eastman Kodak used Mylar as a support for photographic film and called it "ESTAR Base". The very thin and tough film allowed reels to be exposed on long-range U-2 reconnaissance flights. In 1964, NASA launched Echo II, a diameter balloon constructed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
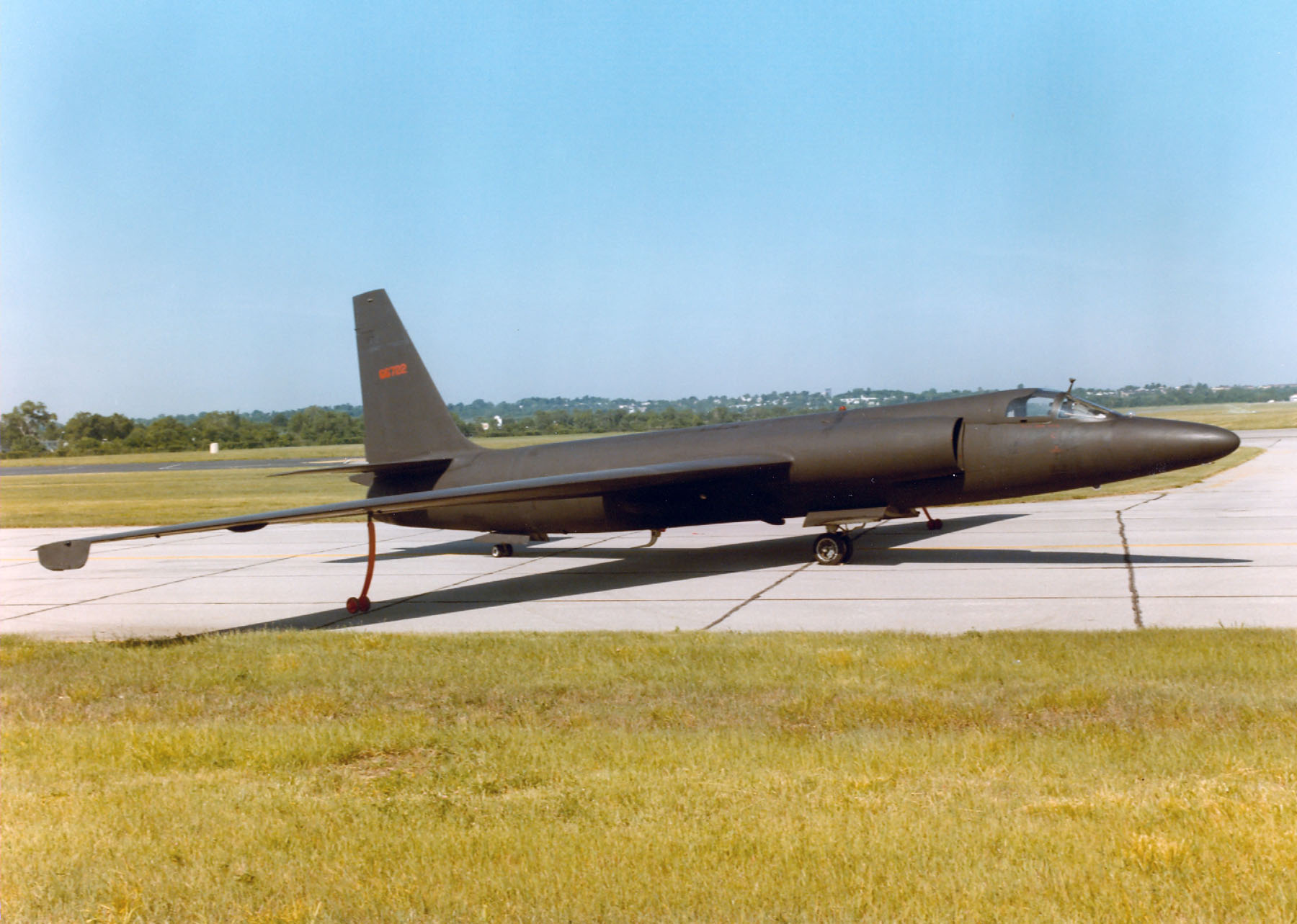
Lockheed U-2
The Lockheed U-2, nicknamed "''Dragon Lady''", is an American single-jet engine, high altitude reconnaissance aircraft operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and previously flown by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). It provides day and night, high-altitude (), all-weather intelligence gathering. Lockheed Corporation originally proposed it in 1953, it was approved in 1954, and its first test flight was in 1955. It was flown during the Cold War over the Soviet Union, China, Vietnam War, Vietnam, and Cuba. In 1960, Francis Gary Powers, Gary Powers was 1960 U-2 incident, shot down in a CIA U-2C over the Soviet Union by a surface-to-air missile (SAM). Major Rudolf Anderson, Rudolf Anderson Jr. was shot down in a U-2 during the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962. U-2s have taken part in post-Cold War conflicts in War in Afghanistan (2001–2021), Afghanistan and Operation Iraqi Freedom, Iraq, and supported several multinational NATO operations. The U-2 has also been used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor Deposition
Vacuum deposition is a group of processes used to deposit layers of material atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule on a solid surface. These processes operate at pressures well below atmospheric pressure (i.e., vacuum). The deposited layers can range from a thickness of one atom up to millimeters, forming freestanding structures. Multiple layers of different materials can be used, for example to form optical coatings. The process can be qualified based on the vapor source; physical vapor deposition uses a liquid or solid source and chemical vapor deposition uses a chemical vapor. Description The vacuum environment may serve one or more purposes: * reducing the particle density so that the mean free path for collision is long * reducing the particle density of undesirable atoms and molecules (contaminants) * providing a low pressure plasma environment * providing a means for controlling gas and vapor composition * providing a means for mass flow control into the processing chambe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallised Film
Metallised films (or metallized films) are polymer films coated with a thin layer of metal, usually aluminium. They offer the glossy metallic appearance of an aluminium foil at a reduced weight and cost. Metallised films are widely used for decorative purposes and food packaging, and also for specialty applications including insulation and electronics. Manufacture Metallisation is performed using a physical vapor deposition process. Aluminium is the most common metal used for deposition, but other metals such as nickel and chromium are also used. The metal is heated and evaporated under vacuum. This condenses on the cold polymer film, which is unwound near the metal vapour source. This coating is much thinner than a metal foil could be made, in the range of 0.5 micrometres.Hanlon, J. (1992). 1st ed. ''Handbook of Package Engineering'', Lancaster, PA, Technomic Publishing: . Chapter 4 Coatings and Laminations This coating will not fade or discolour over time. While oriented polyprop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, opal and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Structure In the majority of silicates, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a linear molecule. The starkly different structures of the dioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicrystalline
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a big influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion. In an ideal gas, the relative positions of the atoms or molecules are completely random. Amorphous materials, such as liquids and glasses, represent an intermediate case, having order over short distances (a few atomic or molecular spacings) but not over longer distances. Many materials, such as glass-ceramics and some polymers, can be prepared in such a way as to produce a mixture of crystalline and amorphous regions. In such cases, crystallinity is usually specified as a percentage of the volume of the material that is crystalline. Even within materials that are completely crystalline, however, the degree of structural perfection can vary. For instance, most metallic alloys are crystalline, but they usually comprise many independent cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young's Modulus
Young's modulus E, the Young modulus, or the modulus of elasticity in tension or compression (i.e., negative tension), is a mechanical property that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness of a solid material when the force is applied lengthwise. It quantifies the relationship between tensile/compressive stress \sigma (force per unit area) and axial strain \varepsilon (proportional deformation) in the linear elastic region of a material and is determined using the formula: E = \frac Young's moduli are typically so large that they are expressed not in pascals but in gigapascals (GPa). Example: * Silly Putty (increasing pressure: length increases quickly, meaning tiny E) * Aluminum (increasing pressure: length increases slowly, meaning high E) Higher Young's modulus corresponds to greater (lengthwise) stiffness. Although Young's modulus is named after the 19th-century British scientist Thomas Young, the concept was developed in 1727 by Leonhard Euler. The first experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Set
Heat setting is a term used in the textile industry to describe a thermal process usually taking place in either a steam atmosphere or a dry heat environment. The effect of the process gives fibers, yarns or fabric dimensional stability and, very often, other desirable attributes like higher volume, wrinkle resistance or temperature resistance. Very often, heat setting is also used to improve attributes for subsequent processes. Heat setting can eliminate the tendency of undesirable torquing. At the winding, twisting, weaving, tufting and knitting processes, the increased tendency to torquing can cause difficulties in processing the yarn. When using heat setting for carpet yarns, desirable results include not only the diminishing of torquing but also the stabilization or fixing of the fiber thread. Both twist stabilization and stabilization of frieze effect are results of the heat setting process. Heat setting benefits staple yarns as well as bulked continuous filament (BCF) ya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonality
In mathematics, orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. By extension, orthogonality is also used to refer to the separation of specific features of a system. The term also has specialized meanings in other fields including art and chemistry. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics * In optics, polarization states are said to be orthogonal when they propagate independently of each other, as in vertical and horizontal linear polarization or right- and left-handed circular polarization. * In special relativity, a time axis determined by a rapidity of motion is hyperbolic-orthogonal to a space axis of simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawing (manufacturing)
Drawing is a metalworking process that uses tensile forces to stretch (elongate) metal, glass, or plastic. As the metal is drawn (pulled), it stretches to become thinner, to achieve a desired shape and thickness. Drawing is classified into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. Sheet metal drawing is defined as a plastic deformation over a curved axis. For wire, bar, and tube drawing, the starting stock is drawn through a die to reduce its diameter and increase its length. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process; however, drawing may also be performed at elevated temperatures to hot work large wires, rods or hollow sections in order to reduce forces.Degarmo, p. 432.Kalpakjian, pp. 415–419. Drawing differs from rolling in that the pressure of drawing is not transmitted through the turning action of the mill but instead depends on force applied locally near the area of compression. This means the amoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
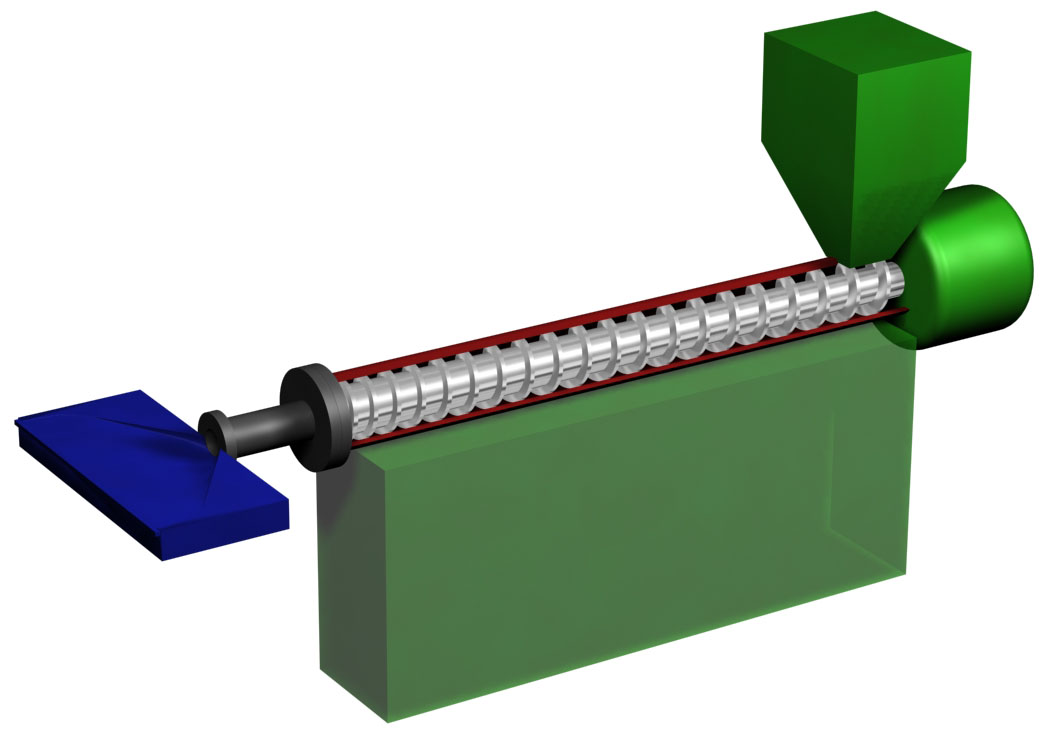
Plastics Extrusion
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation. This process starts by feeding plastic material (pellets, granules, flakes or powders) from a hopper into the barrel of the extruder. The material is gradually melted by the mechanical energy generated by turning screws and by heaters arranged along the barrel. The molten polymer is then forced into a die, which shapes the polymer into a shape that hardens during cooling. History The first precursors to the modern extruder were developed in the early 19th century. In 1820, Thomas Hancock invented a rubber "masticator" designed to reclaim processed rubber scraps, and in 1836 Edwin Chaffee developed a two-roller machine to mix additives into rubber. The first thermoplastic extrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |