|
Mycolic Acids
Mycolic acids are long fatty acids found in the cell walls of the Mycolata taxon, a group of bacteria that includes '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', the causative agent of the disease tuberculosis. They form the major component of the cell wall of mycolata species. Despite their name, mycolic acids have no biological link to fungi; the name arises from the filamentous appearance their presence gives mycolata under high magnification. The presence of mycolic acids in the cell wall also gives mycolata a distinct gross morphological trait known as " cording". Mycolic acids were first isolated by Stodola ''et al.'' in 1938 from an extract of ''M. tuberculosis''. Mycolic acids are composed of a longer beta-hydroxy chain with a shorter alpha-alkyl side chain. Each molecule contains between 60 and 90 carbon atoms. The exact number of carbons varies by species and can be used as an identification aid. Most mycolic acids also contain various functional groups. Mycolic acids of ''M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
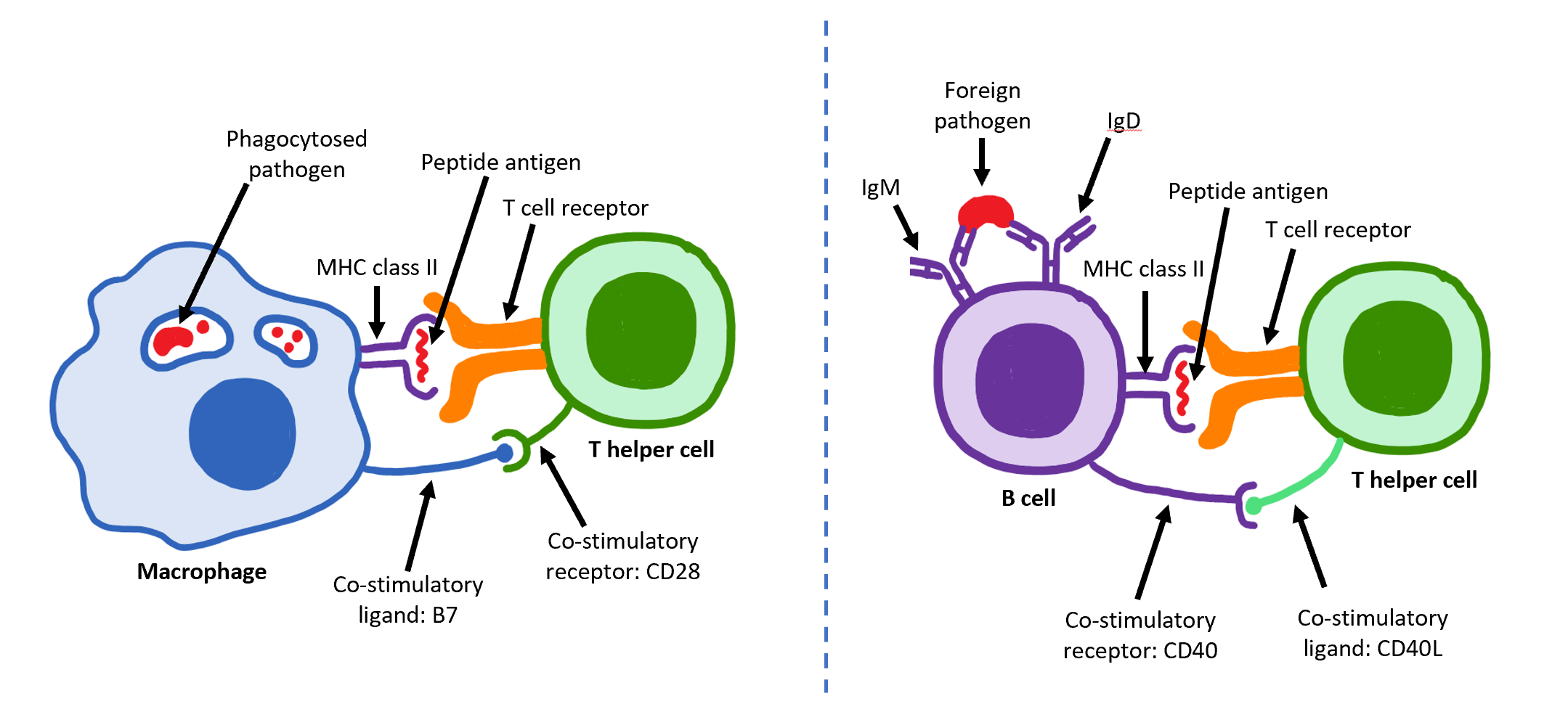
Th17
T helper 17 cells (Th17) are a subset of pro-inflammatory T helper cells defined by their production of interleukin 17 (IL-17). They are related to T regulatory cells and the signals that cause Th17s to differentiate actually inhibit Treg differentiation. However, Th17s are developmentally distinct from Th1 and Th2 lineages. Th17 cells play an important role in maintaining mucosal barriers and contributing to pathogen clearance at mucosal surfaces; such protective and non-pathogenic Th17 cells have been termed as Treg17 cells. They have also been implicated in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. The loss of Th17 cell populations at mucosal surfaces has been linked to chronic inflammation and microbial translocation. These regulatory Th17 cells can be generated by TGF-beta plus IL-6 in vitro. Differentiation Like conventional regulatory T cells (Treg), induction of regulatory Treg17 cells could play an important role in modulating and preventing certain autoimmune diseases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Th1 Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: ''total synthesis'', ''semisynthesis'', and ''methodology''. Total synthesis A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple, commercially available petrochemical or natural precursors. Total synthesis may be accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed one after another until the molecule is complete; the chemical compounds made in each step are called synthetic intermediates. Most often, each step in a synthesis refers to a separate rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atopic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-ketoacyl-(acyl-carrier-protein) Synthase III
In enzymology, a β-ketoacyl- cyl-carrier-proteinsynthase III () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :acetyl-CoA + malonyl- acyl carrier protein">acyl_carrier_protein.html" ;"title="/nowiki>acyl carrier protein">/nowiki>acyl carrier protein/nowiki> \rightleftharpoons acetoacetyl- /nowiki>acyl carrier protein">acyl_carrier_protein.html" ;"title="/nowiki> /nowiki>acyl carrier protein/nowiki> + CoA + CO2 Thus, the two substrate (biochemistry)">substrates of this enzyme are acetyl-CoA">acyl carrier protein">/nowiki>acyl carrier protein/nowiki> + CoA + CO2 Thus, the two substrate (biochemistry)">substrates of this enzyme are acetyl-CoA and malonyl-[acyl-carrier-protein], whereas its 3 product (chemistry), products are acetoacetyl-[acyl-carrier-protein], coenzyme A, CoA, and carbon dioxide, CO2. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. This enzyme participates in fatty aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyketide Synthase
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity. History Naturally produced polyketides by various plants and organisms have been used by humans since before studies on them began in the 19th and 20th century. In 1893, J. Norman Collie synthesized detectable amounts of orcinol by heating dehy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid Synthase
Fatty acid synthase (FAS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''FASN'' gene. Fatty acid synthase is a multi-enzyme protein that catalyzes fatty acid synthesis. It is not a single enzyme but a whole enzymatic system composed of two identical 272 kDa multifunctional polypeptides, in which substrates are handed from one functional domain to the next. Its main function is to catalyze the synthesis of palmitate (C16:0, a long-chain saturated fatty acid) from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA, in the presence of NADPH. The fatty acids are synthesized by a series of decarboxylative Claisen condensation reactions from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA. Following each round of elongation the beta keto group is reduced to the fully saturated carbon chain by the sequential action of a ketoreductase (KR), dehydratase (DH), and enoyl reductase (ER). The growing fatty acid chain is carried between these active sites while attached covalently to the phosphopantetheine prosthetic group of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |