|
Mycobacterium Abscessus
''Mycobacteroides abscessus'' (formerly ''Mycobacterium abscessus'') is a species of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous mycobacteria that is a common soil and water contaminant. Although ''M. abscessus'' most commonly causes chronic lung infection and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), it can also cause infection in almost all human organs, mostly in patients with suppressed immune systems. Amongst NTM species responsible for disease, infection caused by ''M. abscessus'' complex are more difficult to treat due to antimicrobial drug resistance. Description ''Mycobacteroides abscessus'' cells are Gram-positive, nonmotile, acid-fast rods about 1.0–2.5 µm long by 0.5 µm wide. They may form colonies on Löwenstein–Jensen medium that appear smooth or rough, white or greyish, and nonphotochromogenic. Etymology ''Abscessus'' is named for abscesses. It is a Latin word derived from ("away") + ("to go") because it was the ancient medical n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prokaryotic Names With Standing In Nomenclature
List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and taxonomy Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ... of prokaryotes, following the taxonomy requirements and rulings of the International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes. The database was curated from 1997 to June 2013 by Jean P. Euzéby. From July 2013 to January 2020, LPSN was curated by Aidan C. Parte. In February 2020, a new version of LPSN was published as a service of the Leibniz Institute DSMZ, thereby also integrating the Prokaryotic Nomenclature Up-to-date service. References External links List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picrate
A picrate is a salt containing the anion (O2N)3C6H2O− or an ester derivative of the picrate anion. These salts are often produced by reactions of picric acid (2,4,6-trinitrophenol). The picrate ion is intensely yellow, although many of its salts are brown or orange-red. Explosives Many picrates are explosives, for example ammonium picrate (known as Dunnite). Some are used as primary explosives, namely lead picrate or potassium picrate which find their use as primers for cartridge ammunition. Picrates of some metals tend to be significantly more sensitive to impact, friction and shock than picric acid itself. As a result, storage of picric acid (or mixtures containing it) in metal containers is strongly discouraged due to the high risk of accidental explosion. Other uses Ferrous picrate is used in some applications as a diesel fuel additive to achieve better mileage. Sodium picrate is used as an etchant in metallography to differ preeutectoid ferrite in hypoeutectoid s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
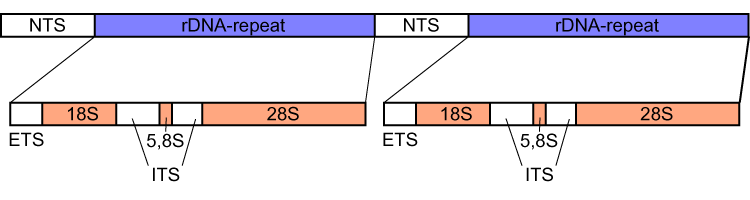
Internal Transcribed Spacer
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. ITS across life domains In bacteria and archaea, there is a single ITS, located between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Conversely, there are two ITSs in eukaryotes: ITS1 is located between 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes, while ITS2 is between 5.8S and 28S (in opisthokonts, or 25S in plants) rRNA genes. ITS1 corresponds to the ITS in bacteria and archaea, while ITS2 originated as an insertion that interrupted the ancestral 23S rRNA gene. Organization In bacteria and archaea, the ITS occurs in one to several copies, as do the flanking 16S and 23S genes. When there are multiple copies, these do not occur adjacent to one another. Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16S Ribosomal RNA
16 S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome ( SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure. The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rRNA gene and are used in reconstructing phylogenies, due to the slow rates of evolution of this region of the gene. Carl Woese and George E. Fox were two of the people who pioneered the use of 16S rRNA in phylogenetics in 1977. Multiple sequences of the 16S rRNA gene can exist within a single bacterium. Functions * Like the large (23S) ribosomal RNA, it has a structural role, acting as a scaffold defining the positions of the ribosomal proteins. * The 3-end contains the anti- Shine-Dalgarno sequence, which binds upstream to the AUG start codon on the mRNA. The 3-end of 16S RNA binds to the proteins S1 and S21 which are known to be involved in initiation of protein synthesis * Interacts with 23S, aiding in the binding of the two ribo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate. Structure The ion is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a formal charge of −1. This charge results from a combination formal charge in which each of the three oxygens carries a − charge, whereas the nitrogen carries a +1 charge, all these adding up to formal charge of the polyatomic nitrate ion. This arrangement is commonly used as an example of resonance. Like the isoelectronic carbonate ion, the nitrate ion can be represented by resonance structures: Dietary nitrate A rich source of inorganic nitrate in the human diets come from leafy green foods, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Peregrinum
Mycobacterium peregrinum is a species of ''Mycobacterium ''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (''M. tuberculosis'') and l ...''. References External links Type strain of ''Mycobacterium peregrinum'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase peregrinum {{Mycobacterium-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Fortuitum
''Mycobacterium fortuitum'' is a nontuberculous species of the phylum Actinomycetota (Gram-positive bacteria with high guanine and cytosine content, one of the dominant phyla of all bacteria), belonging to the genus ''Mycobacterium''. Background ''Mycobacterium fortuitum'' is a fast-growing species that can cause infections. The term "fast growing" is a reference to a growth rate of 3 or 4 days, when compared to other Mycobacteria that may take weeks to grow out on laboratory media. Pulmonary infections of ''M. fortuitum'' are uncommon, but ''Mycobacterium fortuitum'' can cause local skin disease, osteomyelitis (inflammation of the bone), joint infections and infections of the eye after trauma. ''Mycobacterium fortuitum'' has a worldwide distribution and can be found in natural and processed water, sewage, and dirt. Bacteria classified as Mycobacteria, include the causative agents for tuberculosis and leprosy. Mycobacteria are sometimes referred to as “acid-fast bacteria,” ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacteroides Chelonae
''Mycobacteroides chelonae'' (formerly ''Mycobacterium chelonae'') is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota belonging to the genus ''Mycobacteroides''. ''Mycobacteroides chelonae'' is a rapidly growing mycobacterium that is found all throughout the environment, including sewage and tap water. It can occasionally cause opportunistic infection An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens (bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses) that take advantage of an opportunity not normally available. These opportunities can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immune ...s of humans. It is grouped in Runyon group IV. The complete genome sequence of the ''M. chelonae'' CCUG 47445 type strain was deposited and published in DNA Data Bank of Japan, European Nucleotide Archive, and GenBank in 2016 under the accession numbeCP007220 Epidemiology On average, two cases of nonpulmonary ''M. chelonae'' infection are reported in South Australia each ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citrate
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms. More than two million tons of citric acid are manufactured every year. It is used widely as an acidifier, as a flavoring, and a chelating agent. A citrate is a derivative of citric acid; that is, the salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion found in solution. An example of the former, a salt is trisodium citrate; an ester is triethyl citrate. When part of a salt, the formula of the citrate anion is written as or . Natural occurrence and industrial production Citric acid occurs in a variety of fruits and vegetables, most notably citrus fruits. Lemons and limes have particularly high concentrations of the acid; it can constitute as much as 8% of the dry weight of these fruits (about 47&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalate
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl oxalate (C2O4(CH3)2). It is a conjugate base of oxalic acid. At neutral pH in aqueous solution, oxalic acid converts completely to oxalate. Relationship to oxalic acid The dissociation of protons from oxalic acid proceeds in a stepwise manner; as for other polyprotic acids, loss of a single proton results in the monovalent hydrogenoxalate anion . A salt with this anion is sometimes called an acid oxalate, monobasic oxalate, or hydrogen oxalate. The equilibrium constant ( ''K''a) for loss of the first proton is (p''K''a = 1.27). The loss of the second proton, which yields the oxalate ion, has an equilibrium constant of (p''K''a = 4.28). These values imply, in solutions with neutral pH, no oxalic acid and only tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a ketonic simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed by the gut directly into the blood of the portal vein during digestion. The liver then converts both fructose and galactose into glucose, so that dissolved glucose, known as blood sugar, is the only monosaccharide present in circulating blood. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847. The name "fructose" was coined in 1857 by the English chemist William Allen Miller. Pure, dry fructose is a sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid, and is the most water-soluble of all the sugars. Fructose is found in honey, tree and vine fruits, flowers, berries, and most root vegetables. Commercially, fructose is derived from sugar cane, sugar beets, and maize. High-fructose corn syrup is a mixture of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |