|
Muzo
Muzo () is a town and municipality in the Western Boyacá Province, part of the department of Boyacá, Colombia. It is widely known as the world capital of emeralds for the mines containing the world's highest quality gems of this type. Muzo is situated at a distance of from the departmental capital Tunja and from the capital of the Western Boyacá Province, Chiquinquirá. The urban centre is at an altitude of above sea level. Muzo borders Otanche and San Pablo de Borbur in the north, Maripí and Coper in the east, Quípama in the west and the department of Cundinamarca in the south. Etymology The town of Muzo was called Villa de la Santísima Trinidad de los Muzos, or simply Trinidad, when the Spanish conquistadors first founded the settlement in western Boyacá. Muzo is the autonym of the Muzo, the indigenous people who inhabited the region before the Spanish conquest. Climate The median temperature of Muzo is and the annual precipitation . History Before the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzo People
The Muzo people were a Cariban-speaking indigenous group who inhabited the western slopes of the eastern Colombian Andes. They were a highly war-like tribe who frequently clashed with their neighbouring indigenous groups, especially the Muisca. It is said they performed cannibalism on their conquered neighbours. The Muzo inhabited the right banks of the Magdalena River in the lower elevations of western Boyacá and Cundinamarca and were known as the Emerald People, thanks to their exploitation of the gemstone in Muzo. During the time of conquest, they resisted heavily against the Spanish invaders taking twenty years to submit the Muzo. Knowledge about the Muzo people has been provided by chroniclers Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, Pedro Simón, Juan de Castellanos, Lucas Fernández de Piedrahita and others. Muzo territory The Muzo were inhabiting the lower-elevation northwestern areas of the Cundinamarca department and western portion of the Boyacá Department, closer to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzo Formation
Muzo () is a town and municipality in the Western Boyacá Province, part of the department of Boyacá, Colombia. It is widely known as the world capital of emeralds for the mines containing the world's highest quality gems of this type. Muzo is situated at a distance of from the departmental capital Tunja and from the capital of the Western Boyacá Province, Chiquinquirá. The urban centre is at an altitude of above sea level. Muzo borders Otanche and San Pablo de Borbur in the north, Maripí and Coper in the east, Quípama in the west and the department of Cundinamarca in the south. Etymology The town of Muzo was called Villa de la Santísima Trinidad de los Muzos, or simply Trinidad, when the Spanish conquistadors first founded the settlement in western Boyacá. Muzo is the autonym of the Muzo, the indigenous people who inhabited the region before the Spanish conquest. Climate The median temperature of Muzo is and the annual precipitation . History Before the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis Lanchero
Luis Lanchero, also known as Luis Lancheros (?, Spanish Empire, Castile - 1562, Tunja, New Kingdom of Granada) was a Spanish List of conquistadors in Colombia, conquistador and the founder of the town of Muzo, Trinidad de los Muzos, Boyacá Department, Boyacá, the most important Colombian Emeralds, emerald settlement in Colombia. Muzo was founded after twenty years of unsuccessful attempts to subjugate the Muzo people, Muzo to Spanish rule. Lanchero arrived in the New World in 1533 and died impoverished in Tunja in 1562. Biography Early career Luis Lanchero was born in Castile in a noble family. As a young man he was employed in the guard of Spanish king Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Carlos V, in which role he participated in the Sack of Rome (1527), Sack of Rome in 1527.Luis Lanchero - Bank of the Republ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
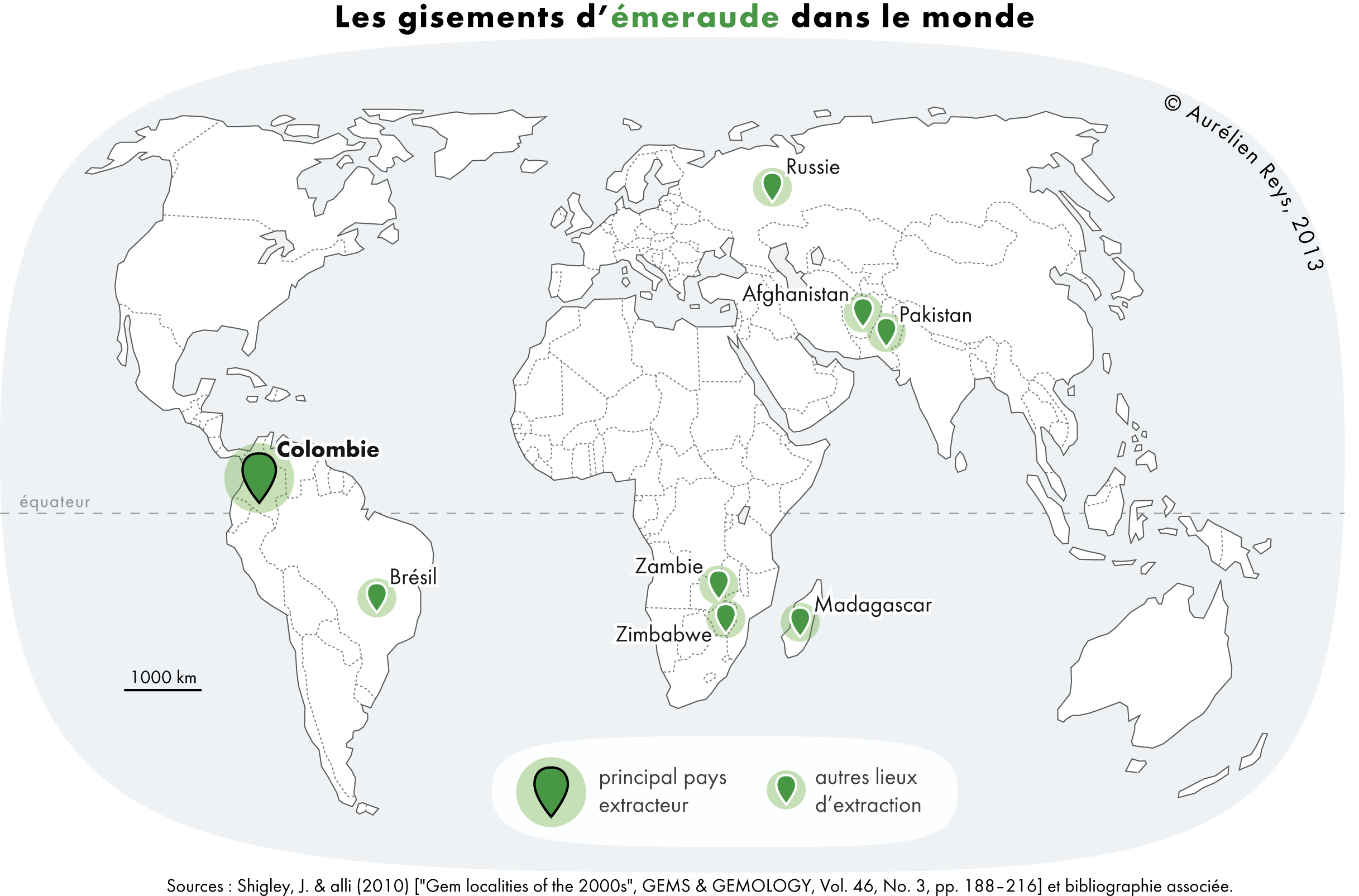
Colombian Emeralds
Emeralds are green precious gemstones that are mined in various geological settings. They are minerals in the beryl group of silicates. For more than 4,000 years, emeralds have been among the most valuable of all jewels. Colombia, located in northern South America, is the country that mines and produces the most emeralds for the global market, as well as the most desirable. It is estimated that Colombia accounts for 70–90% of the world's emerald market. While commercial grade emeralds are quite plentiful, fine and extra fine quality emeralds are extremely rare. Colombian emeralds over 50 carat can cost much more than diamonds of the same size. The Colombian departments of Boyacá and Cundinamarca, both in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, are the locations where most of the emerald mining takes place. Although the Colombian emerald trade has a rich history that dates as far back as the pre-Columbian era, the increase in worldwide demand for the industry of the gems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of The Muisca
The Spanish conquest of the Muisca took place from 1537 to 1540. The Muisca were the inhabitants of the central Andean highlands of Colombia before the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors. They were organised in a loose confederation of different rulers; the '' psihipqua'' of Muyquytá, with his headquarters in Funza, the '' hoa'' of Hunza, the ''iraca'' of the sacred City of the Sun Sugamuxi, the Tundama of Tundama, and several other independent ''caciques''. The most important rulers at the time of the conquest were ''psihipqua'' Tisquesusa, ''hoa'' Eucaneme, ''iraca'' Sugamuxi and Tundama in the northernmost portion of their territories. The Muisca were organised in small communities of circular enclosures (''ca'' in their language Muysccubbun; literally "language of the people"), with a central square where the '' bohío'' of the ''cacique'' was located. They were called "Salt People" because of their extraction of salt in various locations throughout their territories, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panche People
The Panche or Tolima is an indigenous group of people in what is now Colombia. Their language is unclassified – and possibly unclassifiable – but may have been Cariban. They inhabited the southwestern parts of the department of Cundinamarca and the northeastern areas of the department of Tolima, close to the Magdalena River. At the time of the Spanish conquest, more than 30,000 Panche were living in what would become the New Kingdom of Granada. Early knowledge about the Panche has been compiled by scholar Pedro Simón. According to the latter, the word ''panche'' in their own Panche language means "cruel" and "murderer". Panche territory The Panche were inhabiting the lower altitude southwestern areas of the Cundinamarca department, close to the Magdalena River. Their northern neighbours were the Muzo in the northeast and the Pantágora in the northwest, in the east the Muisca, in the southeast the Sutagao and to the south and southwest the Pijao. The northern limits we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muisca People
The Muisca (also called Chibcha) are an indigenous people and culture of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Colombia, that formed the Muisca Confederation before the Spanish conquest. The people spoke Muysccubun, a language of the Chibchan language family, also called ''Muysca'' and ''Mosca''. They were encountered by conquistadors dispatched by the Spanish Empire in 1537 at the time of the conquest. Subgroupings of the Muisca were mostly identified by their allegiances to three great rulers: the '' hoa'', centered in Hunza, ruling a territory roughly covering modern southern and northeastern Boyacá and southern Santander; the '' psihipqua'', centered in Muyquytá and encompassing most of modern Cundinamarca, the western Llanos; and the ''iraca'', religious ruler of Suamox and modern northeastern Boyacá and southwestern Santander. The territory of the Muisca spanned an area of around from the north of Boyacá to the Sumapaz Páramo and from the summits to the western p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Conquistadors In Colombia
This is a list of conquistadors who were active in the conquest of terrains that presently belong to Colombia. The nationalities listed refer to the state the conquistador was born into; Granada and Castile are currently part of Spain, but were separate states at the time of birth of the early conquistadors. Important conquistadors and explorers were Alonso de Ojeda, who landed first at Colombian soil and founded the first settlement ''Santa Cruz'',Personajes de la Conquista a América – |
Emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 203, . Beryl has a hardness of 7.5–8 on the Mohs scale. Most emeralds are highly included, so their toughness (resistance to breakage) is classified as generally poor. Emerald is a cyclosilicate. Etymology The word "emerald" is derived (via fro, esmeraude and enm, emeraude), from Vulgar Latin: ''esmaralda''/''esmaraldus'', a variant of Latin ''smaragdus'', which was a via grc, σμάραγδος (smáragdos; "green gem") from a Semitic language. According to Webster's Dictionary the term emerald was first used in the 14th century. Properties determining value Emeralds, like all colored gemstones, are graded using four basic parameters–the four ''C''s of connoisseurship: ''color'', ''clarity,'' ''cut'' and ''carat weight''. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Boyacá Province
The Western Boyacá Province is a province of the Colombian Department of Boyacá. The province is formed by 15 municipalities. The province hosts the western belt of the rich emerald deposits of Boyacá. Municipalities Briceño • Buenavista • Caldas • Chiquinquirá • Coper • La Victoria • Maripí • Muzo • Otanche • Pauna • Quipama • Saboyá • San Miguel de Sema • San Pablo de Borbur San Pablo de Borbur is a town and municipality in the Colombian Department of Boyacá, part of the subregion of the Western Boyacá Province The Western Boyacá Province is a province of the Colombian Department of Boyacá. The province is ... • Tununguá References Provinces of Boyacá Department {{Boyacá-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the largest cities in the world. The city is administered as the Capital District, as well as the capital of, though not part of, the surrounding department of Cundinamarca. Bogotá is a territorial entity of the first order, with the same administrative status as the departments of Colombia. It is the political, economic, administrative, and industrial center of the country. Bogotá was founded as the capital of the New Kingdom of Granada on 6 August 1538 by Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada after a harsh expedition into the Andes conquering the Muisca, the indigenous inhabitants of the Altiplano. Santafé (its name after 1540) became the seat of the government of the Spanish Royal Audiencia of the New Kingdom of Granada (cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muisca Religion
Muisca religion describes the religion of the Muisca people, Muisca who inhabited the central highlands of the Colombian Andes before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca. The Muisca formed a Muisca Confederation, confederation of holy Muisca rulers, rulers and had a variety of deity, deities, temples and rituals incorporated in their culture. Supreme being of the Muisca was Chiminigagua who created light and the Earth. He was not directly honoured, yet that was done through Chía (goddess), Chía, goddess of the Moon, and her husband Sué, god of the Sun. The representation of the two main celestial bodies as husband and wife showed the complementary character of man and Women in Muisca society, woman and the sacred status of marriage.Muisca religion - Pueblos Originarios - accessed 04-05-2016 The Muisca worshipped the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |