|
Muskerry Hurlers
Muskerry ( ga, Múscraí) is a central region of County Cork, Ireland which incorporates the baronies of Muskerry West - Muskerry West and . It is located along the valley of the and is bounded by the to the north and the |
County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns are Mallow, Macroom, Midleton, and Skibbereen. the county had a population of 581,231, making it the third- most populous county in Ireland. Cork County Council is the local authority for the county, while Cork City Council governs the city of Cork and its environs. Notable Corkonians include Michael Collins, Jack Lynch, Roy Keane, Sonia O'Sullivan and Cillian Murphy. Cork borders four other counties: Kerry to the west, Limerick to the north, Tipperary to the north-east and Waterford to the east. The county contains a section of the Golden Vale pastureland that stretches from Kanturk in the north to Allihies in the south. The south-west region, including West Cork, is one of Ireland's main tourist destinations, known for its rugged coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilnamartyra
Kilnamartyra ( , meaning ''church of the martyr'' or ''church of the relic'') is a village and civil parish in County Cork, Ireland. It is located around half-way between Killarney and Macroom. The parish is a kilometre from the L3402 local road which joins the N22 road, three kilometres away. Historically its townlands were part of the barony of Muskerry West. The local national school is called ''Scoil Lachtain Naofa''. It is a ''gaelscoil'' and is named after Saint Lachtain, the patron saint of Cill na Martra. Other amenities in the village include a GAA pitch and two pubs. History The Irish St Lachtin is believed to have found a monastery in the area in the 8th century, and the village name of ''Church of the relic'' likely refers to him, while the Shrine of Saint Lachtin's Arm, now in the National Museum of Ireland The National Museum of Ireland ( ga, Ard-Mhúsaem na hÉireann) is Ireland's leading museum institution, with a strong emphasis on national and some interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Institute For Advanced Studies
The Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies (DIAS) ( ga, Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath) is a statutory independent research institute in Ireland. It was established in 1940 on the initiative of the Taoiseach, Éamon de Valera, in Dublin. The institute consists of three schools: the School of Theoretical Physics, the School of Cosmic Physics and the School of Celtic Studies. The directors of these schools are, as of 2022, Professor Denjoe O'Connor, Professor Chris Bean and Professor Ruairí Ó hUiginn. The institute, under its governing act, is empowered to "train students in methods of advanced research" but does not itself award degrees; graduate students working under the supervision of Institute researchers can, with the agreement of the governing board of the appropriate school, be registered for a higher degree in any university worldwide. Following a comprehensive review of the higher education sector and its institutions, conducted by the Higher Education Auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donegan (other)
Donegan ( ga, Ó Donnagáin), most commonly refers to a Gaelic Irish clan from Munster. The name is diminutive of ''Donn'' which means, "the Dark One", or in modern Irish, "brown", referring to hair colour. The most prominent dynasty were an Érainn people of the Múscraige and provided a King of Munster in the 10th century in the form of Flaithbertach mac Inmainén. Much later, the family provided the Dungan Baronets and two Earls of Limerick, the most notable of which Thomas Dongan, 2nd Earl of Limerick was a Governor of New York. Naming conventions Numerous spelling variations of the surname Donegan exist in Anglicised form. Different spellings include Donegan, Donnegan, Doneghan, Donneghan, Donagan, Donnagan, Donnaghan, Dunegan, Dunnegan, O'Donegan, O'Dunnegan, O'Donnaghan, Dongan, Donegin, Donnegin, Donnagen, Donagen, Donnegen, Donegen, Donnigan, Donigan, Dunnican, Dunican, Dunigan, Dunnigan, McDunnigan, McDonegan, Dongane, Dongan, Dongen, Dungan, and many more. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Cyra
Saint Cyra (also Chera, Crea, and Cere filia Duibhrea) was an early Irish abbess. Her feast day is 16 October. The virgin saint was abbess of the monastery of ''Killchere'' ("Cyra's Church") in that part of Munster which was called ''Muscragia'' or Muskerry. The site is now occupied by the ruins of a later Franciscan Kilcrea Friary. References * Richard Challoner Richard Challoner (29 September 1691 – 12 January 1781) was an English Roman Catholic bishop, a leading figure of English Catholicism during the greater part of the 18th century. The titular Bishop of Doberus, he is perhaps most famous for hi .... ''Britannia Sancta: or, The Lives of the most Celebrated British, English, Scottish, and Irish Saints. Part II.'' London: Thomas Meighan, 1745. {{DEFAULTSORT:Cyra, Saint Christian saints in unknown century Medieval Irish saints Female saints of medieval Ireland Medieval Gaels from Ireland Women of medieval Ireland Year of birth unknown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Gobnait
Saint Gobnait (?), also known as Gobnat or Mo Gobnat or Abigail or Deborah, is the name of a medieval, female Irish saint whose church was Móin Mór, later Bairnech, in the village of Ballyvourney ( ga, Baile Bhuirne), County Cork in Ireland.Johnston, "Munster, saints of (act. ''c''.450–''c''.700)." She was associated with the Múscraige and her church and convent lay on the borders between the Múscraige Mittine and Eóganacht Locha Léin. Her feast day is February 11. Sources No hagiographical ''Life'' is known to have described her life and miracles, but she appears in the ''Life'' of her senior companion St Abbán moccu Corbmaic, written in the early thirteenth century but known only through later recensions. Saint Finbarr's ''Life'' implies that Gobnait's church belonged to Finbarr's foundation at Cork by alleging that it was not founded by her, but by one of his disciples. In spite of this, Gobnait's cult continued to thrive here and the ruins of a medieval church dedic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork And Muskerry Light Railway
The Cork and Muskerry Light Railway was a narrow gauge railway in County Cork, Ireland. The first part of the railway opened in 1887 and closed in 1934. A major reason for building the railway was to exploit tourist traffic to Blarney Castle. Initial route The railway operated from its own station. the Cork Western Road railway station, in Cork city. The initial lines westwards from Cork to Blarney and Coachford opened in 1887 and 1888 respectively. The railway operated as a roadside tramway, and the locomotives were fitted with cowcatchers. The railway was built close to the south bank of the River Lee as far as a station at Coachford Junction, west of Cork. From Coachford Junction the branch to the Blarney line terminus station was , and the line to the terminus station at Coachford was . Throughout the railway's existence, the line was equipped with nine steam locomotives. The Cork Electric Tramways and Lighting Company was later to share railways' line out of Cork ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baron Muskerry
Baron Muskerry is a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created in 1781 for Sir Robert Deane, 6th Baronet. He had previously represented County Cork in the Irish House of Commons. His great-grandson, the fourth Baron, sat in the House of Lords as an Irish Representative Peer from 1892 to 1929. On the death in 1954 of his younger son, the sixth Baron, this line of the family failed. The late Baron was succeeded by his first cousin once removed, the seventh Baron. He was the son of the Hon. Hastings Fitzmaurice Deane, third son of the third Baron. the titles are held by his grandson, the ninth Baron, who succeeded his father in 1988. Lord Muskerry lives in South Africa. The Deane Baronetcy, of Muskerry in the County of Cork, was created in the Baronetage of Ireland in 1710 for the first Baron's great-great-grandfather Matthew Deane. His grandson, the third Baronet, sat as a Member of the Irish House of Commons for County Cork. He was succeeded by his eldest son, the fourth Baro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Clancarty
Earl of Clancarty is a title that has been created twice in the Peerage of Ireland. History The title was created for the first time in 1658 in favour of Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl of Clancarty, Donough MacCarty, 2nd Viscount Muskerry, of the MacCarthy of Muskerry dynasty. He had earlier represented Cork County (Parliament of Ireland constituency), County Cork in the Irish House of Commons. Lord Clancarty had already been created a baronet in the Baronetage of Nova Scotia in , before he succeeded his father in the viscountcy. The title of Viscount Muskerry had been created in the Peerage of Ireland in 1628 for his father Charles MacCarthy, 1st Viscount Muskerry, Charles MacCarthy. The first Earl Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl of Clancarty, Donough MacCarty was succeeded by his grandson Charles, the second Earl; he was the son of Charles MacCarty, Viscount Muskerry, who was killed during the Second Anglo-Dutch War. Charles, Lord Clancarty died as an infant and was succeeded by his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscount Muskerry
A viscount ( , for male) or viscountess (, for female) is a Title#Aristocratic titles, title used in certain European countries for a nobility, noble of varying status. In many countries a viscount, and its historical equivalents, was a non-hereditary, administrative or judiciary, judicial position, and did not develop into a hereditary title until much later. In the case of French viscounts, it is customary to leave the title untranslated as vicomte . Etymology The word ''viscount'' comes from Old French (French language, Modern French: ), itself from Medieval Latin , accusative case, accusative of , from Vulgar Latin, Late Latin "deputy" + Latin (originally "companion"; later Roman imperial courtier or trusted appointee, ultimately count). History During the Carolingian Empire, the kings appointed counts to administer Government of the Carolingian Empire#subdivision, provinces and other smaller regions, as governors and military commanders. Viscounts were appointed to ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacCarthy Of Muskerry
The MacCarthy dynasty of Muskerry is a tacksman branch of the MacCarthy Mor dynasty, the Kings of Desmond. Origins and advancement The MacCarthy of Muskerry are a cadet branch of the MacCarthy Mor dynasty, MacCarthy Mor, Kings of Desmond. This cadet branch was founded by Dermot MacCarthy, 1st Lord of Muskerry, second son of Cormac MacCarthy Mor, King of Desmond, who was in 1353 created Lord of Muskerry by the English. This title's position is unclear. Cormac Laidir MacCarthy, 9th Lord of Muskerry was called Dominus and F. Dermot's descendant Cormac Oge MacCarthy, 17th Lord of Muskerry, was in 1628 created Charles MacCarthy, 1st Viscount Muskerry, and his son, the 2nd Viscount Muskerry, was in 1658 created Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl of Clancarty. Lands The family's ancestral lands of were situated along the River Lee in the baronies of Muskerry West and Muskerry East, in central County Cork west of the City of Cork. Castles * Bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
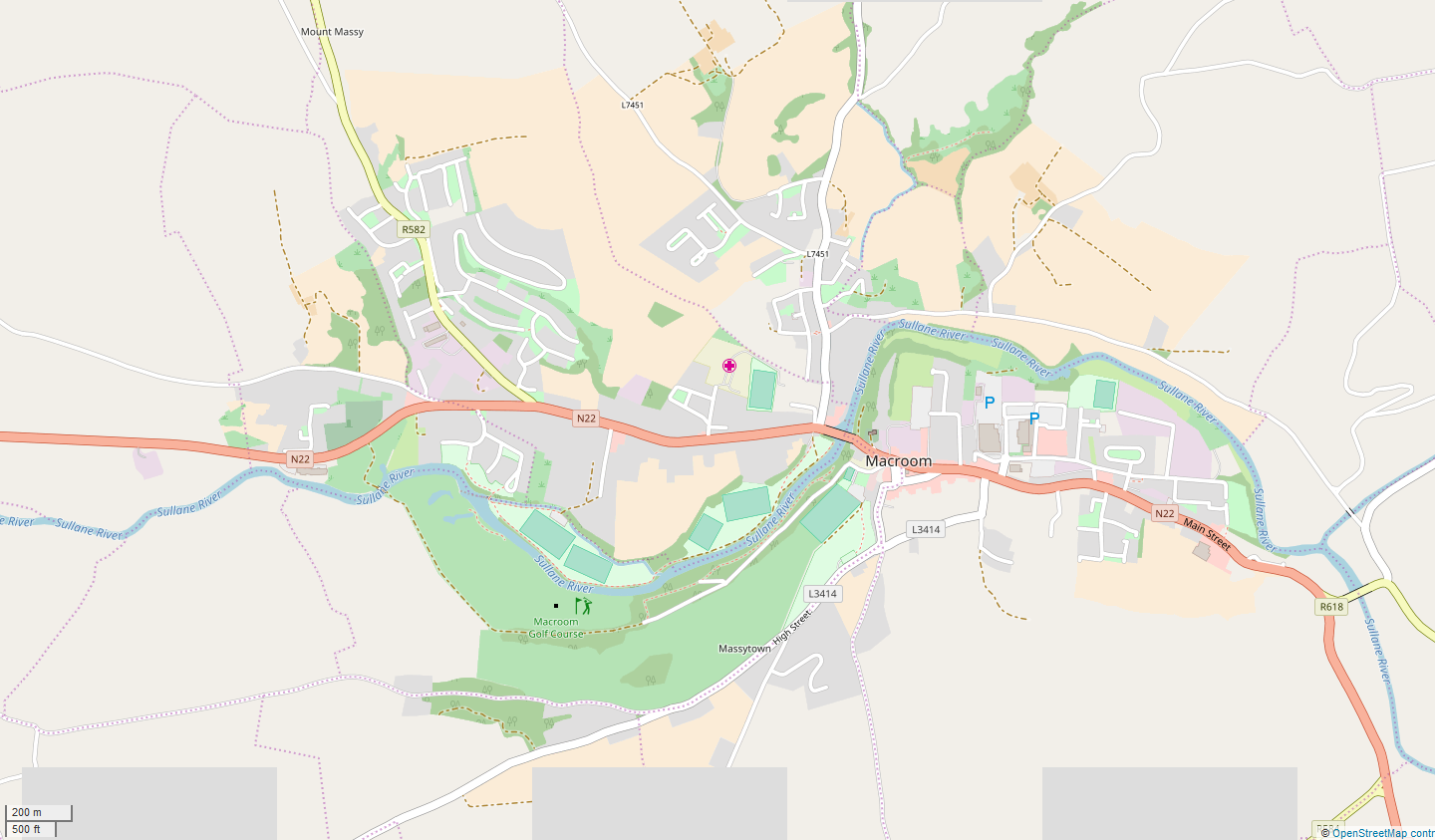
Macroom
Macroom (; ga, Maigh Chromtha) is a market town in County Cork, Ireland, located in the valley of the River Sullane, halfway between Cork city and Killarney. Its population has grown and receded over the centuries as it went through periods of war, famine and workhouses, forced emigration and intermittent prosperity. The 2011 census gave an urban population of 3,879 people, while the 2016 census recorded 3,765 people. Macroom began as a meeting place for the druids of Munster. It is first mentioned is in 6th-century records, and the immediate area hosted a major battle involving the Irish king Brian Boru. During the middle ages, the town was invaded by a succession of warring clans, including the Murcheatach Uí Briain and Richard de Cogan families. In the early modern period the MacCarthy's took control and later the area found prosperity via milling. The MacCarthys built a series of tower houses, some of which survive. The family lost influence during the Williamite wars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |