|
Mushku
The Mushki (sometimes transliterated as Muški) were an Iron Age people of Anatolia who appear in sources from Assyria but not from the Hittites. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi (Μόσχοι) of Greek sources and the Georgian tribe of the Meskhi. Josephus Flavius identified the ''Moschoi'' with the Biblical Meshech. Two different groups are called ''Muški'' in Assyrian sources ( Diakonoff 1984:115), one from the 12th to the 9th centuries BC near the confluence of the Arsanias and the Euphrates ("Eastern Mushki") and the other from the 8th to the 7th centuries BC in Cappadocia and Cilicia ("Western Mushki"). Assyrian sources clearly identify the Western Mushki with the Phrygians, but later Greek sources then distinguish between the Phrygians and the Moschoi. Identification of the Eastern Mushki with the Western Mushki is uncertain, but it is possible that at least some of the Eastern Mushki migrated to Cilicia in the 10th to the 8th centuries BC. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiglath-pileser I
Tiglath-Pileser I (; from the Hebraic form of akk, , Tukultī-apil-Ešarra, "my trust is in the son of Ešarra") was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian period (1114–1076 BC). According to Georges Roux, Tiglath-Pileser was "one of the two or three great Assyrian monarchs since the days of Shamshi-Adad I". He was known for his "wide-ranging military campaigns, his enthusiasm for building projects, and his interest in cuneiform tablet collections". Under him, Assyria became the leading power of the Ancient Near East, a position the kingdom largely maintained for the next five hundred years. He expanded Assyrian control into Anatolia and Syria, and to the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. From his surviving inscriptions, he seems to have carefully cultivated a fear of himself in his subjects and in his enemies alike. The beginning of Tiglath-Pileser's I reign, laid heavy involvement in military campaigns, as suggested from translated texts from the Middle Assyrian period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Language
Armenian ( classical: , reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian Highlands, today Armenian is widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by the priest Mesrop Mashtots. The total number of Armenian speakers worldwide is estimated between 5 and 7 million. History Classification and origins Armenian is an independent branch of the Indo-European languages. It is of interest to linguists for its distinctive phonological changes within that family. Armenian exhibits more satemization than centumization, although it is not classified as belonging to either of these subgroups. Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek (and Phrygian) and Indo-Iranian were dialectally close to each other;''Handbook of Formal Languages'' (1997p. 6 wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabal
Tabal (c.f. biblical ''Tubal''; Assyrian: 𒋫𒁄) was a Luwian speaking Neo-Hittite kingdom (and/or collection of kingdoms) of South Central Anatolia during the Iron Age. According to archaeologist Kurt Bittel, references to Tabal first appeared after the collapse of the Hittite Empire. Tabal was likely an exonym applied by the Assyrian people, Assyrians to Cappadocia. While its native name is uncertain, it is possible that it was called Sura, as mentioned in the records of Yariri, ruler of Carchemish. Originally, Tabal was likely the name of a region or collection of kingdoms. However, Tabal may have later consolidated into a single kingdom, perhaps annexing, or being annexed by, the neighboring kingdom of Melid. According to Lorenzo D'alfonso, the Tabalians may have, at least partially, descended from the Nairi tribe Tuali. The Neo-Assyrian Empire, Assyrian king Shalmaneser III records that he received gifts from their 24 kings in 837 BC and the following year. A century l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trialeti Culture
The Trialeti-Vanadzor culture, previously known as the Trialeti-Kirovakan culture, is named after the Trialeti region of Georgia and the city of Vanadzor, Armenia. It is attributed to the late 3rd and early 2nd millennium BC. Trialeti-Vanadzor culture emerged in the areas of the preceding Kura-Araxes culture. Some scholars speculate that it was an Indo-European culture. It developed into the Lchashen-Metsamor culture. It may have also given rise to the Hayasa-Azzi confederation mentioned in Hittite texts, and the Mushki mentioned by the Assyrians. Background The earliest Shulaveri-Shomu culture existed in the area from 6000 to 4000 BC.Geraldine ReinhardtBronze Age in EurasiaLecture Delivered 29 July 1991/ref> The Kura-Araxes culture followed after. The flourishing stage of the Trialeti-Vanadzor culture began near the end of the third millennium BC.Joan Aruz, Sarah B. Graff, Yelena Rakic''Cultures in Contact: From Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean in the Second Millennium B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, Georgia, and Azerbaijan, which are sometimes collectively known as the Caucasian States. The total area of these countries measures about . The South Caucasus and the North Caucasus together comprise the larger Caucasus geographical region that divides Eurasia. Geography The South Caucasus spans the southern portion of the Caucasus Mountains and their lowlands, straddling the border between the continents of Europe and Asia, and extending southwards from the southern part of the Main Caucasian Range of southwestern Russia to the Turkish and Armenian borders, and from the Black Sea in the west to the Caspian Sea coast of Iran in the east. The area includes the southern part of the Greater Caucasus mountain range, the entire Lesser C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elazığ
Elazığ () is a city in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey, and the administrative centre of Elazığ Province and Elazığ District. It is located in the uppermost Euphrates valley. The plain on which the city extends has an altitude of . Elazığ resembles an inland peninsula surrounded by the natural Lake Hazar and reservoirs of Keban Dam, Karakaya Dam, Kıralkızı and Özlüce. Its population is 443.363 (2021). Name Elazığ With the creation of the Mamuret-ul-Aziz vilayet of the Ottoman Empire, the name ''Mamuret-ul-Aziz'' came into use as a name alternative for the city. This name quickly evolved into ''al-Aziz'' ( tr, Elaziz; ku, Elezîz). In 1937, through an order from Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, this name was Turkified as ''Elazık'' (), but due to difficulties in its pronunciation, it was finally accepted as ''Elazığ''. Mezre An earlier name for the city is ''Mezre'', when Elazığ was once a suburb located on the plain below the ancient fortress town of Harpoot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris River
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the Persian Gulf. Geography The Tigris is 1,750 km (1,090 mi) long, rising in the Taurus Mountains of eastern Turkey about 25 km (16 mi) southeast of the city of Elazığ and about 30 km (20 mi) from the headwaters of the Euphrates. The river then flows for 400 km (250 mi) through Southeastern Turkey before becoming part of the Syria-Turkey border. This stretch of 44 km (27 mi) is the only part of the river that is located in Syria. Some of its affluences are Garzan, Anbarçayi, Batman, and the Great and the Little Zab. Close to its confluence with the Euphrates, the Tigris splits into several channels. First, the artificial Shatt al-Hayy branches off, to join the Euphrates near Nasiriyah. Sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashur-Dan I
Aššur-dān I, m''Aš-šur-dān''(kal)an, was the 83rd king of Assyria, reigning for 46Khorsabad King List and the SDAS King List both read, iii 19, 46 MU.MEŠ KI.MIN. (variant: 36Nassouhi King List reads, 26+x MU. EŠ LUGAL-ta DU.uš.) years, c. 1178 to 1133 BC (variant: c. 1168 to 1133 BC), and the son of Ninurta-apal-Ekur,Brick Ass. 4777 palatial inscription confirming King List filiation. where one of the three variant copies of the ''Assyrian King List'' shows a difference. The ''Synchronistic King List''''Synchronistic King List'', tablet excavation number Ass. 14616c (KAV 216), ii 10. and a fragmentary copy''Synchronistic King List'' fragment, tablet VAT 11261 (KAV 10), i 2. give his Babylonian contemporaries as Zababa-shuma-iddin, Zababa-šum-iddina, c. 1158 BC, and Enlil-nadin-ahi, Enlil-nādin-aḫe, c. 1157—1155 BC, the last of the kings of the Kassites, Kassite dynasty, but it is probable he was contemporary with two more preceding and two following these monarchs, if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. The Middle Assyrian Empire was Assyria's first period of ascendancy as an empire. Though the empire experienced successive periods of expansion and decline, it remained the dominant power of northern Mesopotamia throughout the period. In terms of Assyrian history, the Middle Assyrian period was marked by important social, political and religious developments, including the rising prominence of both the Assyrian king and the Assyrian national deity Ashur. The Middle Assyrian Empire was founded through Assur, a city-state through most of the preceding Old Assyrian period, and the surrounding territories achieving independence from the Mitanni kingdom. Under Ashur-uballit, Assyria began to expand and assert its place as one of the great powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urumeans
The Urumu (often transliterated as Urumeans) were a tribe attested in cuneiform sources in the Bronze Age. They are often considered to be one of the ancestors of the Armenians being one of the tribes which were part of the Armenian Hayasa-Azzi confederation. History The Assyrian first mentioned the Urumu in the early 12th century BC. The Urumu, with their allies the Mushki and Kaska (Apishlu), conquered the lands of Alzi and Purukuzzi (near the source of the Tigris, west of Lake Van), inciting the locals not to pay taxes. Ignace Jay Gelb suggested the Urumeans might have been mentioned much earlier, as the "Urumum" of the Cuthean Legend of Naram-Sin, which dates to the 3rd millennium BC. Igor Diakonoff, however, placed Urumum in Elam. Vyacheslav Ivanov connected them to the "Urameans" in a separate Assyrian text also dated to around 2000 BC. Location The Urumu are believed to have originally come from the north (Hayasa-Azzi) or northwest ( Hatti). However, the Urumu are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
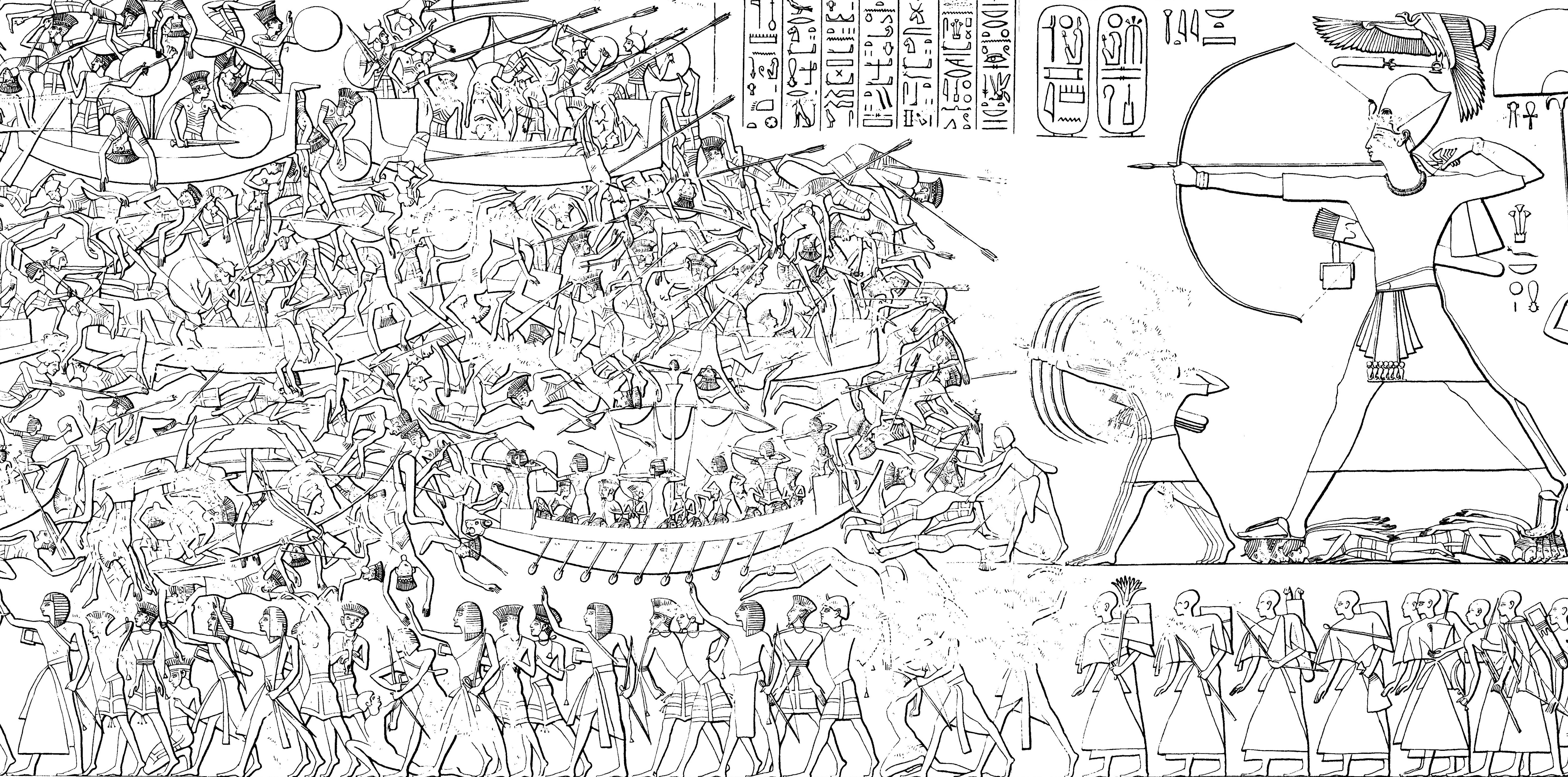
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |