|
Murrod
Murrod or Myrod (Middle Persian: ''Murrōd'', New Persian: ''مورود'') was a 3rd-century Sasanian queen (''banbishn''), the wife of the Sasanian king (shah) Ardashir I () and mother of Sasanian king Shapur I (). She is mentioned in the inscription of Shapur I on the wall of the Ka'ba-ye Zartosht at Naqsh-e Rostam near Persepolis in southern Iran as “Lady Murrod, Mother of the King of Kings”. According to a legend she was a Parthian princess and a daughter of Artabanus IV of Parthia Artabanus IV, also known as Ardavan IV ( Parthian: 𐭍𐭐𐭕𐭓), incorrectly known in older scholarship as Artabanus V, was the last ruler of the Parthian Empire from c. 213 to 224. He was the younger son of Vologases V, who died in 208. N ....Iain Gardner, Jason D. Beduhn, Paul Dilley, ''Mani at the Court of the Persian Kings: Studies on the Chester Beatty Kephalaia Codex'' (2014), p. 86 References Sources * * {{cite encyclopedia , article = Šāpur I , last = Shahbazi , fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩, Šābuhr ) was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the Arab city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire , and seized its cities of Nisibis and Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III (), he was the following year able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman Emperor Philip the Arab () to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most shameful t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardashir I
Ardashir I (Middle Persian: 𐭠𐭥𐭲𐭧𐭱𐭲𐭥, Modern Persian: , '), also known as Ardashir the Unifier (180–242 AD), was the founder of the Sasanian Empire. He was also Ardashir V of the Kings of Persis, until he founded the new empire. After defeating the last Parthian shahanshah Artabanus IV on the Hormozdgan plain in 224, he overthrew the Parthian dynasty and established the Sasanian dynasty. Afterwards, Ardashir called himself "shahanshah" and began conquering the land that he called Iran. There are various historical reports about Ardashir's lineage and ancestry. According to Al-Tabari's History of the Prophets and Kings, Ardashir was son of Papak, son of Sasan. Another narrative that exists in Kar-Namag i Ardashir i Pabagan and Ferdowsi's ''Shahnameh'' also states it says that Ardashir was born from the marriage of Sasan, a descendant of Darius III, with the daughter of Papak, a local governor in Pars. According to Al-Tabari's report, Ardashir was born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
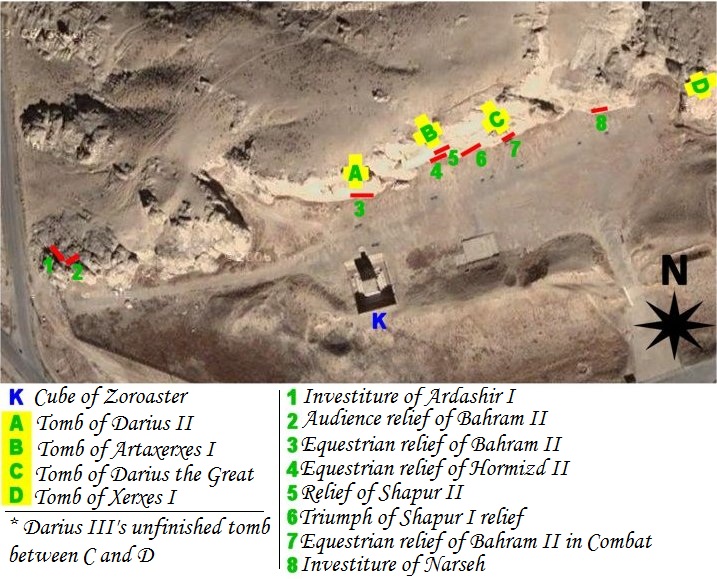
Naqsh-e Rostam
Naqsh-e Rostam ( lit. mural of Rostam, fa, نقش رستم ) is an ancient archeological site and necropolis located about 12 km northwest of Persepolis, in Fars Province, Iran. A collection of ancient Iranian rock reliefs are cut into the face of the mountain and the mountain contains the final resting place of four Achaemenid kings, notably king Darius the Great and his son, Xerxes. This site is of great significance to the history of Iran and to Iranians, as it contains various archeological sites carved into the rock wall through time for more than a millennium from the Elamites and Achaemenids to Sassanians. It lies a few hundred meters from Naqsh-e Rajab, with a further four Sassanid rock reliefs, three celebrating kings and one a high priest. Naqsh-e Rostam is the necropolis of the Achaemenid dynasty ( 550–330 BC), with four large tombs cut high into the cliff face. These have mainly architectural decoration, but the facades include large panels over the doorway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naqsh-e Rostam
Naqsh-e Rostam ( lit. mural of Rostam, fa, نقش رستم ) is an ancient archeological site and necropolis located about 12 km northwest of Persepolis, in Fars Province, Iran. A collection of ancient Iranian rock reliefs are cut into the face of the mountain and the mountain contains the final resting place of four Achaemenid kings, notably king Darius the Great and his son, Xerxes. This site is of great significance to the history of Iran and to Iranians, as it contains various archeological sites carved into the rock wall through time for more than a millennium from the Elamites and Achaemenids to Sassanians. It lies a few hundred meters from Naqsh-e Rajab, with a further four Sassanid rock reliefs, three celebrating kings and one a high priest. Naqsh-e Rostam is the necropolis of the Achaemenid dynasty ( 550–330 BC), with four large tombs cut high into the cliff face. These have mainly architectural decoration, but the facades include large panels over the doorway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century Deaths
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 (CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century Iranian People
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 (CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artabanus IV Of Parthia
Artabanus IV, also known as Ardavan IV (Parthian: 𐭍𐭐𐭕𐭓), incorrectly known in older scholarship as Artabanus V, was the last ruler of the Parthian Empire from c. 213 to 224. He was the younger son of Vologases V, who died in 208. Name ' is the Latin form of the Greek ''Artábanos'' (), itself from the Old Persian ''*Arta-bānu'' ("the glory of Arta."). The Parthian and Middle Persian variant was ''Ardawān'' (). Reign Dynastic struggles and war with the Romans In , Vologases VI succeeded his father Vologases V as king of the Parthian Empire. His rule was unquestioned for a few years, till his brother Artabanus IV rebelled. The dynastic struggle between the two brothers most likely started about 213. Artabanus successfully conquered much of the empire, including Media and Susa. Vologases VI seems to have only managed to keep Seleucia, where he minted coins. The Roman emperor Caracalla sought to take advantage of the conflict between the two brothers. He tried to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, who was rebelling against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I (r. c. 171–132 BC) greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce. The Parthians largely adopted the art, architecture, religious beliefs, and royal insignia of their culturally heterogene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persepolis
, native_name_lang = , alternate_name = , image = Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.jpg , image_size = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the Gate of All Nations, Persepolis. , map = , map_type = Iran#West Asia , map_alt = , map_caption = , map_size = , altitude_m = , altitude_ref = , relief = yes , coordinates = , map_dot_label = , location = Marvdasht, Fars Province, Iran , region = , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , volume = , diameter = , circumference = , height = , builder = , and , material = Limestone, mud-brick, cedar wood , built = 6th century BC , abandoned = , epochs = Achaemenid Empire , cultures = Persian , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = * Battle of the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur I's Inscription At The Ka'ba-ye Zartosht
Shapur I's Ka'ba-ye Zartosht inscription (shortened as Shapur-KZ, ŠKZ, SKZ), also referred to as The Great Inscription of Shapur I, and ''Res Gestae Divi Saporis'' (RGDS), is a trilingual inscription made during the reign of the Sasanian king Shapur I (240–270) after his victories over the Romans. The inscription is carved on the Ka'ba-ye Zartosht, a stone quadrangular and stepped structure located in Naqsh-e Rustam, an ancient necropolis located northwest of Persepolis, in today's Fars Province, Iran. The inscription dates to c. 262. Content The inscription is written in Middle Persian, Parthian, and Greek, containing 35, 30, and 70 lines, respectively. The Middle Persian variant is partially damaged, while the Greek and Parthian versions are better preserved, although they are not exactly the same as the Middle Persian text. In this inscription, Shapur introduces himself, mentions his genealogy, enumerates the provinces of his empire, describes his campaigns against the Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ka'ba-ye Zartosht
The Ka'ba-ye Zartosht ( fa, کعبه زرتشت), or the Cube of Zarathustra, is a stone quadrangular stepped structure in the Naqsh-e Rustam compound beside Zangiabad village in Marvdasht county in Fars, Iran. The Naqsh-e Rustam compound also incorporates memorials of the Elamites, the Achaemenids and the Sasanians. The Ka'ba-ye Zartosht is from the mountain, situated exactly opposite Darius II's mausoleum. It is rectangular and has only one entrance door. The material of the structure is white limestone. It is about high, or if including the triple stairs, and each side of its base is about long. Its entrance door leads to the chamber inside via a thirty-stair stone stairway. The stone pieces are rectangular and are simply placed on top of each other, without the use of mortar; the sizes of the stones varies from to , and they are connected to each other by dovetail joints. Etymology The structure was built in the Achaemenid era and there is no information of the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle Persian continued to function as a prestige language. It descended from Old Persian, the language of the Achaemenid Empire and is the linguistic ancestor of Modern Persian, an official language of Iran, Afghanistan (Dari) and Tajikistan ( Tajik). Name "Middle Iranian" is the name given to the middle stage of development of the numerous Iranian languages and dialects. The middle stage of the Iranian languages begins around 450 BCE and ends around 650 CE. One of those Middle Iranian languages is Middle Persian, i.e. the middle stage of the language of the Persians, an Iranian people of Persia proper, which lies in the south-western highlands on the border with Babylonia. The Persians called their language ''Parsik'', meaning "Persian". Anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


%2C_Nisa_mint.jpg)
