|
Murai Reaction
In organic chemistry, the Murai reaction is an organic reaction that uses C-H activation to create a new C-C bond between a terminal or strained internal alkene and an aromatic compound using a ruthenium catalyst. The reaction, named after Shinji Murai, was first reported in 1993. While not the first example of C-H activation, the Murai reaction is notable for its high efficiency and scope. Previous examples of such hydroarylations required more forcing conditions and narrow scope. Scope and regiochemistry The reaction was initially demonstrated using a ketone as the directing group, but other functional groups have been reported, including esters, imines, nitriles, and imidates. Murai reactions have also been reported with disubstituted alkynes. bidentate directing group allow ''ortho'' alkylation of aromatic rings with α,β-unsaturated ketones, which typically are unreactive in Murai reactions. Early examples of the reaction suffered from side products of alkylation at bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directing Group
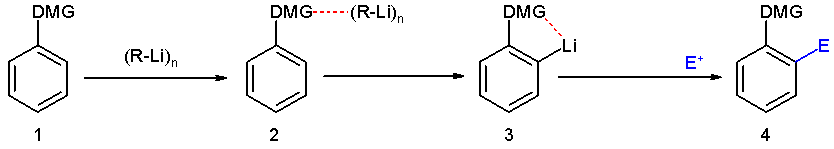
In organic chemistry, a directing group (DG) is a substituent on a molecule or ion that facilitates reactions by interacting with a reagent. The term is usually applied to C-H activation of hydrocarbons, where it is defined as a "coordinating moiety (an “internal ligand”), which directs a metal catalyst into the proximity of a certain C–H bond." In a well known example, the ketone group () in acetophenone is the DG in the Murai reaction. The Murai reaction is related to directed ortho metalation, a reaction is typically applied to the lithiation of substituted aromatic rings.''Directed ortho metalation. Tertiary amide and O-carbamate directors in synthetic strategies for polysubstituted aromatics Victor Snieckus'' Chem. Rev.; 1990; 90(6); 879-933Abstract/ref> A wide variety of functional groups can serve as directing groups. Transient directing groups Since directing groups are ligands, their effectiveness correlates with their affinities for metals. Common fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |