|
Munich East–Deisenhofen Railway
The Munich East–Deisenhofen railway is a continuously-electrified, double-track, railway in the German state of Bavaria. It connects Munich East station with Deisenhofen and was opened on 10 October 1898. Today the line is used by Munich S-Bahn trains. The whole length of the line is served by S-Bahn line S 3 (Mammendorf–Holzkirchen). Between Munich East and Munich-Giesing it is also served by line S 7 (Wolfratshausen–Kreuzstraße). Between Munich East station and the flying junction A flying junction or flyover is a railway junction at which one or more diverging or converging tracks in a multiple-track route cross other tracks on the route by bridge to avoid conflict with other train movements. A more technical term is "gr ... between Munich-Giesing and Fasangarten stations the line is one of the few in Germany that has traffic running on the left. This feature allows S-Bahn services from München St.-Martin-Straße to be inserted into the S-Bahn line at Munich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15 KV AC Railway Electrification
Railway electrification using at are used on transport railways in Rail transport in Germany, Germany, Rail transport in Austria, Austria, Rail transport in Switzerland, Switzerland, Rail transport in Sweden, Sweden, and Rail transport in Norway, Norway. The high voltage enables high power transmission with the lower frequency reducing the losses of the traction motors that were available at the beginning of the 20th century. Globally, railway electrification in late 20th century tends to use 25 kV AC railway electrification, AC systems which has become the preferred standard for new railway electrifications. Nevertheless, local extensions of the existing network is commonplace. In particular, the Gotthard Base Tunnel (opened on 1 June 2016) uses 15 kV, 16.7 Hz electrification. Due to high conversion costs, it is unlikely that existing systems will be converted to despite the fact that this would reduce the weight of the on-board step-down transformers to one t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taufkirchen (bei München)
Taufkirchen is a suburban municipality south of Munich, near Oberhaching and Unterhaching in Bavaria, southern Germany. The Realschule is named after Walter Klingenbeck. The headquarters of Airbus Defence and Space Airbus Defence and Space is a division of Airbus SE. Formed in 2014 in the restructuring of European Aeronautic Defence and Space (EADS), Airbus SE comprises the former Airbus Military, Astrium, and divisions. Contributing 21% of Airbus reven ... is generally considered to be in the neighbouring community Ottobrunn, but most of the ground area belongs to Taufkirchen. References External linksFreiwillige Feuerwehr Taufkirchen Munich (district) {{Munichdistrict-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Lines Opened In 1898
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by diesel or electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or animal power have existed since antiquity, but modern rail transport began with the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom at the beginning of the 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
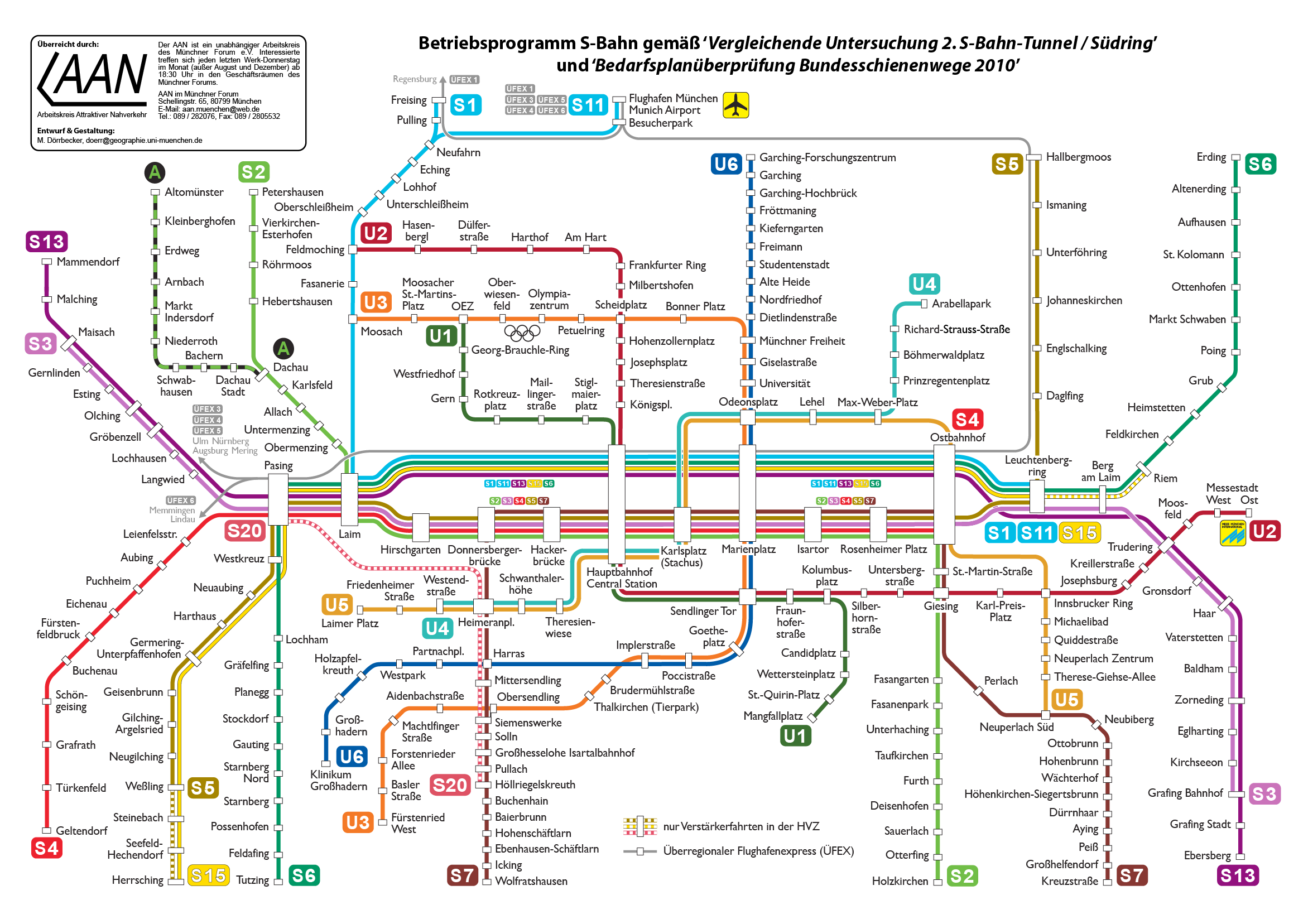
Munich S-Bahn Lines
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is not a state of its own. It ranks as the 11th-largest city in the European Union. The metropolitan area has around 3 million inhabitants, and the broader Munich Metropolitan Region is home to about 6.2 million people. It is the List of EU metropolitan regions by GDP#2021 ranking of top four German metropolitan regions, third largest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. Munich is located on the river Isar north of the Alps. It is the seat of the Upper Bavaria, Upper Bavarian administrative region. With 4,500 people per km2, Munich is Germany's most densely populated municipality. It is also the second-largest city in the Bavarian language, Bavarian dialect area after Vienna. The first record of Munich dates to 1158. The city ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Lines In Bavaria
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by diesel or electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or animal power have existed since antiquity, but modern rail transport began with the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom at the beginning of the 19th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Junction
A flying junction or flyover is a railway junction at which one or more diverging or converging tracks in a multiple-track route cross other tracks on the route by bridge to avoid conflict with other train movements. A more technical term is "grade separation, grade-separated junction". A burrowing junction or dive-under occurs where the diverging line passes below the main line. The alternative to grade separation is a level junction or flat junction, where tracks cross At-grade intersection, at grade, and conflicting routes must be protected by interlocked railway signal, signals. Complexity Simple flying junctions may have a single track pass over or under other tracks to avoid conflict; complex flying junctions may have elaborate infrastructure to allow multiple routings without trains coming into conflict, in the manner of a highway stack interchange. Flying junction without crossings Where two lines each of two tracks merge with a flying junction, they can become a Quadr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfratshausen Station
Wolfratshausen station is a station of the Munich S-Bahn. It is located in the Upper Bavarian town of Wolfratshausen in Germany. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 6 station. It has two platform tracks next to a central platform. The station is located in the network area of the Münchner Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund (Munich Transport and Tariff Association, MVV) and is served by line 7 of the S-Bahn, which is operated by Deutsche Bahn. The station was established on 27 July 1891 as a terminus when the Isar Valley Railway from Munich was put into operation. The line was built and operated by Lokalbahn AG (LAG). The station became a through station on 1 June 1897 when the Isar Valley Railway was extended to Eurasburg. In 1898, the line was extended from Eurasburg to Bichl. Until the nationalisation of the LAG in 1938 the Wolfratshausen station included a locomotive depot. From 1957 to 27 May 1972 Deutsche Bundesbahn closed the line between Bichl and Wolfratshausen in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S7 (Munich)
Line S7 is a line on the Munich S-Bahn network. It is operated by DB Regio Bayern. It runs from Wolfratshausen via Höllriegelskreuth, central Munich, Höhenkirchen-Siegertsbrunn and Aying to Kreuzstraße. Trains reverse in Munich East station and, in order for S-Bahn services from St.-Martin-Straße to be inserted into the S-Bahn line while simultaneously reversing to run into the S-Bahn tunnel under central Munich or vice versa, the line between Munich East station and the flying junction between München-Giesing and Fasangarten stations is one of the few in Germany that has traffic running on the left. The line is operated at 20-minute intervals between Höllriegelskreuth and Höhenkirchen-Siegertsbrunn. Two out of three trains an hour continue from Höllriegelskreuth to Wolfratshausen and from Höhenkirchen-Siegertsbrunn to Aying, so that the gap between trains alternates between 20 and 40 minutes. Only one train an hour continues from Aying to Kreuzstraße. It is operate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammendorf Station
Mammendorf station is a railway station in the municipality of Mammendorf, located in the district of Fürstenfeldbruck in Upper Bavaria, Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu .... References External links {{Authority control Munich S-Bahn stations Railway stations in Bavaria Railway stations in Germany opened in 1840 1840 establishments in Bavaria Buildings and structures in Fürstenfeldbruck (district) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich S-Bahn
The Munich S-Bahn () is an Railway electrification system, electric rail transit system in Munich, Germany. "S-Bahn" is the German abbreviation for ''Stadtschnellbahn'' (literally, "urban rapid rail"), and the Munich S-Bahn exhibits characteristics of both rapid transit and commuter rail systems. The Munich S-Bahn network is operated by S-Bahn München, a subsidiary of DB Regio Bayern, which is itself a subsidiary of the German national railway company, Deutsche Bahn. It is integrated into the Munich Transport and Tariff Association (''Münchner Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund'', MVV) and interconnected throughout the city with the locally owned Munich U-Bahn. Today, the S-Bahn covers most of the populated area of the Munich metropolitan area of about 3 million inhabitants. In terms of system length, the Munich S-Bahn is the fourth-largest in Germany, behind the Rhine-Neckar S-Bahn, Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn and the S-Bahn Mitteldeutschland. The Munich S-Bahn was established on 28 May 1972. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deisenhofen Station
Deisenhofen is a Munich S-Bahn railway station in Deisenhofen, a district of Oberhaching Oberhaching is a Municipalities in Germany, municipality in Bavaria, Germany, with 13,638 inhabitants (2020) on an area of . It is located south of Munich city centre and has a 1,250 year history. Architecture The most important buildings are .... History Deisenhofen station was opened in 1862 on the Munich–Holzkirchen section of the Bavarian Maximilian Railway. Since 10 October 1898 there has also been a connection to Munich East station, the Munich East–Deisenhofen railway. Since 1972, the station has been integrated in the network of the Munich S-Bahn. In 2004 the station was made fully accessible. The platforms were raised and modernised and the station building was renovated. New park-and-ride and bicycle storage facilities were built near the station. The bus stop in the station forecourt was also modernised, with a new turning circle for buses built on the forecourt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich–Holzkirchen Railway
The Munich–Holzkirchen railway is a continuously-electrified, double-track, railway in the German state of Bavaria. It runs from Munich Central Station, Munich to Holzkirchen, Upper Bavaria, Holzkirchen via Deisenhofen station, Deisenhofen. History The Munich–Holzkirchen line was built as a part of the Bavarian Maximilian's Railway along with the Munich-Rosenheim section of the modern Mangfall Valley Railway. The section between Munich and Rosenheim was designed between 1840 and 1850. The first section from Munich to Hesselohe was built from 1845. The continuation to Rosenheim was originally proposed to go via Glonn and Kirchdorf am Haunpold. After it was approved in 1850, the line was finally built via Holzkirchen. This route modified the plans of 1850 by Joseph Anton von Maffei for the Munich-Rosenheim-Salzburg Railway Company (''München-Rosenheim-Salzburger-Eisenbahn-Verein'') in order to run closer to the Miesbach coalfields. Construction of the Großhesselohe Bridge be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |