|
Multiphoton Intrapulse Interference Phase Scan
Multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan (MIIPS) is a method used in ultrashort laser technology that simultaneously measures (phase characterization), and compensates (phase correction) femtosecond laser pulses using an adaptive pulse shaper. When an ultrashort laser pulse reaches a duration of less than a few hundred femtosecond, it becomes critical to characterize its duration, its temporal intensity curve, or its electric field as a function of time. Classical photodetectors measuring the intensity of light are still too slow to allow for a direct measurement, even with the fastest photodiodes or streak cameras. Other means have been developed based on quasi instantaneous non linear optical effects such as autocorrelation, FROG, SPIDER, etc. However, these can only measure the pulse characteristics but not correct for defects in order to make the pulse as short as possible. For instance, the pulse could be linearly chirped or present higher order group delay dispersion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrashort Pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond (10−12 second) or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators. Amplification of ultrashort pulses almost always requires the technique of chirped pulse amplification, in order to avoid damage to the gain medium of the amplifier. They are characterized by a high peak intensity (or more correctly, irradiance) that usually leads to nonlinear interactions in various materials, including air. These processes are studied in the field of nonlinear optics. In the specialized literature, "ultrashort" refers to the femtosecond (fs) and picosecond (ps) range, although such pulses no longer hold the record for the shortest pulses artificially generated. Indeed, x-ray pulses with durations on the attosecond time scale have been reported. The 1999 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, and by analogy other branches of physics dealing with wave propagation, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency; sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used for specificity to optics in particular. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium (plural ''dispersive media''). Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the pulses of light in optical fiber. Physically, dispersion translates in a loss of kinetic energy through absorption. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of refra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions or diffraction angles of these beams depend on the wave (light) incident angle to the diffraction grating, the spacing or distance between adjacent diffracting elements (e.g., parallel slits for a transmission grating) on the grating, and the wavelength of the incident light. The grating acts as a dispersive element. Because of this, diffraction gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers, but other applications are also possible such as optical encoders for high precision motion control and wavefront measurement. For typical applications, a reflective grating has ridges or ''rulings'' on its surface while a transmissive grating has transmissive or hollow slits on its surface. Such a gratin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIIPS Setup
Multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan (MIIPS) is a method used in ultrashort laser technology that simultaneously measures (phase characterization), and compensates (phase correction) femtosecond laser pulses using an adaptive pulse shaper. When an ultrashort laser pulse reaches a duration of less than a few hundred femtosecond, it becomes critical to characterize its duration, its temporal intensity curve, or its electric field as a function of time. Classical photodetectors measuring the intensity of light are still too slow to allow for a direct measurement, even with the fastest photodiodes or streak cameras. Other means have been developed based on quasi instantaneous non linear optical effects such as autocorrelation, FROG, SPIDER, etc. However, these can only measure the pulse characteristics but not correct for defects in order to make the pulse as short as possible. For instance, the pulse could be linearly chirped or present higher order group delay dispersion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Light Modulator
A spatial light modulator (SLM) is an object that imposes some form of spatially varying modulation on a beam of light. A simple example is an overhead projector transparency. Usually when the term SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer. In the 1980s, large SLMs were placed on overhead projectors to project computer monitor contents to the screen. Since then, more modern projectors have been developed where the SLM is built inside the projector. These are commonly used in meetings of all kinds for presentations. Usually, a SLM modulates the intensity of the light beam. However, it is also possible to produce devices that modulate the phase of the beam or both the intensity and the phase simultaneously. SLMs are used extensively in holographic data storage setups to encode information into a laser beam similarly to way a transparency does for an overhead projector. They can also be used as part of a holographic display technology. SLMs ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, *lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Phase
The power spectrum S_(f) of a time series x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, or a spectrum of frequencies over a continuous range. The statistical average of a certain signal or sort of signal (including noise) as analyzed in terms of its frequency content, is called its spectrum. When the energy of the signal is concentrated around a finite time interval, especially if its total energy is finite, one may compute the energy spectral density. More commonly used is the power spectral density (or simply power spectrum), which applies to signals existing over ''all'' time, or over a time period large enough (especially in relation to the duration of a measurement) that it could as well have been over an infinite time interval. The power spectral density (PSD) then refers to the spectral energy distribution that would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-harmonic Generation
Second-harmonic generation (SHG, also called frequency doubling) is a nonlinear optical process in which two photons with the same frequency interact with a nonlinear material, are "combined", and generate a new photon with twice the energy of the initial photons (equivalently, twice the frequency and half the wavelength), that conserves the coherence of the excitation. It is a special case of sum-frequency generation (2 photons), and more generally of harmonic generation. The second-order nonlinear susceptibility of a medium characterizes its tendency to cause SHG. Second-harmonic generation, like other even-order nonlinear optical phenomena, is not allowed in media with inversion symmetry (in the leading electric dipole contribution). However, effects such as the Bloch–Siegert shift (oscillation), found when two-level systems are driven at Rabi frequencies comparable to their transition frequencies, will give rise to second harmonic generation in centro-symmetric systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth-limited Pulse
A bandwidth-limited pulse (also known as Fourier-transform-limited pulse, or more commonly, transform-limited pulse) is a pulse of a wave that has the minimum possible duration for a given spectral bandwidth. Bandwidth-limited pulses have a constant phase across all frequencies making up the pulse. Optical pulses of this type can be generated by mode-locked lasers. Any waveform can be disassembled into its spectral components by Fourier analysis or Fourier transform A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...ation. The length of a pulse thereby is determined by its complex spectral components, which include not just their relative intensities, but also the relative positions ( spectral phase) of these spectral components. For different pulse shapes, the minimum durati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Shaping
In electronics and telecommunications, pulse shaping is the process of changing the waveform of transmitted pulses to optimize the signal for its intended purpose or the communication channel. This is often done by limiting the bandwidth of the transmission and filtering the pulses to control intersymbol interference. Pulse shaping is particularly important in RF communication for fitting the signal within a certain frequency band and is typically applied after line coding and modulation. Need for pulse shaping Transmitting a signal at high modulation rate through a band-limited channel can create intersymbol interference. The reason for this are Fourier correspondences (see Fourier transform). A bandlimited signal corresponds to an infinite time signal, that causes neighbouring pulses to overlap. As the modulation rate increases, the signal's bandwidth increases. As soon as the spectrum of the signal is a sharp rectangular, this leads to a sinc shape in the time domain. This hap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
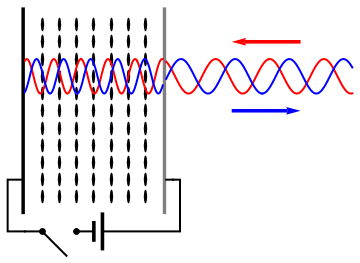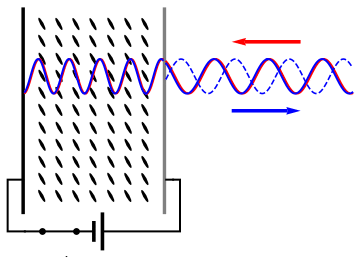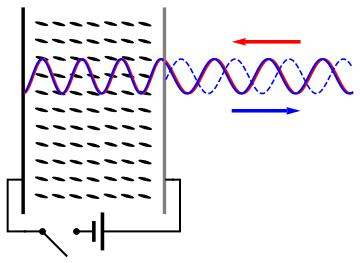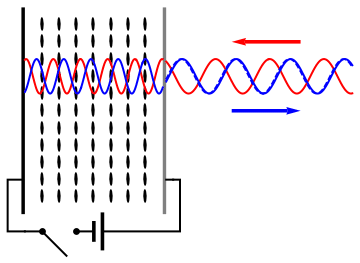
Group Delay Dispersion
In optics, group velocity dispersion (GVD) is a characteristic of a dispersive medium, used most often to determine how the medium will affect the duration of an optical pulse traveling through it. Formally, GVD is defined as the derivative of the inverse of group velocity of light in a material with respect to angular frequency, :\textrm(\omega_0) \equiv \frac \left( \frac \right)_, where \omega and \omega_0 are angular frequencies, and the group velocity v_g(\omega) is defined as v_g(\omega) \equiv \partial \omega / \partial k. The units of group velocity dispersion are imesup>2/ istance often expressed in fs2/mm. Equivalently, group velocity dispersion can be defined in terms of the medium-dependent wave vector k(\omega) according to :\textrm(\omega_0) \equiv \left( \frac\right)_, or in terms of the refractive index n(\omega) according to :\textrm(\omega_0) \equiv \frac \left(\frac\right)_ + \frac\left( \frac\right)_. Applications Group velocity dispersion is most commonly us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |