|
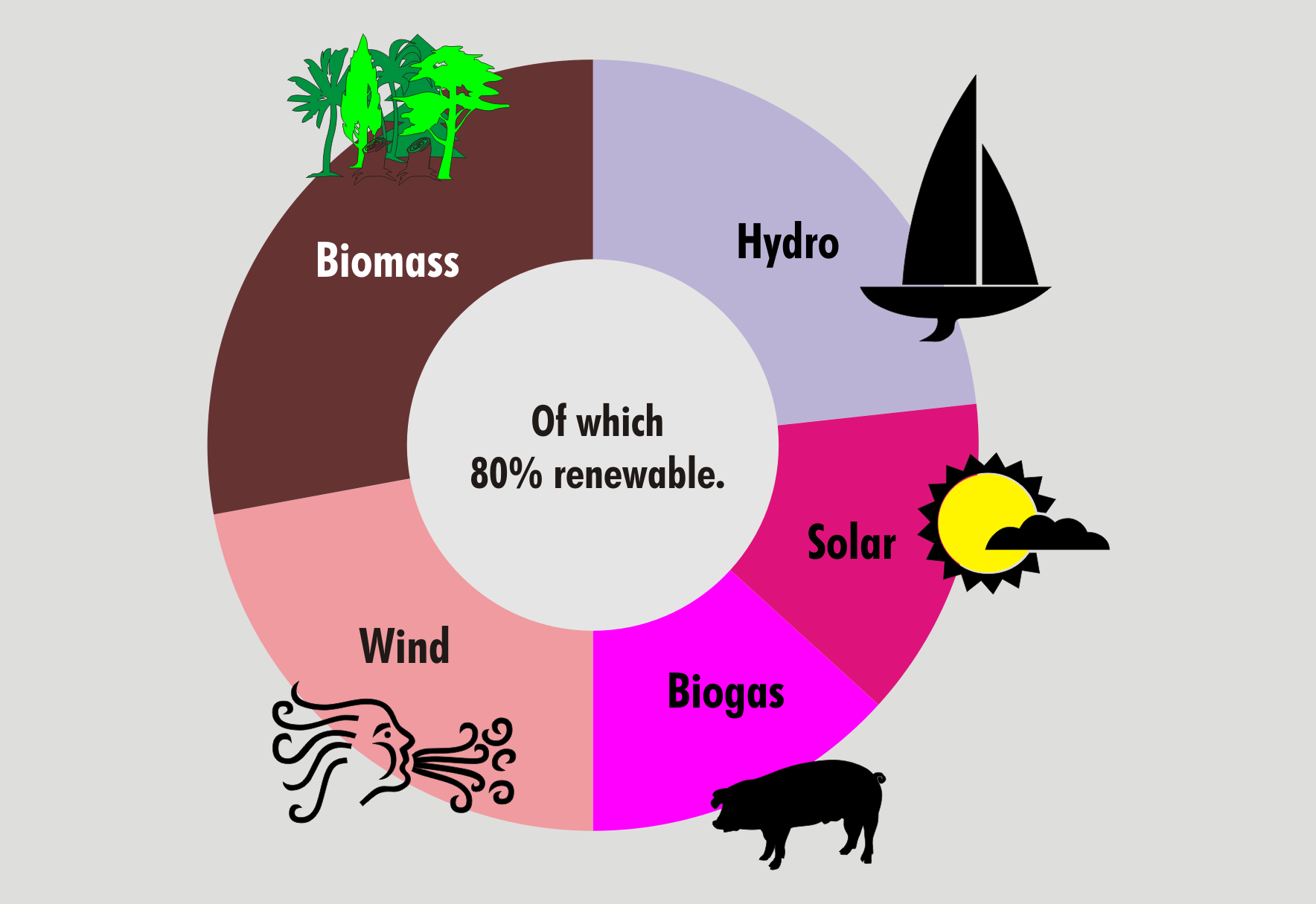
Multilevel Pie Chart
A pie chart (or a circle chart) is a circular statistical graphic, which is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportion. In a pie chart, the arc length of each slice (and consequently its central angle and area) is proportional to the quantity it represents. While it is named for its resemblance to a pie which has been sliced, there are variations on the way it can be presented. The earliest known pie chart is generally credited to William Playfair's ''Statistical Breviary'' of 1801.Spence (2005)Tufte, p. 44 Pie charts are very widely used in the business world and the mass media.Cleveland, p. 262 However, they have been criticized,Wilkinson, p. 23. and many experts recommend avoiding them,Tufte, p. 178.van Belle, p. 160–162.Stephen Few"Save the Pies for Dessert" August 2007, Retrieved 2010-02-02Steve Fento"Pie Charts Are Bad"/ref> as research has shown it is difficult to compare different sections of a given pie chart, or to compare data across different pie c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Dialects1997
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Joseph Minard
Charles Joseph Minard (; ; 27 March 1781 – 24 October 1870) was a French civil engineer recognized for his significant contribution in the field of information graphics in civil engineering and statistics. Minard was, among other things, noted for his representation of numerical data on geographic maps, especially his flow maps. Early life Minard was born in Dijon in the Saint Michel parish. He was the son of Pierre Etienne Minard and Bénigne Boiteux. His father was a clerk of the court and an officer of the secondary school. Minard was baptized at Saint Michel on the day of his birth. From Posted by Edward Tufte. He was very bright and his father encouraged him to study at an early age. At age four he learned to read and write, and when he was six his father enrolled him in an elementary course in anatomy. He completed his fourth year of study at the secondary school at Dijon early, and then applied himself to studying Latin, literature, and physical and math sciences. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunburst
A sunburst is a design or figure commonly used in architectural ornaments and design patterns and possibly pattern books. It consists of rays or "beams" radiating out from a central disk in the manner of sunbeams. Sometimes part of a sunburst, a semicircular or semi-elliptical shape, is used. Traditional sunburst motifs usually show the rays narrowing as they get further from the centre; from the later 19th century they often get wider, as in the Japanese Rising Sun Flag, which is more appropriate in optical terms. In architecture, the sunburst is often used in window designs, including fanlights and rose windows, as well as in decorative motifs. The sunburst motif is characteristic of Baroque church metalwork, especially monstrances and votive crowns, and Art Deco and Art Nouveau styles as well as church architecture. A sunburst is frequently used in emblems and military decorations. Sunbursts can appear in photographs when taking a picture of the Sun through the diap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Usage (Boabab)
du (abbreviated from ''disk usage'') is a standard Unix program used to estimate file space usage—space used under a particular directory or files on a file system. A Windows commandline version of this program is part of Sysinternals suite by Mark Russinovich. History The du utility first appeared in version 1 of AT&T UNIX. The version of du bundled in GNU coreutils was written by Torbjorn Granlund, David MacKenzie, Paul Eggert, and Jim Meyering. The command is also available for FreeDOS. Specification By default, the Single UNIX Specification (SUS) specifies that du is to display the file space allocated to each file and directory contained in the current directory. Links will be displayed as the size of the link file, not what is being linked to; the size of the content of directories is displayed, as expected. As du reports allocation space and not absolute file space, the amount of space on a file system shown by du may vary from that shown by df if files have been d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
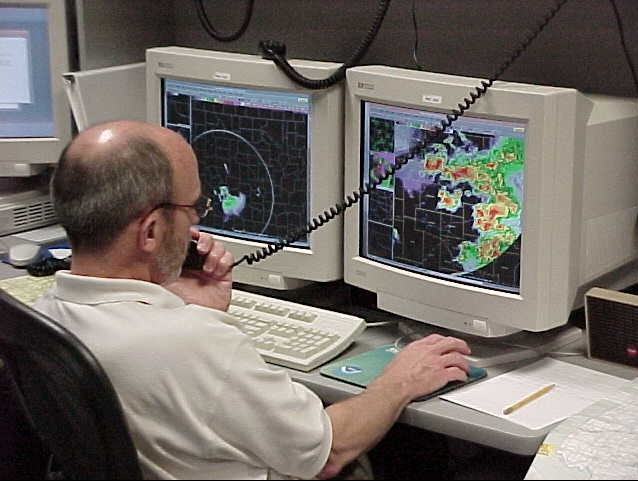
Meteorologist
A meteorologist is a scientist who studies and works in the field of meteorology aiming to understand or predict Earth's atmospheric phenomena including the weather. Those who study meteorological phenomena are meteorologists in research, while those using mathematical models and knowledge to prepare daily weather forecasts are called ''weather forecasters'' or ''operational meteorologists''. Meteorologists work in government agencies, private consulting and research services, industrial enterprises, utilities, radio and television stations, and in education. They are not to be confused with weather presenters, who present the weather forecast in the media and range in training from journalists having just minimal training in meteorology to full fledged meteorologists. Description Meteorologists study the Earth's atmosphere and its interactions with the Earth's surface, the oceans and the biosphere. Their knowledge of applied mathematics and physics allows them to understand t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
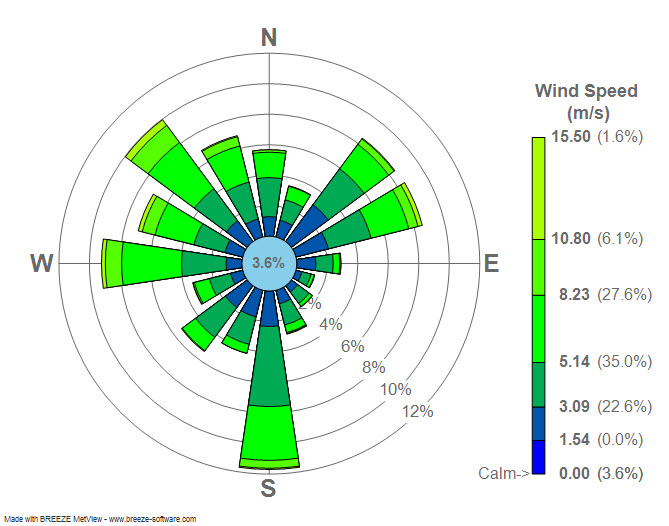
Wind Rose
A wind rose is a graphic tool used by meteorologists to give a succinct view of how wind speed and direction are typically distributed at a particular location. Historically, wind roses were predecessors of the compass rose (found on charts), as there was no differentiation between a cardinal direction and the wind which blew from such a direction. Using a polar coordinate system of gridding, the frequency of winds over a time period is plotted by wind direction, with colour bands showing wind speed ranges. The direction of the longest spoke shows the wind direction with the greatest frequency. History Before the development of the compass rose, a wind rose was included on maps in order to let the reader know which directions the 8 major winds (and sometimes 8 half-winds and 16 quarter-winds) blew within the plan view. No differentiation was made between cardinal directions and the winds which blew from those directions. North was depicted with a fleur de lis, while eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léon Lalanne
Léon Louis Lalanne (; real surname: Chrétien-Lalanne; 3 July 1811 – 12 March 1892) was a French engineer and politician. Life Lalanne was born in Paris on 3 July 1811, as Léon Louis Chrétien, the son of François Julien Léon Chrétien, a physician, and his wife Aurore Marie Damaris Langlois; his surname became Lalanne-Chrétien in 1820, Lalanne being the unmarried name of his father's first wife, and he dropped the Chrétien for practical use. He was the brother of the historian Ludovic Lalanne (1815–1898). Lalanne studied at the Lycée Louis-le-Grand, where he was a classmate of Évariste Galois. From 1829 at the École Polytechnique, he went on to the École des ponts et chaussées in 1831. After that, he was a civil engineer, working mostly in northern France from 1832 to 1843. In 1837 he went on the group visit to Southern Russia organized by Anatoly Demidov (the future Count Demidov and 1st Prince of San Donato). From 1839 he was working also with Jean-Claude-Répub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André-Michel Guerry
André-Michel Guerry (; December 24, 1802 – April 9, 1866) was a French lawyer and amateur statistician. Together with Adolphe Quetelet he may be regarded as the founder of moral statistics which led to the development of criminology, sociology and ultimately, modern social science. Early life and education Guerry was born in Tours, Indre-et-Loire, the only child of Michel Guerry, a building contractor, whose family had a long history as innkeepers, merchants, farmers and trades-people. About 1817-1820 he studied at the Imperial College of Tours (now the Lyceum Descartes, founded in 1807) and subsequently studied law at the University of Poitiers. About 18241825 he moved to Paris and was admitted to the bar as a royal advocate. Shortly after, he was employed by the Ministry of Justice. Guerry worked with the data on crime statistics in France collected as part of the ''General office for administration of criminal justice'' in France, the first centralized national syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pie Chart EP Election 2004 Exploded
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients. Sweet pies may be filled with fruit (as in an apple pie), nuts ( pecan pie), brown sugar ( sugar pie), sweetened vegetables (rhubarb pie), or with thicker fillings based on eggs and dairy (as in custard pie and cream pie). Savoury pies may be filled with meat (as in a steak pie or a Jamaican patty), eggs and cheese (quiche) or a mixture of meat and vegetables (pot pie). Pies are defined by their crusts. A ''filled'' pie (also ''single-crust'' or ''bottom-crust''), has pastry lining the baking dish, and the filling is placed on top of the pastry but left open. A ''top-crust'' pie has the filling in the bottom of the dish and is covered with a pastry or other covering before baking. A ''two-crust'' pie has the filling completely enclosed in the pastry shell. Shortcrust pastry is a typical kind of pastry used for pie crusts, but many things can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Example Of A Doughnut Chart
Example may refer to: * '' exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example" * .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet ** example.com, example.net, example.org, example.edu, second-level domain names reserved for use in documentation as examples * HMS ''Example'' (P165), an Archer-class patrol and training vessel of the Royal Navy Arts * ''The Example'', a 1634 play by James Shirley * ''The Example'' (comics), a 2009 graphic novel by Tom Taylor and Colin Wilson * Example (musician), the British dance musician Elliot John Gleave (born 1982) * ''Example'' (album), a 1995 album by American rock band For Squirrels See also * * Exemplar (other), a prototype or model which others can use to understand a topic better * Exemplum, medieval collections of short stories to be told in sermons * Eixample The Eixample (; ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspective (visual)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(cropped).jpg)