|
Mukunda Manikya
Mukunda Manikya (d. 1739) was the Maharaja of Tripura from 1729 to 1739. Life Originally named Chandramani Thakur, he was the youngest of the four surviving sons of Maharaja Rama Manikya. Each of his elder brothers had successively ruled Tripura; under Ratna II's rule, Chandramani had been sent as a hostage to the Mughal viceregal court at Murshidabad, while during the reigns of Mahendra and Dharma II, he was appointed ''Barathakur'' and ''Yuvraj'' respectively. When he succeeded Dharma in 1729, Chandramani assumed the regnal name Mukunda Manikya. He proved to be a pious monarch, donating lands to Brahmins and Kshatriyas. He attempted to maintain cordial relations with the Mughals, sending his son Panch Cowrie Thakur as a hostage and informing on a plot to kill the Mughal Faujdar at Udaipur by his cousin Rudramani. However, in 1739, he was overthrown by the Mughals due to failing to provide Tripura's annual tribute of five elephants. Udaipur was raided and Mukunda, alongsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twipra Kingdom
The Twipra Kingdom (Sanskrit: Tripura, Anglicisation, Anglicized: Tippera) was one of the largest historical kingdoms of the Tripuri people in North East India, Northeast India. Geography The present political areas which were part of the Twipra Kingdom are: * Barak Valley (Cachar Plains), Hailakandi and Karimganj in present-day Assam * Comilla, Sylhet and the Chittagong Hill Tracts in Bangladesh * The present-day states of Tripura and Mizoram The Twipra Kingdom in all its various ages comprised the areas with the borders: # The Khasi Hills in the North # The Manipur Hills in the North-East # THe Rakhine State, Arakan Hills of Myanmar, Burma in the East # The Bay of Bengal to the South # The Brahmaputra River to the West Legend A list of legendary Tripuri kings is given in the Rajmala chronicle, a 15th-century chronicle in Bengali written by the court pandits of Dharma Manikya I (r. 1431). The chronicle traces the king's ancestry to the mythological Lunar Dynasty. List of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru or acharya). The other three varnas are the Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra. The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood at the Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and rite of passage rituals such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, the Brahmins are accorded the highest ritual status of the four social classes. Their livelihood is prescribed to be one of strict austerity and voluntary poverty ("A Brahmin should acquire what just suffices for the time, what he earns he should spend all that the same day"). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1739 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 – Bouvet Island is discovered by French explorer Jean-Baptiste Charles Bouvet de Lozier, in the South Atlantic Ocean. * January 3: A 7.6 earthquake shakes the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region in China killing 50,000 people. * February 24 – Battle of Karnal: The army of Iranian ruler Nader Shah defeats the forces of the Mughal emperor of India, Muhammad Shah. * March 20 – Nader Shah occupies Delhi, India and sacks the city, stealing the jewels of the Peacock Throne, including the Koh-i-Noor. April–June * April 7 – English highwayman Dick Turpin is executed by hanging for horse theft. * May 12 – John Wesley lays the foundation stone of the New Room, Bristol in England, the world's first Methodist meeting house. * June 13 – (June 2 Old Style); The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences is founded in Stockholm, Sweden. July–September * July 9 – The first group purporting to repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dethroned Monarchs
Ring of Honor (ROH) is an American professional wrestling promotion based in Jacksonville, Florida. The promotion was founded by Rob Feinstein on February 23, 2002, and was operated by Cary Silkin from 2004 until 2011, when the promotion was sold to the Sinclair Broadcast Group. After a deal was struck in March 2022, ROH was officially sold to All Elite Wrestling (AEW) founder, co-owner, president, and CEO Tony Khan two months later. Throughout the 2010s, Ring of Honor was considered a major wrestling promotion in the United States, alongside WWE and Impact Wrestling. Under Sinclair Broadcast Group's ownership, ROH began talent-sharing deals with wrestling companies outside the U.S., expanded their television visibility through Sinclair's broadcast stations, and eventually established its own streaming service in 2018 called Honor Club. But as time went on and the industry saw the creation and subsequent rise of All Elite Wrestling (AEW), ROH would be seen as a smaller promotio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Tripura
The State of Tripura has a long history. The Twipra Kingdom at its peak included the whole eastern region of Bongal from the Brahmaputra River in the north and west, the Bay of Bengal in the south and Burma to the east during the 14th and 15th centuries AD. The last ruler of the princely state of Tripura was Kirit Bikram Kishore Manikya Bahadur Debbarma who reigned from 1947 to 1949 Agartala after whom the kingdom was merged with India on 9 September 1949, and the administration was taken over on 15 October 1949. Tripura became a Union Territory on 1 July 1963, and attained the status of a full-fledged state on 21 January 1972. Prehistorical period The origins of the kingdom are shrouded in the stories written in ''Rajmala'', the chronicle of the Kings of Tripura, which meanders from Hindu traditional histories and Tripuri folklores. Ancient period The ancient period can be said to be from around the 7th century when the Tripuri kings ruled from Kailashahar in North Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Tripura
The Manikya dynasty was the ruling house of the Twipra Kingdom and later the princely Tripura State, what is now the Indian state of Tripura. Ruling since the early 15th century, the dynasty at its height controlled a large swathe of the north-east of the Indian subcontinent. After coming under British influence, in 1761 they transitioned from feudal monarchs into rulers of a princely state, though the Manikyas maintain control of the region until 1949, when it ascended in union with India. History Tracing a descent from the mythological Lunar dynasty, the ''Rajmala'' royal chronicle records an unbroken line of 144 (likely legendary) monarchs of Tripura up to the ascension of one Ratna Fa, who is stated to have become the first Manikya after being granted the cognomen by the Sultan of Bengal. However, it is now believed that the ''Rajmala'' had been mistaken in the genealogy and chronology of the initial Manikya rulers. Numismatic evidence suggests that the first historical Mani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sati (practice)
Sati or suttee is a Hindu practice, now largely historical, in which a widow sacrifices herself by sitting atop her deceased husband's funeral pyre. Quote: Between 1943 and 1987, some thirty women in Rajasthan (twenty-eight, according to official statistics) immolated themselves on their husband's funeral pyre. This figure probably falls short of the actual number. (p. 182) Although it is debated whether it received scriptural mention in early Hinduism, it has been linked to related Hindu practices in the Indo-Aryan speaking regions of India which diminished the rights of women, especially those to the inheritance of property. A cold form of sati, or the neglect and casting out of Hindu widows has been prevalent in India from ancient times. Quote: Sati is a particularly relevant social practice because it is often used as a means to prevent inheritance of property by widows. In parallel, widows are also sometimes branded as witches – and subjected to violent expulsion fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udai Manikya II
Udai Manikya II was the Maharaja of Tripura briefly during the mid-18th-century, having laid claim to the throne during a power struggle between his relatives Joy Manikya II and Indra Manikya II. Life Originally named Gangadhar Thakur, he was the eldest son of Maharaja Dharma Manikya II. During Dharma's reign, both Gangadhar and his younger brother Gadadhar Thakur were passed over for the naming of ''Yuvraj'' (crown prince), possibly due to a quarrel, with the title instead falling to their uncle Chandramani, who later ascended the throne under the name Mukunda Manikya. When the latter was deposed by the Mughals in 1739, Gangadhar was captured alongside Mukunda's sons Bhadramani and Krishnamani. By 1744, Tripura was in conflict due to a power struggle between Joy Manikya II and Indra Manikya II. Taking advantage of the situation, Gangadhar bribed the Mughal Naib Nazim of Dhaka, Nawazish Muhammad Khan, and secured a '' fatwa'' in his favour. He arrived in Comilla Comill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudramani
Joy Manikya II (died 1746) was the Maharaja of Tripura during the mid-18th-century. He originally gained the throne through popular approval for his military hostility to the Mughal Empire. However, Joy spent much of his reign warring against various relations to maintain his grip on it, in particular with his cousin Indra Manikya II. Background Originally named Rudramani Thakur, he belonged to a cadet branch of the royal family; his father Haradhan Thakur had been a grandson of Jagannath Thakur, the younger brother of Maharaja Govinda Manikya. As a young man, Rudramani had been a prominent general and had opposed the suzerainty of the Mughal Empire over Tripura. To this end, he aimed to form a national militia against the occupying force. From his base in the Matia Hills (where he had been sent to capture elephants), Rudramani organised a strong force with the aid of tribal chiefs. He wrote to the then-monarch, Mukunda Manikya, stating that the people of Tripura were opposed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
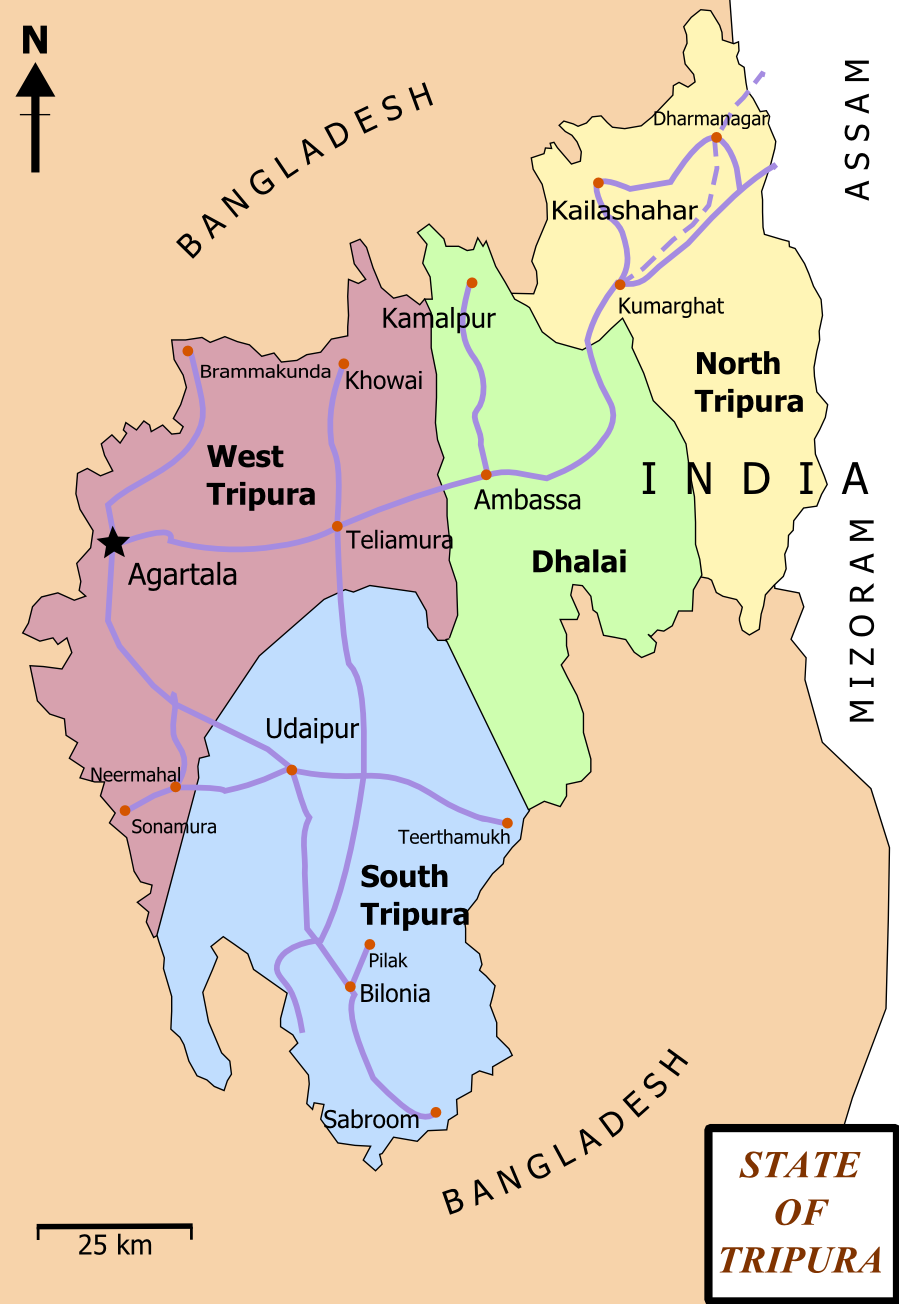
Udaipur, Tripura
Udaipur ( Pron:/uːˈdaɪpʊə or ˈuːdaɪˌpʊə/), formerly known as Rangamati, is the third biggest urban area in the Indian state of Tripura. The town was a capital of the state during the reign of the Manikya Dynasty. It is famous for the Tripura Sundari temple also known as ''Tripureswari'' temple, one of the 51 Shakti Peethas.It is a Municipal Council in Gomati district & also the headquarters of Gomati district. Udaipur is about 51 km from Agartala, the capital of Tripura. Geography Udaipur is located at . It has an average elevation of 22 metres (72 feet).The Gomati river passes through the heart of Udaipur and helps in irrigation of its lands. Demographics As of 2011 India census, Udaipur nagar panchayat had a population of 32,758, of which 16,593 were males and 16,165 were females. The total number of literates in Udaipur were 28,378, of which 14,563 were males and 13,8155 were females. Udaipur has an effective literacy rate (for population 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faujdar
Faujdar is a term of pre-Mughal origins. Under the Mughals it was an office that combined the functions of a military commander along with judicial and land revenue functions. In pre-Mughal times, the term referred to a military officer but did not refer to a specific rank. With the administrative reforms performed by Mughal emperor Akbar, this rank was systemised. It constituted an independent administrative unit and its territorial limits varied from place to place and from time to time. A faujadari comprised a number of thanas or military outposts. At each of these the number of swears were stationed under a thanadar. Faujdari carried with it a fixed number of sawars and it was up to the faujdar to station soldiers in various thanas under him. In addition in some faujdaris there were a number of thanas described as huzuri or huzuri mashruti. In these thanas the Thanadars were appointed directly by the central government via royal orders or at the recommendations of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panch Cowrie Thakur
Indra Manikya II (d. 1746) was the Maharaja of Tripura during the mid-18th-century. His reign was spent struggling for control of the kingdom with his relative Joy Manikya II. Life Originally named Panch Cowrie Thakur, he was one of the sons of Maharaja Mukunda Manikya by his wife Prabhavati. During his father's reign, he was sent to the Mughal court of Murshidabad as a hostage. In 1739, after having been arrested by the Mughals on the grounds of neglecting to pay his tribute of elephants, Mukunda committed suicide. His cousin Joy Manikya was chosen by the populace as his successor over Mukunda's sons after the former drove the Mughals out of Udaipur. Panch Cowrie, who developed a grudge against Joy, approached Alivardi Khan, the Nawab of Bengal, for aid in claiming Tripura in 1744. With his military support, he overthrew Joy and took the throne, assuming the reginal name Indra Manikya. However, Indra was unable to rule peacefully, as Joy ran a parallel government from the Mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
_Bhumi_Puja%2C_yajna.jpg)

.jpg)



_and_Mir_Miran_(right).jpg)