|
Muiryfold
Muiryfold was one of the Roman fortifications built by Septimius Severus in northern Caledonia (modern-day Scotland). The site is located east of Keith in Moray. Discovery and excavation The site was discovered by aerial photography in 1959, and two small trenches were excavated across the north west and south east sides by Kenneth St Joseph the same year. The camp was almost rectangular, measuring from north west to south east, and from north east to south west, covering an area of just over . History In 210 AD, the Emperor Septimius Severus made an attempt to conquer all Caledonia reaching the Moray Firth. He created a huge marching camp at Muiryfold, near the one created in 84 AD by Agricola at Auchinhove. The possibility that Agricola and Septimius Severus reached the northernmost area of Scotland can be confirmed by discoveries north of Inverness, specifically at Portmahomack on the Dornoch Firth, and Tarradale on the north shore of the Beauly Firth. The Roman legions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellie
Bellie is a locality in Moray, Scotland. Little survives of the old parish church at Bellie, located 2 miles north of Fochabers, although its Kirkyard, graveyard is preserved. There is a Bellie Kirk in Fochabers, which replaced the old church in 1798. There are up to two possible Roman camps at Bellie. Either of these sites, if accepted as a Roman camp, would constitute the most northerly example known, being 10 miles north-west of the known camps at Auchinhove and Muiryfold. Possible Roman sites The first site is known as Romancamp Gate, and lies 100 metres to the north-east of the old church of Bellie, with a cliff to the north-west that lies on the east bank of the River Spey. The site was recorded by the antiquarian George Chalmers (antiquarian), George Chalmers in 1799 as "the remains of the Roman encampment overlooking the low ground by the river ... on plan nearly a rectangular parallelogram of 888' by 333', but the W and most of the N sides have been destroyed." In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ythan Wells
Ythan Wells, also known as Glenmailen, is the site of a Roman military camp, near the farm of Glenmellan, east of the village of Ythanwells in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The site is a designated scheduled monument. Traces of two marching camps have been found at the site. The larger camp, covering some was discovered in 1785 by Col. Alex Shand. A smaller camp, extending to and partially overlapping the area of the first, was discovered by J. K. St Joseph in 1968. This smaller camp predates the larger and has been dated to the campaigns of Agricola. The site is situated at the headwaters of the River Ythan, where a series of natural springs supplies potable water, that was convenient for the large marching camp installed here by the Romans in the first few centuries AD. The Roman legions established a chain of very large forts at Ardoch, Strageath, Inchtuthil, Battledykes, Stracathro and Raedykes, taking the Elsick Mounth on the way to Normandykes, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenmailen
Ythan Wells, also known as Glenmailen, is the site of a Roman military camp, near the farm of Glenmellan, east of the village of Ythanwells in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The site is a designated scheduled monument. Traces of two marching camps have been found at the site. The larger camp, covering some was discovered in 1785 by Col. Alex Shand. A smaller camp, extending to and partially overlapping the area of the first, was discovered by J. K. St Joseph in 1968. This smaller camp predates the larger and has been dated to the campaigns of Agricola. The site is situated at the headwaters of the River Ythan, where a series of natural springs supplies potable water, that was convenient for the large marching camp installed here by the Romans in the first few centuries AD. The Roman legions established a chain of very large forts at Ardoch, Strageath, Inchtuthil, Battledykes, Stracathro and Raedykes, taking the Elsick Mounth on the way to Normandykes, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normandykes
Normandykes (Grid Reference: NO 830994) is the site of a Roman marching camp to the southwest of Peterculter, City of Aberdeen, Scotland. The near-rectangular site, measuring approximately , covers about of the summit and eastern slopes of a hill overlooking the River Dee and the B9077 road further south. Aerial photographs for Normandykes have been archived between 1947 and 1976. The camp is about , or less than half a day's march, north of the Raedykes camp. It is possible that the actual route taken would have entailed one day's march, over a route likely chosen to avoid the Red Moss, a virtually uncrossable bog near the present day village of Netherley. Normandykes was first excavated in the year 1935 by Richmond and MacIntyre; construction is thought to date to the Antonine or Severan periods. The site is designated a scheduled ancient monument. See also * Raedykes * Balbridie * Crynoch Burn * Deers Den * Glenmailen * Leuchar Burn * Maryculter House * Ythan Wells * Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cropmark
Cropmarks or crop marks are a means through which sub-surface archaeological, natural and recent features may be visible from the air or a vantage point on higher ground or a temporary platform. Such marks, along with parch marks, soil marks and frost marks, can reveal buried archaeological sites that are not visible from the ground. Description Crop marks are due to the principle of differential growth. One of the factors controlling the growth of vegetation is the condition of the soil. A buried stone wall, for example, will affect crop growth above it, as its presence channels water away from its area and occupies the space of the more fertile soil. Conversely, a buried ditch, with a fill containing more organic matter than the natural earth, provides much more conducive conditions and water will naturally collect there, nourishing the plants growing above. The differences in conditions will cause some plants to grow more strongly and therefore taller, and others less str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
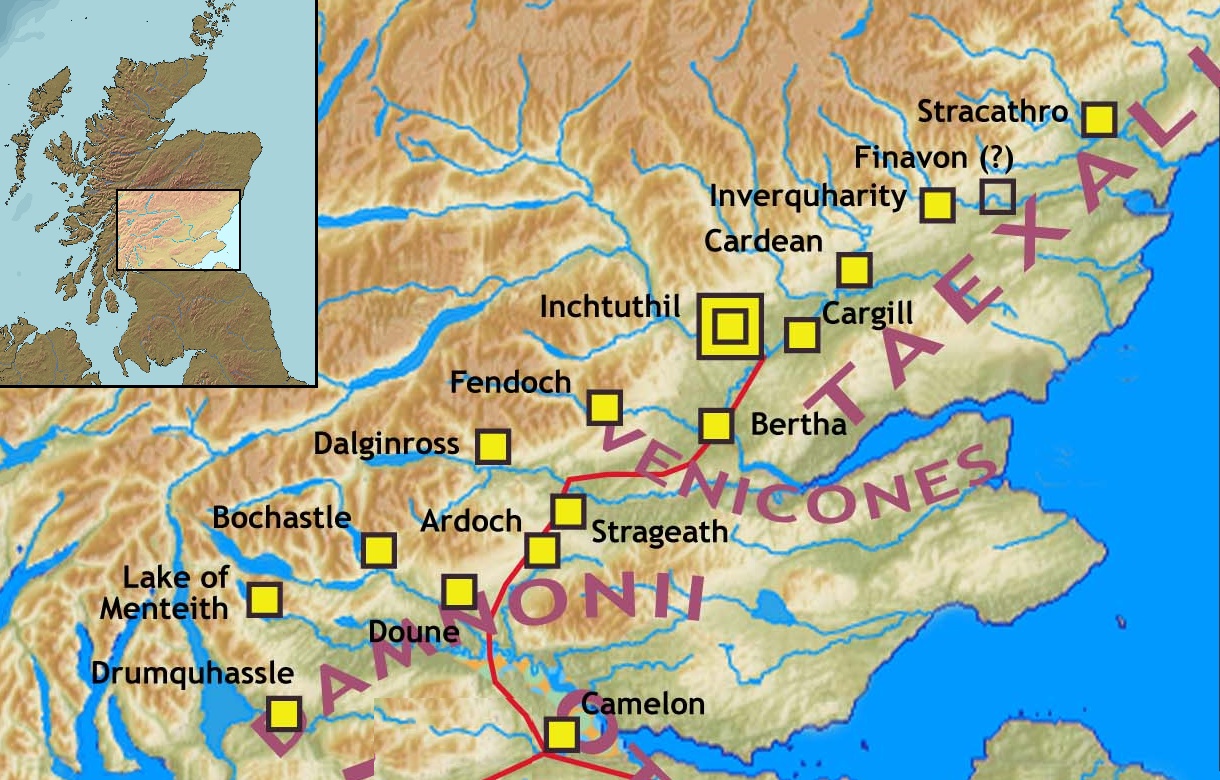
Strageath
Strageath is a Roman camp near the River Earn in eastern Scotland. Strageath was one of a chain of camps that the Romans used in their march northward. Other notable camps in this chain are Ardoch, Battledykes, Stracathro, Raedykes and Normandykes. In the Middle Ages the parish church of ''Strogeath'' lay within the area of the fort. The dedication was to St. Patrick ST, St, or St. may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Stanza, in poetry * Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band * Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise * Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy an .... The site is marked by a graveyard, and some scant remains of the church building. Footnotes Roman fortified camps in Scotland Scheduled monuments in Scotland Roman auxiliary forts in Scotland {{AncientRome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gask Ridge
The Gask Ridge is the modern name given to an early series of fortifications, built by the Romans in Scotland, close to the Highland Line. Modern excavation and interpretation has been pioneered by the Roman Gask Project, with Birgitta Hoffmann and David Woolliscroft. The ridge fortifications: forts, fortlets and watchtowers were only in operation for a few years, probably less than ten. Name The name "Gask Ridge" refers to the ridge of land to the north of the River Earn in Perthshire. In Scottish Gaelic, a ''gasg'' is a projecting tail or strip of land. In the early 20th century, a line of Roman signal-towers (or watch-towers) was discovered along this ridge between the Roman forts of Strageath and Bertha. History The Gask Ridge system was constructed sometime between 70 and 80 AD. Construction on Hadrian's Wall was started 42 years after completion of the Gask Ridge (from 122 to 130 AD), and the Antonine Wall was started 12 years after completion of Hadrian's Wall (fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennymuir Roman Camps
The Pennymuir Roman camps are situated southeast of Jedburgh in the Scottish Borders area of Scotland, near the Anglo-Scottish border, in the former Roxburghshire. The site, alongside the course of the Roman road known as Dere Street, consists of the remains of four Roman temporary camps, a linear earthwork and an area of rig. The site is also sometimes referred to as the Towford camps. Overview The camps at Pennymuir lie on rough moorland in the Cheviot Hills beside Dere Street, a short distance north of Tow Ford where the Roman road crossed the Kale Water.Pennymuir Towford; Dere Street , accessed 8 May 2014 Camps A and B are considered amongst the best preserved Roman camps in Scotla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deers Den
Deers Den is an archaeological site at Kintore, Scotland in Aberdeenshire. The site has mesolithic remains, Iron Age artefacts and is a known Roman Camp. History The area includes evidence of settlement dating back to the Bronze Age, with at least seven roundhouses, likely to date from the Iron Age, up to the time of the Roman Empire. Subsequently, the area would have been used as a Roman marching camp, and has associations with the Severan invasion, ca 200 CE.Aberdeenshire Council: Recent Archaeological Work at Deers Den The marching camp would have been large enough for 10,000 troops to rest. Excavations in the area have found 44 bread ovens and 20 separate buildings over the area. The excavation of 44 bread ovens is the largest number of Roman bread ovens found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balnageith
Balnageith, located on the western edge of the suburbs of Forres in Moray, Scotland, is the site of an excavated linear cropmark with a rounded corner that has been interpreted as a possible Roman military camp or fort. The enclosure may originally have been of up to in size. Blalnageith was the birthplace of Duncan Dunbar (senior) in the 1760s Dunbar moved to London and became a brewer in Limehouse, London London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo .... Administrative Area * Council: Moray * Parish: Forres References Bibliography * * Archaeological sites in Moray {{AncientRome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raedykes
Raedykes is the site of a Roman marching camp located just over northwest of Stonehaven, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. National Grid Reference NO 842902. It is designated as a scheduled monument. A marching camp was a temporary camp used mainly for overnight stops on a long route between more permanent forts, or as a temporary base while on campaign in hostile territory. The site Raedykes probably dates from the late 1st century AD ( Agricolan), though it has been argued that it could be Antonine (2nd century) or Severan (early 3rd century). The camp rampart (vallum) encloses the summit and eastern slopes of Garrison Hill (), a prominent spur overlooking the valley of the Cowie Water, a small river draining into the North Sea on the outskirts of Stonehaven. The camp covered an area of about , and a computer model suggests that this would have been sufficient to house three full legions, or around 16,000 troopsRoger J.A.Wilson "A Guide to the Roman Remains in Britain" 2002 Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |