|
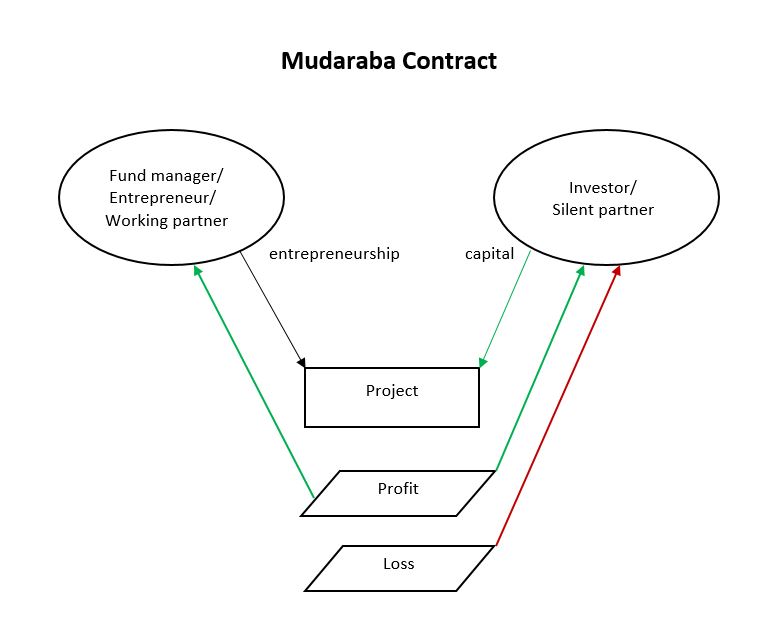
Mudaraba
Profit and Loss Sharing (also called PLS or participatory banking) refers to Sharia-compliant forms of equity financing such as mudarabah and musharakah. These mechanisms comply with the religious prohibition on interest on loans that most Muslims subscribe to. ''Mudarabah'' (مضاربة) refers to "trustee finance" or passive partnership contract, while ''Musharakah'' (مشاركة or مشركة) refers to equity participation contract. Other sources include sukuk (also called "Islamic bonds") and direct equity investment (such as purchase of common shares of stock) as types of PLS. Khan, ''Islamic Banking in Pakistan'', 2015: p.91 The profits and losses shared in PLS are those of a business enterprise or person which/who has obtained capital from the Islamic bank/financial institution (the terms "debt", "borrow", "loan" and "lender" are not used). As financing is repaid, the provider of capital collects some agreed upon percentage of the profits (or deducts if there are losses) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musharaka2
Profit and Loss Sharing (also called PLS or participatory banking) refers to Sharia-compliant forms of equity financing such as mudarabah and musharakah. These mechanisms comply with the religious prohibition on interest on loans that most Muslims subscribe to. ''Mudarabah'' (مضاربة) refers to "trustee finance" or passive partnership contract, while ''Musharakah'' (مشاركة or مشركة) refers to equity participation contract. Other sources include sukuk (also called "Islamic bonds") and direct equity investment (such as purchase of common shares of stock) as types of PLS. Khan, ''Islamic Banking in Pakistan'', 2015: p.91 The profits and losses shared in PLS are those of a business enterprise or person which/who has obtained capital from the Islamic bank/financial institution (the terms "debt", "borrow", "loan" and "lender" are not used). As financing is repaid, the provider of capital collects some agreed upon percentage of the profits (or deducts if there are losses) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudaraba
Profit and Loss Sharing (also called PLS or participatory banking) refers to Sharia-compliant forms of equity financing such as mudarabah and musharakah. These mechanisms comply with the religious prohibition on interest on loans that most Muslims subscribe to. ''Mudarabah'' (مضاربة) refers to "trustee finance" or passive partnership contract, while ''Musharakah'' (مشاركة or مشركة) refers to equity participation contract. Other sources include sukuk (also called "Islamic bonds") and direct equity investment (such as purchase of common shares of stock) as types of PLS. Khan, ''Islamic Banking in Pakistan'', 2015: p.91 The profits and losses shared in PLS are those of a business enterprise or person which/who has obtained capital from the Islamic bank/financial institution (the terms "debt", "borrow", "loan" and "lender" are not used). As financing is repaid, the provider of capital collects some agreed upon percentage of the profits (or deducts if there are losses) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Banking
Islamic banking, Islamic finance ( ar, مصرفية إسلامية), or Sharia-compliant finance is banking or financing activity that complies with Sharia (Islamic law) and its practical application through the development of Islamic economics. Some of the modes of Islamic banking/finance include ''Mudarabah'' (profit-sharing and loss-bearing), ''Wadiah'' (safekeeping), ''Musharaka'' (joint venture), ''Murabahah'' (cost-plus), and ''Ijara'' ( leasing). Sharia prohibits ''riba'', or usury, defined as interest paid on all loans of money (although some Muslims dispute whether there is a consensus that interest is equivalent to ''riba''). Investment in businesses that provide goods or services considered contrary to Islamic principles (e.g. pork or alcohol) is also ''haram'' ("sinful and prohibited"). These prohibitions have been applied historically in varying degrees in Muslim countries/communities to prevent un-Islamic practices. In the late 20th century, as part of the revi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Finance
Islamic banking, Islamic finance ( ar, مصرفية إسلامية), or Sharia-compliant finance is banking or financing activity that complies with Sharia (Islamic law) and its practical application through the development of Islamic economics. Some of the modes of Islamic banking/finance include ''Mudarabah'' (profit-sharing and loss-bearing), ''Wadiah'' (safekeeping), ''Musharaka'' (joint venture), ''Murabahah'' (cost-plus), and ''Ijara'' (leasing). Sharia prohibits ''riba'', or usury, defined as interest paid on all loans of money (although some Muslims dispute whether there is a consensus that interest is equivalent to ''riba''). Investment in businesses that provide goods or services considered contrary to Islamic principles (e.g. pork or alcohol) is also ''haram'' ("sinful and prohibited"). These prohibitions have been applied historically in varying degrees in Muslim countries/communities to prevent un-Islamic practices. In the late 20th century, as part of the revival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murabaha
''Murabaḥah'', ''murabaḥa'', or ''murâbaḥah'' ( ar, مرابحة, derived from ''ribh'' ar, ربح, meaning profit) was originally a term of ''fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence) for a sales contract where the buyer and seller agree on the markup (profit) or "cost-plus" price for the item(s) being sold. In recent decades it has become a term for a very common form of Islamic (i.e., "shariah compliant") financing, where the price is marked up in exchange for allowing the buyer to pay over time—for example with monthly payments (a contract with deferred payment being known as ''bai-muajjal''). ''Murabaha'' financing is similar to a rent-to-own arrangement in the non-Muslim world, with the intermediary (e.g., the lending bank) retaining ownership of the item being sold until the loan is paid in full. There are also Islamic investment funds and ''sukuk'' (Islamic bonds) that use ''murabahah'' contracts. Jamaldeen, ''Islamic Finance For Dummies'', 2012:188-9, 220-1 The purpose o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umer Chapra
Muhammad Umer Chapra (born 1 February 1933) is a Pakistani-Saudi economist. he serves as Advisor at the Islamic Research and Training Institute (IRTI) of the Islamic Development Bank (IDB) in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Prior to this position, he worked at the Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency (SAMA), Riyadh, for nearly 35 years, as Economic Advisor and then Senior Economic Advisor. Personal life Chapra was born in Bombay, British India on 1 February 1933 to Abdul Karim Chapra, and grew up in Karachi, Pakistan. He completed undergraduate studies from the University of Sindh in 1950, followed by undergraduate and postgraduate degrees in commerce at the University of Karachi in 1954 and 1956 respectively. He then moved to the United States, where he pursued a PhD in economics and sociology from the University of Minnesota in 1961, and worked as an academic for six years. In 1965, at a time when there was high demand for skilled Pakistani migrants, he moved to Saudi Arabia after being offere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional-reserve Banking
Fractional-reserve banking is the system of banking operating in almost all countries worldwide, under which banks that take deposits from the public are required to hold a proportion of their deposit liabilities in liquid assets as a reserve, and are at liberty to lend the remainder to borrowers. Bank reserves are held as cash in the bank or as balances in the bank's account at the central bank. The country's central bank determines the minimum amount that banks must hold in liquid assets, called the "reserve requirement" or "reserve ratio". Most commercial banks hold more than this minimum amount as excess reserves. Bank deposits are usually of a relatively short-term duration, and may be "at call", while loans made by banks tend to be longer-term, resulting in a risk that customers may at any time collectively wish to withdraw cash out of their accounts in excess of the bank reserves. The reserves only provide liquidity to cover withdrawals within the normal pattern. Banks a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taqi Usmani
Muhammad Taqi Usmani (born 5 October 1943) is a Pakistani Islamic scholar and former judge who is the current president of the Wifaq ul Madaris Al-Arabia and the vice president and Hadith professor of the Darul Uloom Karachi. An intellectual leader of the Deobandi movement, he has authored 143 books in Urdu, Arabic and English, including a translation of the Qur'an in both English and Urdu as well a 6-volume commentary on the ''Sahih Muslim'' in Arabic, ''Takmilat Fath al-Mulhim'' and ''Uloomu-l-Quran''. He has written and lectured extensively on hadith, and Islamic finance. He chairs the Shariah Board of the Bahrain-based Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI). He is also a permanent member of the Jeddah-based International Islamic Fiqh Academy, an organ of the OIC. In Pakistan, Usmani served as a scholar judge on the Shariat Appellate Bench of the Supreme Court from 1982 to 2002, and on the Federal Shariat Court from 1981 to 1982. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khadija Bint Khuwaylid
Khadijah bint Khuwaylid ( ar, خَدِيجَة بِنْت خُوَيْلِد, Khadīja bint Khuwaylid, 555 – November 619 CE) was the first wife and is considered to be the first follower of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Khadija was the daughter of Khuwaylid ibn Asad, a leader of the Quraysh tribe in Makkah and a successful businesswoman. Khadija is often referred to by Muslims as "The Mother of Believers". In Islam, she is an important female figure as one of the four 'ladies of heaven', alongside Asiya, Maryam, and her daughter Fatimah.Encyclopaedia of the Quran. Leidan: Brill, 2001. Print. Muhammad ibn Abdullah was monogamously married to her for 25 years. Before marrying Muhammad Family Khadija's mother, Fatima bint Za'idah, who died in 575, was a member of the Amir ibn Luayy clan of the Quraysh and a third cousin of Muhammad's mother. Khadija's father, Khuwaylid ibn Asad, was a merchant and leader. According to some accounts, he died in the Sacrilegious War, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Of Profit
In economics and finance, the profit rate is the relative profitability of an investment project, a capitalist enterprise or a whole capitalist economy. It is similar to the concept of rate of return on investment. Historical cost ''vs.'' market value The rate of profit depends on the definition of ''capital invested''. Two measurements of the value of capital exist: capital at historical cost and capital at market value. Historical cost is the original cost of an asset at the time of purchase or payment. Market value is the re-sale value, replacement value, or value in present or alternative use. To compute the rate of profit, replacement cost of capital assets must be used to define the capital cost. Assets such as machinery cannot be replaced at their historical cost but must be purchased at the current market value. When inflation occurs, historical cost would not take account of rising prices of equipment. The rate of profit would be overestimated using lower historical co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libor
The London Inter-Bank Offered Rate is an interest-rate average calculated from estimates submitted by the leading banks in London. Each bank estimates what it would be charged were it to borrow from other banks. The resulting average rate is usually abbreviated to Libor () or LIBOR, or more officially to ICE LIBOR (for Intercontinental Exchange LIBOR). It was formerly known as BBA Libor (for British Bankers' Association Libor or the trademark bba libor) before the responsibility for the administration was transferred to Intercontinental Exchange. It is the primary benchmark, along with the Euribor, for short-term interest rates around the world. Libor was phased out at the end of 2021, and market participants are being encouraged to transition to risk-free interest rates. As of late 2022, parts of it have been discontinued, and the rest is scheduled to end within 2023; the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) is its replacement. Libor rates are calculated for five currenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imputed Rent
Imputed rent is the rental price an individual would pay for an asset they own. The concept applies to any capital good, but it is most commonly used in housing markets to measure the rent homeowners would pay for a housing unit equivalent to the one they own. Imputing housing rent is necessary to measure economic activity in national accounts. Because asset owners do not pay rent, owners' imputed rent must be measured indirectly. Imputed housing rent is the economic theory of imputation applied to real estate: that the value is more a matter of what the buyer is willing to pay than the cost the seller incurs to create it. In this case, market rents are used to estimate the value to the property owner. Thus, imputed rent offers a way to compare homeowners' and tenants' economic decisions. More formally, in owner-occupancy, the landlord–tenant relationship is short-circuited. Consider a model: two people, A and B, each of whom owns property. If A lives in B's property, and B li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
