|
Mucous Neck Cell
Foveolar cells or surface mucous cells are mucus-producing cell (biology), cells which cover the inside of the stomach, protecting it from the corrosive nature of gastric acid. These cells line the gastric mucosa (mucous neck cells are found in the necks of the gastric pits). The mucus-secreting cells of the stomach can be distinguished histologically from the intestinal goblet cells, another type of mucus-secreting cell. Structure The gastric mucosa that lines the inner wall of the stomach has a set of microscopic features called gastric glands which, depending on the location within the stomach, secrete different substances into the lumen (anatomy), lumen of the organ. The openings of these glands into the stomach are called gastric pits which foveolar cells line in order to provide a protective alkaline secretion against the corrosive gastric acid. Microanatomy Foveolar cells line the surface of the stomach, the gastric pits, and the top part of fundic glands, gastric glands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food ( chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microvillus
Microvilli (singular: microvillus) are microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that increase the surface area for diffusion and minimize any increase in volume, and are involved in a wide variety of functions, including absorption, secretion, cellular adhesion, and mechanotransduction. Structure Microvilli are covered in plasma membrane, which encloses cytoplasm and microfilaments. Though these are cellular extensions, there are little or no cellular organelles present in the microvilli. Each microvillus has a dense bundle of cross-linked actin filaments, which serves as its structural core. 20 to 30 tightly bundled actin filaments are cross-linked by bundling proteins fimbrin (or plastin-1), villin and espin to form the core of the microvilli. In the enterocyte microvillus, the structural core is attached to the plasma membrane along its length by lateral arms made of myosin 1a and Ca2+ binding protein calmodulin. Myosin 1a functions through a binding site for filamentous ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Cell Types Derived From The Germ Layers
This is a list of cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Cells derived from ectoderm Surface ectoderm Skin * Trichocyte * Keratinocyte Anterior pituitary * Gonadotrope * Corticotrope * Thyrotrope * Somatotrope * Lactotroph Tooth enamel * Ameloblast Neural crest Peripheral nervous system * Neuron * Glia ** Schwann cell ** Satellite glial cell Neuroendocrine system * Chromaffin cell * Glomus cell Skin * Melanocyte ** Nevus cell * Merkel cell Teeth * Odontoblast * Cementoblast Eyes * Corneal keratocyte Neural tube Central nervous system * Neuron * Glia ** Astrocyte ** Ependymocytes ** Muller glia (retina) ** Oligodendrocyte ** Oligodendrocyte progenitor cell ** Pituicyte (posterior pituitary) Pineal gland * Pinealocyte Cells derived from mesoderm Paraxial mesoderm Mesenchymal stem cell =Osteochondroprogenitor cell= * Bone ( Osteoblast → Osteocyte) * Cartilage (Chondroblast → Chondrocyte) =Myofibroblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site. It is one of three principal endopeptidases (enzymes cutting proteins in the middle) in the human digestive system, the other two being chymotrypsin and trypsin. There are also exopeptidases which remove individual amino acids at both ends of proteins (carboxypeptidases produced by the pancreas and aminopeptidases secreted by the small intestine). During the process of digestion, these enzymes, each of which is specialized in severing links between particular types of amino acids, collaborate to break down dietary proteins into their components, i.e., peptides and amino acids, which can be readily absorbed by the sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Chief Cell
A gastric chief cell (or peptic cell, or gastric zymogenic cell) is a type of gastric gland cell that releases pepsinogen and gastric lipase. It is the cell responsible for secretion of chymosin in ruminant animals. The cell stains basophilic upon H&E staining due to the large proportion of rough endoplasmic reticulum in its cytoplasm. Gastric chief cells are generally located deep in the mucosal layer of the stomach lining, in the fundus and body of the stomach.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stomachnormalhistology.html Chief cells release the zymogen (enzyme precursor) pepsinogen when stimulated by a variety of factors including cholinergic activity from the vagus nerve and acidic condition in the stomach. Gastrin and secretin may also act as secretagogues. It works in conjunction with the parietal cell, which releases gastric acid, converting the pepsinogen into pepsin. Nomenclature The terms ''chief cell'' and ''zymogenic cell'' are often used without the word "gastric" to n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Cells
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the stomach. They contain an extensive secretory network of canaliculi from which the HCl is secreted by active transport into the stomach. The enzyme hydrogen potassium ATPase (H+/K+ ATPase) is unique to the parietal cells and transports the H+ against a concentration gradient of about 3 million to 1, which is the steepest ion gradient formed in the human body. Parietal cells are primarily regulated via histamine, acetylcholine and gastrin signalling from both central and local modulators. Structure Canaliculus A canaliculus is an adaptation found on gastric parietal cells. It is a deep infolding, or little channel, which serves to increase the surface area, e.g. for secretion. The parietal cell membrane is dynamic; the numbers of canalic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach Mucosal Layer Labeled
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
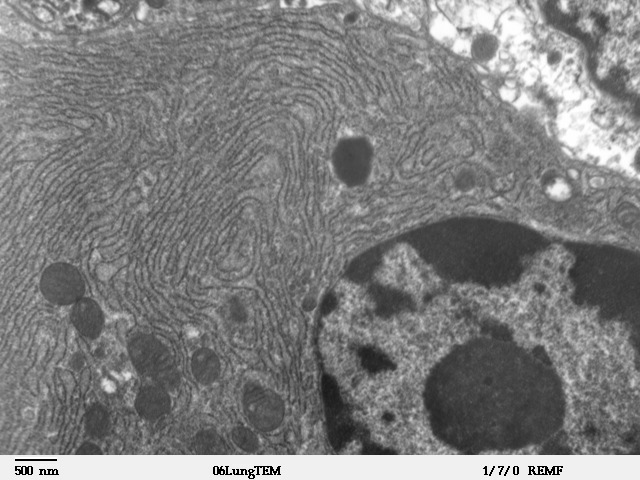
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi and was named after him in 1898. Discovery Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolonium Chloride
Toluidine blue, also known as TBO or tolonium chloride (INN) is a blue cationic (basic) dye used in histology (as the toluidine blue stain) and sometimes clinically. Test for lignin Toluidine blue solution is used in testing for lignin, a complex organic molecule that bonds to cellulose fibres and strengthens and hardens the cell walls in plants. A positive toluidine blue test causes the solution to turn from blue to pink. A similar test can be performed with phloroglucinol-HCl solution, which turns red. Histological uses Toluidine blue is a basic thiazine metachromatic dye with high affinity for acidic tissue components. It stains nucleic acids blue and polysaccharides purple and also increases the sharpness of histology slide images. It is especially useful today for staining chromosomes in plant or animal tissues, as a replacement for Aceto-orcein stain. Toluidine blue is often used to identify mast cells, by virtue of the heparin in their cytoplasmic granules. It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |