|
Mucor Racemosus
''Mucor racemosus'' is a rapidly growing, weedy mould belonging to the division Mucoromycota. It is one of the earliest fungi to be grown in pure culture and was first isolated in 1886. It has a worldwide distribution and colonizes many habitats such as vegetational products, soil and houses. The fungus is mostly known for its ability to exhibit both filamentous and yeast-like morphologies, often referred to as dimorphism. Stark differences are seen in both forms and conditions of the environment heavily affect the phases of the ''M. racemosus''. Like many fungi, it also reproduces both sexually and asexually. The dimorphic capacity of this species has been proposed as an important factor in its pathogenicity and has enhanced the industrial importance. This species is considered an opportunistic pathogen, generally limited to immunocompromised individuals. It also been associated with allergy and inflammations of facial sinuses. Its association with allergy has made it a common fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucor Racemosus
''Mucor racemosus'' is a rapidly growing, weedy mould belonging to the division Mucoromycota. It is one of the earliest fungi to be grown in pure culture and was first isolated in 1886. It has a worldwide distribution and colonizes many habitats such as vegetational products, soil and houses. The fungus is mostly known for its ability to exhibit both filamentous and yeast-like morphologies, often referred to as dimorphism. Stark differences are seen in both forms and conditions of the environment heavily affect the phases of the ''M. racemosus''. Like many fungi, it also reproduces both sexually and asexually. The dimorphic capacity of this species has been proposed as an important factor in its pathogenicity and has enhanced the industrial importance. This species is considered an opportunistic pathogen, generally limited to immunocompromised individuals. It also been associated with allergy and inflammations of facial sinuses. Its association with allergy has made it a common fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ras Subfamily
Ras, from "Rat sarcoma virus", is a family of related proteins that are expressed in all animal cell lineages and organs. All Ras protein family members belong to a class of protein called small GTPase, and are involved in transmitting signals within cells (cellular signal transduction). Ras is the prototypical member of the Ras superfamily of proteins, which are all related in three-dimensional structure and regulate diverse cell behaviours. When Ras is 'switched on' by incoming signals, it subsequently switches on other proteins, which ultimately turn on genes involved in cell growth, differentiation, and survival. Mutations in Ras genes can lead to the production of permanently activated Ras proteins, which can cause unintended and overactive signaling inside the cell, even in the absence of incoming signals. Because these signals result in cell growth and division, overactive Ras signaling can ultimately lead to cancer. The three Ras genes in humans (''HRAS'', ''KRAS'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
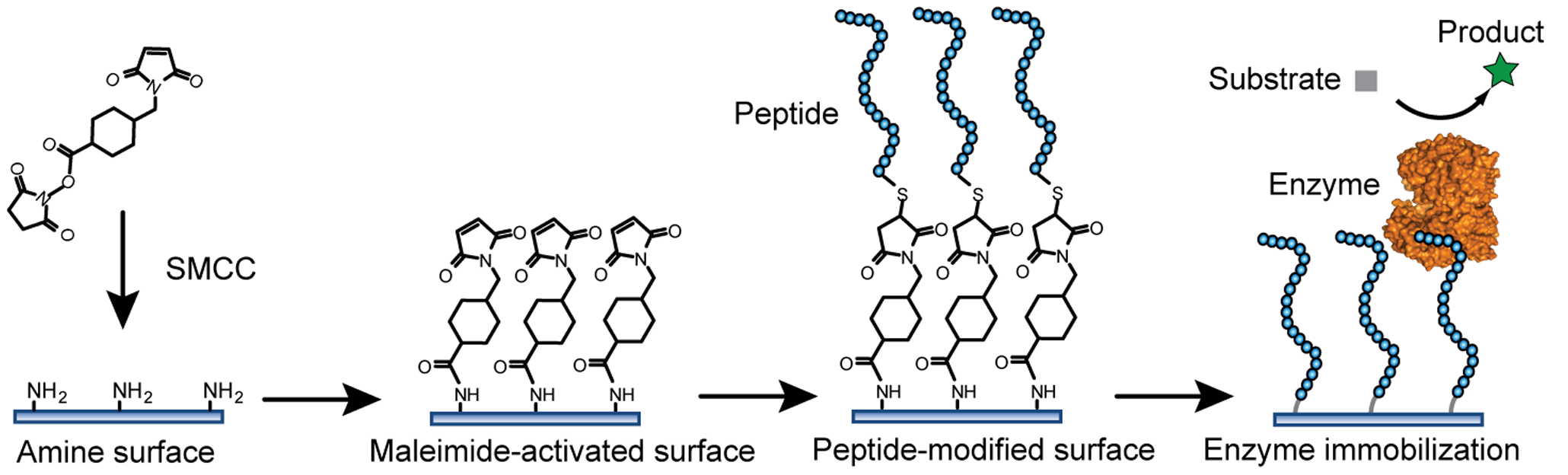
Industrial Enzyme
Industrial enzymes are enzymes that are commercially used in a variety of industries such as Pharmaceutical drug, pharmaceuticals, chemical production, biofuels, food processing, food & beverage, and consumer products. Due to advancements in recent years, biocatalysis through isolated enzymes is considered more economical than use of whole cells. Enzymes may be used as a unit operation within a process to generate a desired product, or may be the product of interest. Industrial biological catalysis through enzymes has experienced rapid growth in recent years due to their ability to operate at mild conditions, and exceptional Chirality, chiral and positional specificity, things that traditional chemical processes lack. Isolated enzymes are typically used in Hydrolysis, hydrolytic and isomerization reactions. Whole cells are typically used when a reaction requires a Cofactor (biochemistry), co-factor. Although co-factors may be generated in vitro, it is typically more cost-effective to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytase
A phytase (''myo''-inositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolase) is any type of phosphatase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phytic acid (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate) – an indigestible, organic form of phosphorus that is found in many plant tissues, especially in grains and oil seeds – and releases a usable form of inorganic phosphorus. While phytases have been found to occur in animals, plants, fungi and bacteria, phytases have been most commonly detected and characterized from fungi. History The first plant phytase was found in 1907 from rice bran and in 1908 from an animal (calf's liver and blood). In 1962 began the first attempt at commercializing phytases for animal feed nutrition enhancing purposes when International Minerals & Chemicals (IMC) studied over 2000 microorganisms to find the most suitable ones for phytase production. This project was launched in part due to concerns about mineable sources for inorganic phosphorus eventually running out (see peak ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atopic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
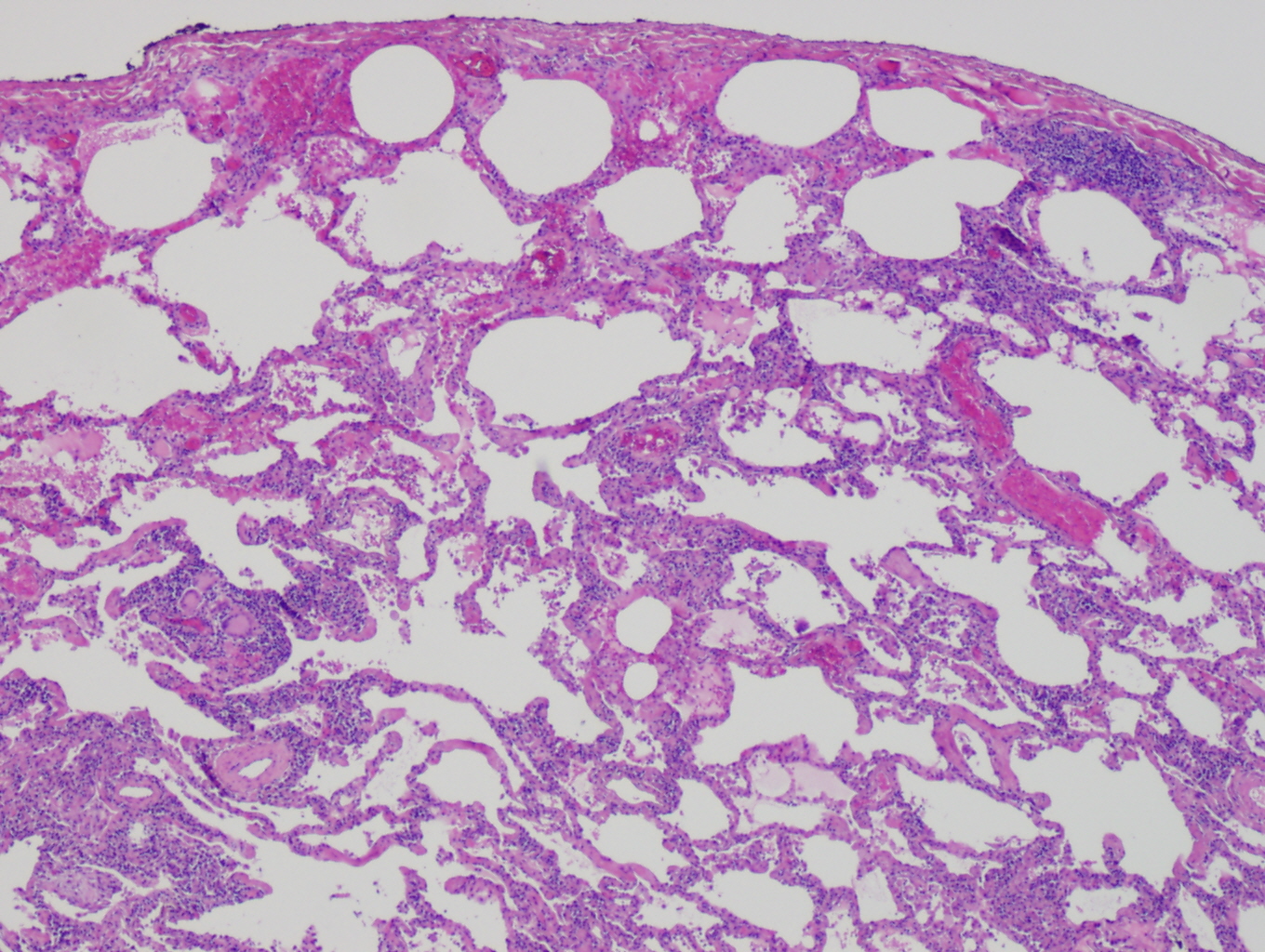
Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease. Signs and symptoms Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) can be categorized as acute, subacute, and chronic based on the duration of the illness. Acute In the acute form of HP dose of antigen exposure tends to be very high but only for a short duration. Symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinitis
Rhinitis, also known as coryza, is irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. Common symptoms are a stuffy nose, runny nose, sneezing, and post-nasal drip. The inflammation is caused by viruses, bacteria, irritants or allergens. The most common kind of rhinitis is allergic rhinitis, which is usually triggered by airborne allergens such as pollen and dander. Allergic rhinitis may cause additional symptoms, such as sneezing and nasal itching, coughing, headache, fatigue, malaise, and cognitive impairment. The allergens may also affect the eyes, causing watery, reddened, or itchy eyes and puffiness around the eyes. The inflammation results in the generation of large amounts of mucus, commonly producing a runny nose, as well as a stuffy nose and post-nasal drip. In the case of allergic rhinitis, the inflammation is caused by the degranulation of mast cells in the nose. When mast cells degranulate, they release histamine and other chemicals, starting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the nasal mucosa, mucous membranes that line the paranasal sinuses, sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick Mucus#Respiratory system, nasal mucus, a nasal congestion, plugged nose, and Orofacial pain, facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, headaches, a hyposmia, poor sense of smell, sore throat, a feeling that phlegm is oozing out from the back of the nose to the throat along with a necessity to clear the throat frequently and frequent attacks of cough. Generally sinusitis starts off as a common viral infection like common cold. This infection generally subsides within 5 to 7 days. During this time the nasal structures can swell and facilitate the stagnation of fluids in sinuses that leads to acute (medicine), acute sinusitis which lasts from 6th day of the infection to 15th day. From the 15th day to 45th day of the infection comes the subacute stage followed by chronic (medicine), chronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
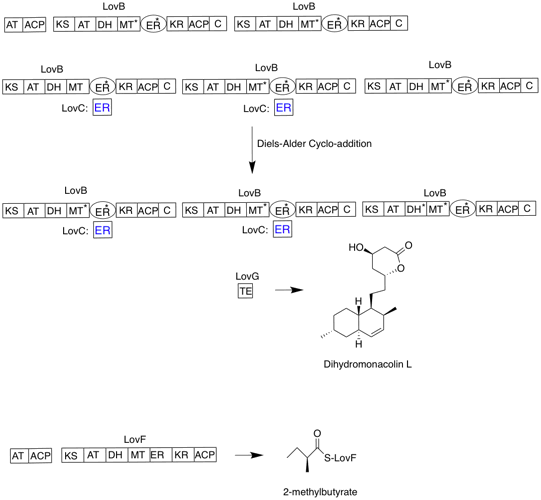
Lovastatin
Lovastatin, sold under the brand name Mevacor among others, is a statin medication, to treat hypercholesterolemia, high blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its use is recommended together with lifestyle changes. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include diarrhea, constipation, headache, muscles pains, rash, and trouble sleeping. Serious side effects may include liver problems, rhabdomyolysis, muscle breakdown, and kidney failure. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby and use during breastfeeding is not recommended. It works by decreasing the liver's ability to produce cholesterol by blocking the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Lovastatin was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1987. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 99th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 7mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |