|
Mt. Kongtong
Kongtong Mountains () is one of the sacred mountains of Taoism. It is located in Pingliang City, Gansu Province, People's Republic of China. It is the mythical meeting site between the Yellow Emperor The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Soverei ... (also known as ''Huangdi'' or by his given name 'Xuan Yuan') and Guangchengzi. See also * Kongtong Sect Landforms of Gansu Mountains of Gansu Parks in Gansu {{Gansu-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Mountains Of Taoism
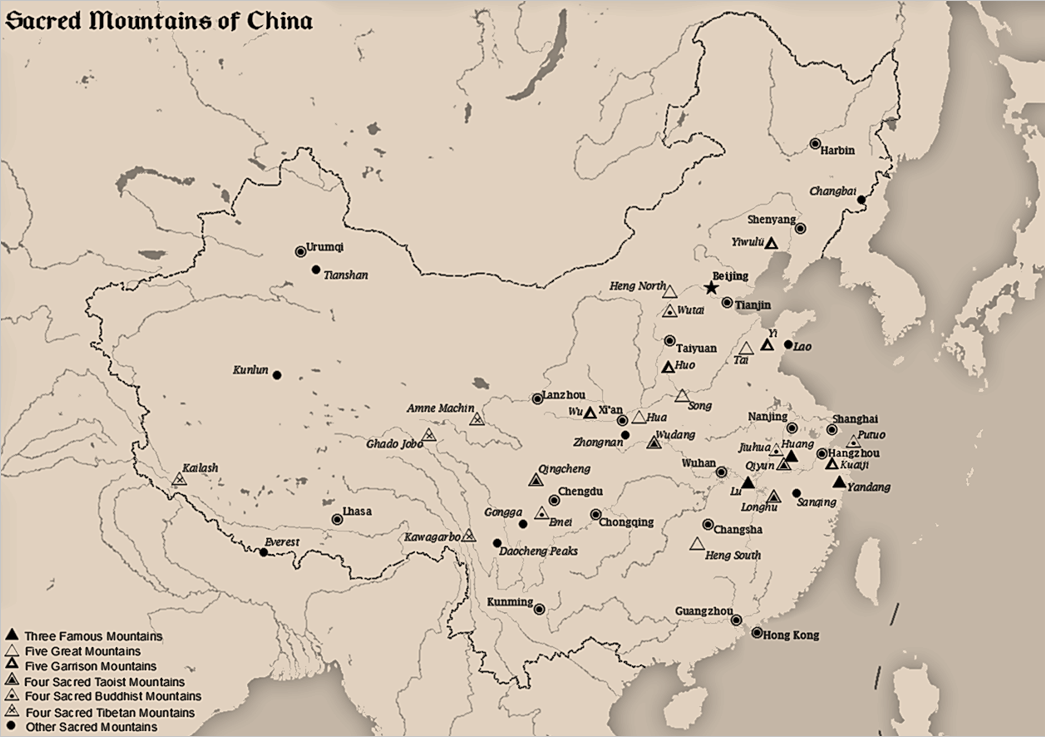
The Sacred Mountains of China are divided into several groups. The ''Five Great Mountains'' () refers to five of the most renowned mountains in Chinese history, and they were the subjects of imperial pilgrimage by emperors throughout ages. They are associated with the supreme God of Heaven and the five main cosmic deities of Chinese traditional religion. The group associated with Buddhism is referred to as the ''Four Sacred Mountains of Buddhism'' (), and the group associated with Taoism is referred to as the ''Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism'' (). The sacred mountains have all been important destinations for pilgrimage, the Chinese expression for pilgrimage () being a shortened version of an expression which means ''"paying respect to a holy mountain"'' (). The Five Great Mountains The ''Five Great Mountains'' or ''Wuyue'' are arranged according to the five cardinal directions of Chinese geomancy, which includes the center as a direction. The grouping of the five mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pingliang City
Pingliang () is a prefecture-level city in eastern Gansu province, China, bordering Shaanxi province to the south and east and the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region to the north. The city was established in 376 AD. It has a residential population of 2,125,300 in 2019. The urban population is almost 900,000. Pingliang is well known for the nearby Kongtong Mountains, which are sacred to Taoism and location of the mythical meeting place of the Yellow Emperor and Guangchengzi, an immortal. List of divisions Geography Pingliang ranges in latitude from 34° 54' to 35° 46' N and in longitude from 105° 20' to 107° 51' E. Bordering prefecture-level cities are Xianyang (Shaanxi) to the east, Baoji (Shaanxi) and Tianshui to the south, Dingxi and Baiyin to the west, and Guyuan (Ningxia) and Qingyang to the north. It is located on the Loess Plateau with elevations ranging from ; the city proper itself is at an elevation of around . Due to its elevation of around , Pingliang has a monsoon-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gansu Province
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan and Loess plateaus and borders Mongolia (Govi-Altai Province), Inner Mongolia and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south and Shaanxi to the east. The Yellow River passes through the southern part of the province. Part of Gansu's territory is located in the Gobi Desert. The Qilian mountains are located in the south of the Province. Gansu has a population of 26 million, ranking 22nd in China. Its population is mostly Han, along with Hui, Dongxiang and Tibetan minorities. The most common language is Mandarin. Gansu is among the poorest administrative divisions in China, ranking 31st, last place, in GDP per capita as of 2019. The State of Qin originated in what is now southeastern Gansu and we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors and cosmological Five Regions' Highest Deities (). Calculated by Jesuit missionaries on the basis of Chinese chronicles and later accepted by the twentieth-century promoters of a universal calendar starting with the Yellow Emperor, Huangdi's traditional reign dates are 2697–2597 or 2698–2598 BC. Huangdi's cult became prominent in the late Warring States and early Han dynasty, when he was portrayed as the originator of the centralized state, as a cosmic ruler, and as a patron of esoteric arts. A large number of texts – such as the ''Huangdi Neijing'', a medical classic, and the '' Huangdi Sijing'', a group of political treatises – were thus attributed to him. Having waned in influence during most of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangchengzi
Guang Chengzi ({{zh, s=广成子, t=廣成子, p=Guǎngchéngzǐ, w=Kuang ch'eng-tzu) (Literarily "Person Who Knows All" ) is a Taoist deity and a character in the classic Chinese novel ''Fengshen Yanyi''. Taoist mythology From the idea of Taoism, Guang Chengzi was the avatar of Taishang Laojun (also named Daode Tianzun) during the period of Yellow Emperor in ancient Chinese history. According to Zhuangzi's recording, he lived in Kongtong Mountains, the Yellow Emperor visited him there for his teaching. He gave the Yellow Emperor several books that talked about the moral, natural, and philosophical issues, which helped the Yellow Emperor create the early Chinese civilization. It is said that Guang Chengzi had a long life of 1200 years. There is another saying that Guang Chengzi was the avatar of the Dao, who appeared in the human world three times – the first time as Guang Chengzi during the Yellow Emperor time; second as Laozi during the Spring and Autumn period; and third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Rui-Xuan Yuan Inquires Of The Dao
Shi or SHI may refer to: Language * ''Shi'', a Japanese title commonly used as a pronoun * ''Shi'', proposed gender-neutral pronoun * Shi (kana), a kana in Japanese syllabaries * Shi language * ''Shī'', transliteration of Chinese Radical 44 * Tachelhit or the Shilha language (ISO 639 code) Art * Shi, a piece in Chinese chess * ''Shi'' (comics), a comic book series created by William Tucci * Shi (poetry), the Chinese conception of poetry * ''Poetry'' (film) or ''Shi'', a 2010 South Korean film directed by Lee Chang-dong People * Shi (class) (), the low aristocratic class of Shang/Zhou China, later the scholar-gentry class of imperial China * Shi (rank) (), rank group for non-commissioned officers * Shi (personator) (), a ceremonial "corpse" involved in early forms of ancestor worship in China Names * ''Shì'' (氏), a Chinese clan name previously distinguished from ancestral or family names; see Origin of Chinese surnames * Shī (surname), the romanization of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kongtong Sect
The Kongtong School is a martial arts school mentioned in several works of ''wuxia'' fiction. It is commonly featured as a leading orthodox school in the '' wulin'' (martial artists' community). It is named after the place where it is based, the Kongtong Mountains. History According to legend, the school was founded by a shepherd boy. The boy met an immortal in the Kongtong Mountains, who taught him extraordinary martial arts. The boy was Mulingzi, the founder of the Kongtong School. Mulingzi attained a remarkable level of prowess in martial arts and led Kongtong towards its rise to prominence in the '' wulin'' as one of the major orthodox schools alongside Shaolin, Wudang and others. Mulingzi is known for his most powerful skill, the 'Seven Harms Fist', Cha, Louis. ''The Heaven Sword and Dragon Saber'' (倚天屠龍記). ''Ming Pao'', 1961. and his chivalry. Mulingzi hated villainy so he often roamed the ''jianghu'' in his younger days as a ''youxia'' to help the poor and punis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Gansu
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Gansu
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)
