|
Mrp Superfamily
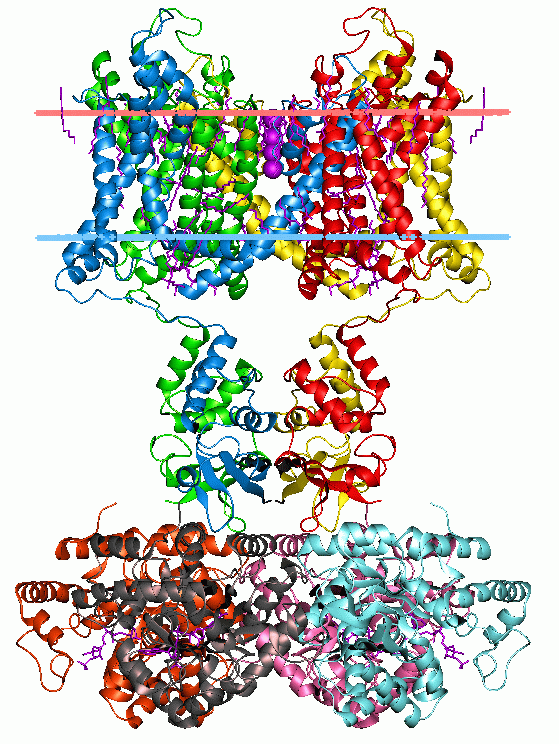
The Na+ Transporting Mrp Superfamily is a superfamily of integral membrane transport proteins. It includes the TC families:2.A.63- The Monovalent Cation (K+ or Na+):Proton Antiporter-3 (CPA3) Family3.D.1- The H+ or Na+-translocating NADH Dehyrogenase (NDH) Family3.D.9- The H+-translocating F420H2 Dehydrogenase (F420H2DH) Family Mrp of ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a 7 subunit Na+/H+ antiporter An antiporter (also called exchanger or counter-transporter) is a cotransporter and integral membrane protein involved in secondary active transport of two or more different molecules or ions across a phospholipid membrane such as the plasma memb ... comple(TC# 2.A.63.1.4) All subunits are homologous to the subunits in other members of this monovalent cation (K+ or Na+):proton antiporter-3 (CPA3) family as well as subunits in the archaeal hydrogenasesTC#s 3.D.1.4.1an3.D.1.4.2, which share several subunits with NADH dehydrogenase subunits (3.D.1). The largest subunits of the Mrp complex (MrpA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Superfamily
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred (see homology (biology), homology). Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarity is evident. Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent (due to low sequence similarity). Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within each family. The term ''protein clan'' is commonly used for protease and glycosyl hydrolases superfamilies based on the MEROPS and CAZy classification systems. Identification Superfamilies of proteins are identified using a number of methods. Closely related members can be identified by different methods to those needed to group the most evolutionarily divergent members. Sequence similarity Historically, the similarity of different amino acid sequences has been the most common method of inferring Sequence homology, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Transport Protein
A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Transport proteins are integral transmembrane proteins; that is they exist permanently within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion or active transport. The two main types of proteins involved in such transport are broadly categorized as either ''channels'' or ''carriers''. The solute carriers and atypical SLCs are secondary active or facilitative transporters in humans. Collectively membrane transporters and channels are known as the transportome. Transportomes govern cellular influx and efflux of not only ions and nutrients but drugs as well. Difference between channels and carriers A carrier is not open simultaneously to both the extracellular and intracellular environments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Antiporter-3
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek for "first", and this name was given to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquinone Reductase (H+-translocating)
Ubiquinone reductase may refer to: * NADH dehydrogenase NADH dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) from its reduced form (NADH) to its oxidized form (NAD+). Members of the NADH dehydrogenase family and analogues are commonly systematically named using the for ..., an enzyme * NADH:ubiquinone reductase (non-electrogenic), an enzyme {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F420H2DH Family
The H+-translocating F420H2 Dehydrogenase (F420H2DH) Family''(TC# 3.D.9)is a member of the Na+ transporting Mrp superfamily. A single F420H2 dehydrogenase (also referred to as F420H2:quinol oxidoreductase) from the methanogenic archaeon, ''Methanosarcina mazei'' Gö1, has been shown to be a redox driven proton pump. The F420H2DH of ''M. mazei'' has a molecular size of about 120 kDa and contains Fe-S clusters and FAD. A similar five-subunit enzyme has been isolated from '' Methanolobus tindarius''. The sulfate-reducing ''Archaeoglobus fulgidus'' (and several other archaea) also have this enzyme. Function Reduction of 2-hydroxyphenazine by F420H2DH is accompanied by the translocation of 1 H+ per 2 electrons transferred. Transport Reaction The overall vectorial reaction catalyzed by F420H2DH is : Reduced donor (2e−) + H+ (in) ⇌ oxidized acceptor (2e−) + H+ (out) Role in Methanogenesis ''Methanomassiliicoccus luminyensis'' has been isolated from the human gut and requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'', known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, and renamed ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiporter
An antiporter (also called exchanger or counter-transporter) is a cotransporter and integral membrane protein involved in secondary active transport of two or more different molecules or ions across a phospholipid membrane such as the plasma membrane in opposite directions, one into the cell and one out of the cell. Na+/H+ antiporters have been reviewed. In secondary active transport, one species of solute moves along its electrochemical gradient, allowing a different species to move against its own electrochemical gradient. This movement is in contrast to primary active transport, in which all solutes are moved against their concentration gradients, fueled by ATP. Transport may involve one or more of each type of solute. For example, the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, found in the plasma membrane of many cells, moves three sodium ions in one direction, and one calcium ion in the other. Role in Homeostatic Mechanisms Na+/H+ Antiporters Antiporters, such as Na+/H+ antiporter protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Superfamilies
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred (see homology). Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarity is evident. Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent (due to low sequence similarity). Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within each family. The term ''protein clan'' is commonly used for protease and glycosyl hydrolases superfamilies based on the MEROPS and CAZy classification systems. Identification Superfamilies of proteins are identified using a number of methods. Closely related members can be identified by different methods to those needed to group the most evolutionarily divergent members. Sequence similarity Historically, the similarity of different amino acid sequences has been the most common method of inferring homology. Sequence similarity is consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment. Function Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Proteins
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not pass t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Transporters
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not pass t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |