|
Mrk 421
Markarian 421 (Mrk 421, Mkn 421) is a blazar located in the constellation Ursa Major. The object is an active galaxy and a BL Lacertae object, and is a strong source of gamma rays. It is about 397 million light-year A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...s (redshift: z=0.0308 eq. 122M pc) to 434 million light-years (133Mpc) from the Earth. It is one of the closest blazars to Earth, making it one of the brightest quasars in the night sky. It is suspected to have a supermassive black hole (SMBH) at its center due to its active nature. An early-type high inclination spiral galaxy (Markarian 421-5) is located 14 arc-seconds northeast of Markarian 421. It was first determined to be a very high energy gamma ray emitter in 1992 by M. Punch at the Whipple Observatory, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDSS Mrk 421 , a school in Delta, British Columbia, Canada
{{disambiguation ...
SDSS may refer to: * Sloan Digital Sky Survey, a major multi-filter imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey * Social Democratic Party of Slovakia * Spatial Decision Support System, a GIS based decision aiding system * Independent Democratic Serb Party, a political party of Croatian Serbs (''Samostalna demokratska srpska stranka'' in Serbo-Croatian) * South Delta Secondary School South Delta Secondary (SDSS) is a public high school in Tsawwassen, British Columbia, Canada. There are approximately 1,500 students enrolled in each grade 8 through 12 (as of 2019/2020). Graduation rates in the years 2005 to 2010 vary between 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BL Lacertae Object
A BL Lacertae object or BL Lac object is a type of active galactic nucleus (AGN) or a galaxy with such an AGN, named after its prototype, BL Lacertae. In contrast to other types of active galactic nuclei, BL Lacs are characterized by rapid and large-amplitude flux variability and significant optical polarization. Because of these properties, the prototype of the class ( BL Lac) was originally thought to be a variable star. When compared to the more luminous active nuclei (quasars) with strong emission lines, BL Lac objects have spectra dominated by a relatively featureless non-thermal emission continuum over the entire electromagnetic range. This lack of spectral lines historically hindered identification of the nature and distance of such objects. In the unified scheme of radio-loud active galactic nuclei, the observed nuclear phenomenology of BL Lacs is interpreted as being due to the effects of the relativistic jet closely aligned to the line of sight of the observer. BL Lacs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markarian Galaxies
The Markarian galaxies are a class of galaxies that have nuclei with excessive amounts of ultraviolet emissions compared with other galaxies. Benjamin Markarian drew attention to these types of galaxies starting in 1963. The nuclei of the galaxies had a blue colour, associated to stars in the classes from O to A. This blue core did not match the rest of the galaxy. The spectrum in detail tends to show a continuum that Markarian concluded was produced non- thermally. Most of these have emission lines and are characterized by highly energetic activity. Markarian Catalogue entries are of the form "Markarian ####", and can frequently use the abbreviations Mrk, Mkr, Mkn; and rarely Ma, Mk, Mark. History In 1964 Markarian decided to search for this kind of galaxy. The First Byurakan Survey commenced in 1965 using the Schmidt telescope at the Byurakan Astrophysical Observatory in Armenian SSR. The telescope used a 132 cm mirror and 102 cm correcting plate. When this st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoveries By Benjamin Markarian
Discoveries may refer to: Music * ''Discoveries'' (Cannonball Adderley album), 1955 * ''Discoveries'' (Josh Nelson album), 2011 * ''Discoveries'' (Northlane album), 2011 Other uses * ''Discoveries'' (film), a 1939 British film * Discoveries (horse), a racehorse * ''Discoveries'' (Robertson Davies), a 2002 book by Robertson Davies * ''Discoveries'' (TV series), a Canadian youth science television series which aired on CBC Television in 1957 * ''Abrams Discoveries'', a series of illustrated non-fiction books published by Harry N. Abrams * ''Discoveries'', a work by William Butler Yeats, written in 1907 * ''Discoveries'', a magazine published by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center See also * Age of Discoveries * Discovery (other) Discovery may refer to: * Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown * Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown * Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence Discovery, The Discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blazars
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the jet makes blazars appear much brighter than they would be if the jet were pointed in a direction away from Earth. Blazars are powerful sources of emission across the electromagnetic spectrum and are observed to be sources of high-energy gamma ray photons. Blazars are highly variable sources, often undergoing rapid and dramatic fluctuations in brightness on short timescales (hours to days). Some blazar jets exhibit apparent superluminal motion, another consequence of material in the jet traveling toward the observer at nearly the speed of light. The blazar category includes BL Lac objects and optically violently variable (OVV) quasars. The generally accepted theory is that BL Lac objects are intrinsically low-power radio galaxies while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Major (constellation)
Ursa Major (; also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, drawing on earlier works by Greek, Egyptian, Babylonian, and Assyrian astronomers. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Major is primarily known from the asterism of its main seven stars, which has been called the "Big Dipper," "the Wagon," "Charles's Wain," or "the Plough," among other names. In particular, the Big Dipper's stellar configuration mimics the shape of the "Little Dipper." Two of its stars, named Dubhe and Merak ( α Ursae Majoris and β Ursae Majoris), can be used as the navigational pointer towards the place of the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BL Lacertae Objects
A BL Lacertae object or BL Lac object is a type of active galactic nucleus (AGN) or a galaxy with such an AGN, named after its prototype, BL Lacertae. In contrast to other types of active galactic nuclei, BL Lacs are characterized by rapid and large-amplitude flux variability and significant optical polarization. Because of these properties, the prototype of the class ( BL Lac) was originally thought to be a variable star. When compared to the more luminous active nuclei ( quasars) with strong emission lines, BL Lac objects have spectra dominated by a relatively featureless non-thermal emission continuum over the entire electromagnetic range. This lack of spectral lines historically hindered identification of the nature and distance of such objects. In the unified scheme of radio-loud active galactic nuclei, the observed nuclear phenomenology of BL Lacs is interpreted as being due to the effects of the relativistic jet closely aligned to the line of sight of the observer. BL Lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Earth Blazar Telescope
The Whole Earth Blazar Telescope (WEBT) is an international consortium of astronomers created in 1997, with the aim to study a particular category of Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) called blazars, which are characterized by strong and fast brightness variability, on time scales down to hours or less. This collaboration involves many telescopes observing at optical, near-infrared, and radio (millimetric and centimetric) wavelengths. Thanks to their different geographic location all around the world, the emission variations of the pointed source can be monitored 24 hours a day, with the observing task moving from east to west as the Earth rotates. WEBT observations are often carried out in conjunction with observations at higher frequencies, from ultraviolet to gamma rays, performed by both space and ground-based telescopes. In this way, information on blazar emission over almost the whole electromagnetic spectrum can be obtained. The multi-wavelength studies performed by the WEBT hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very-high-energy Gamma Ray
Very-high-energy gamma ray (VHEGR) denotes gamma radiation with photon energies of 100 GeV (gigaelectronvolt) to 100 TeV (teraelectronvolt), i.e., 1011 to 1014 electronvolts. This is approximately equal to wavelengths between 10−17 and 10−20 meters, or frequencies of 2 × 1025 to 2 × 1028 Hz. Such energy levels have been detected from emissions from astronomical sources such as some binary star systems containing a compact object. For example, radiation emitted from Cygnus X-3 has been measured at ranges from GeV to exaelectronvolt-levels. Other astronomical sources include BL Lacertae, 3C 66A Markarian 421 and Markarian 501. Various other sources exist that are not associated with known bodies. For example, the H.E.S.S. catalog contained 64 sources in November 2011. Detection Instruments to detect this radiation commonly measure the Cherenkov radiation produced by secondary particles generated from an energetic photon entering the Earth's atmosphere. This method is calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
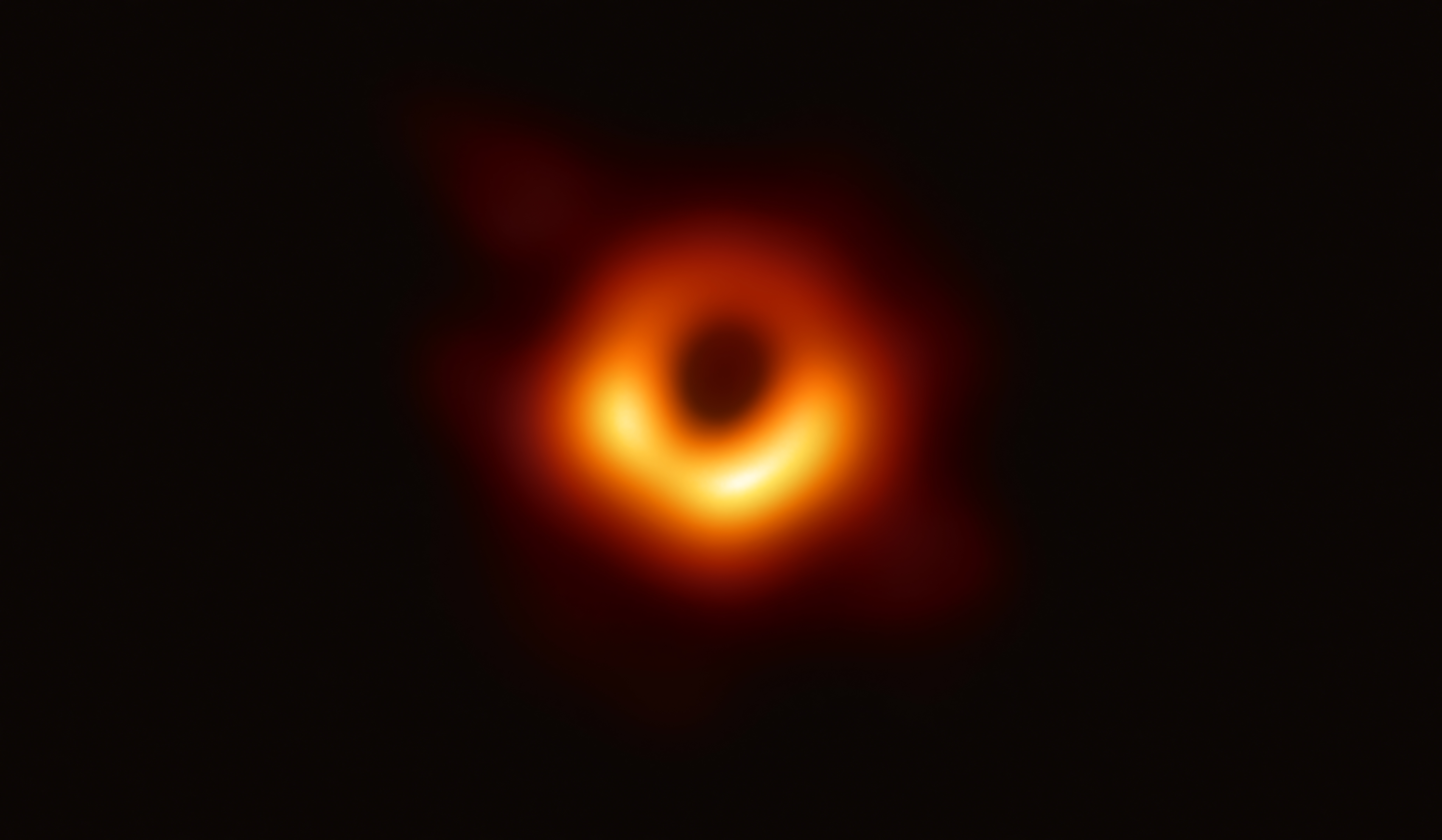
Supermassive Black Hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical objects that have undergone gravitational collapse, leaving behind spheroidal regions of space from which nothing can escape, not even light. Observational evidence indicates that almost every large galaxy has a supermassive black hole at its Central massive object, center. For example, the Milky Way has a Galactic Center#Supermassive black hole, supermassive black hole in its Galactic Center, corresponding to the Astronomical radio source, radio source Sagittarius A*. Accretion (astrophysics), Accretion of Interstellar medium, interstellar gas onto supermassive black holes is the process responsible for powering Active galactic nucleus, active galactic nuclei (AGNs) and quasars. Two supermassive black holes have been directly imaged by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon. Natural light sources in a night sky include moonlight, starlight, and airglow, depending on location and timing. Aurorae light up the skies above the polar circles. Occasionally, a large coronal mass ejection from the Sun or simply high levels of solar wind may extend the phenomenon toward the Equator. The night sky and studies of it have a historical place in both ancient and modern cultures. In the past, for instance, farmers have used the status of the night sky as a calendar to determine when to plant crops. Many cultures have drawn constellations between stars in the sky, using them in association with legends and mythology about their deities. The anciently developed belief of astrology is generally based on the belief that relationships between heavenly bodies infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasars
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is pronounced , and sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. This emission from a galaxy nucleus is powered by a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses, surrounded by a gaseous accretion disc. Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up because of friction and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiant energy of quasars is enormous; the most powerful quasars have luminosities thousands of times greater than that of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Usually, quasars are categorized as a subclass of the more general category of AGN. The redshifts of quasars are of cosmological origin. The term originated as a contraction of "quasi-stellar '' tar-like' radio source"—because quasars were first identified during the 1950s as sources of radio-wave emission of unknown physical origin—and when identifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |