|
Moving Load
In structural dynamics, a moving load changes the point at which the load is applied over time. Examples include a vehicle that travels across a bridge and a train moving along a track. Properties In computational models, load is usually applied as * a simple massless force, * an oscillator, or * an inertial force (mass and a massless force). Numerous historical reviews of the moving load problem exist. Several publications deal with similar problems. The fundamental monograph is devoted to massless loads. Inertial load in numerical models is described in Unexpected property of differential equations that govern the motion of the mass particle travelling on the string, Timoshenko beam, and Mindlin plate is described in. It is the discontinuity of the mass trajectory near the end of the span (well visible in string at the speed ''v''=0.5''c''). The moving load significantly increases displacements. The critical velocity, at which the growth of displacements is the maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Dynamics
Structural dynamics is a type of structural analysis which covers the behavior of a structure subjected to dynamic (actions having high acceleration) loading. Dynamic loads include people, wind, waves, traffic, earthquakes, and blasts. Any structure can be subjected to dynamic loading. Dynamic analysis can be used to find dynamic displacements, time history, and modal analysis. Structural analysis is mainly concerned with finding out the behavior of a physical structure when subjected to force. This action can be in the form of load due to the weight of things such as people, furniture, wind, snow, etc. or some other kind of excitation such as an earthquake, shaking of the ground due to a blast nearby, etc. In essence all these loads are dynamic, including the self-weight of the structure because at some point in time these loads were not there. The distinction is made between the dynamic and the static analysis on the basis of whether the applied action has enough acceleration in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timoshenko Beam Theory
Tymoshenko ( uk, Тимошенко, translit=Tymošenko), Timoshenko (russian: Тимошенко), or Tsimashenka/Cimašenka ( be, Цімашэнка) is a surname of Ukrainian origin. It derives from the Christian name Timothy, and its Ukrainian derivatives, Tymofiy or Tymish. The surname, Tymoshenko, was created by adding the Ukrainian patronymic suffix, ''-enko'', meaning someone ''of Tymish'', usually the ''son of Tymish''. Notable people Tymoshenko * Eugenia Tymoshenko (born 1980), Ukrainian businesswoman, daughter of Yulia * Illya Tymoshenko (born 1999), Ukrainian footballer * Kyrylo Tymoshenko (born 1989), Ukrainian statesman * Maksym Tymoshenko (born 1972), Ukrainian culturologist and social activist * Oleksandr Tymoshenko (born 1960), Ukrainian businessman, husband of Yulia * Olexandra Tymoshenko (born 1972), Soviet-Ukrainian rhythmic gymnast * Yulia Tymoshenko (born 1960), former Prime Minister of Ukraine Timoshenko * Daria Timoshenko (born 1980), Russian-Azerbaij ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindlin–Reissner Plate Theory
The Uflyand-Mindlin theory of vibrating plates is an extension of Kirchhoff–Love plate theory that takes into account shear deformations through-the-thickness of a plate. The theory was proposed in 1948 by Yakov Solomonovich UflyandUflyand, Ya. S.,1948, Wave Propagation by Transverse Vibrations of Beams and Plates, PMM: Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, Vol. 12, 287-300 (in Russian) (1916-1991) and in 1951 by Raymond Mindlin with Mindlin making reference to Uflyand's work. Hence, this theory has to be referred to as Uflyand-Mindlin plate theory, as is done in the handbook by Elishakoff, and in papers by Andronov, Elishakoff, Hache and Challamel, Loktev, Rossikhin and Shitikova and Wojnar. In 1994, Elishakoff suggested to neglect the fourth-order time derivative in Uflyand-Mindlin equations. A similar, but not identical, theory in static setting, had been proposed earlier by Eric Reissner in 1945. Both theories are intended for thick plates in which the normal to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Element Method
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. The FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two or three space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). To solve a problem, the FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts that are called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numerical domain for the solution, which has a finite number of points. The finite element method formulation of a boundary value problem finally results in a system of algebraic equations. The method approximates the unknown function over the domain. The sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space-time Finite Element Method
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur. Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of spacetime as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates: * The laws of physics are invariant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
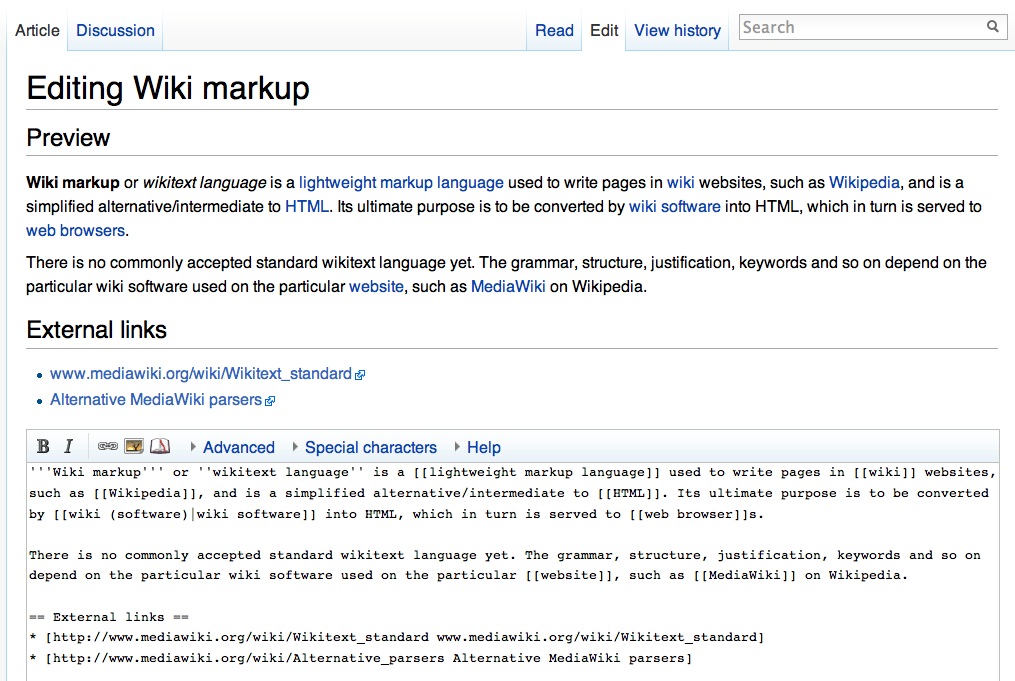
Wiki01f50
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiki05f50
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiki01m50
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication Collaborative editing, collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web application, web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a Online rich-text editor, rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |