|
Moving Horizon Estimation
Moving horizon estimation (MHE) is an optimization approach that uses a series of measurements observed over time, containing noise (random variations) and other inaccuracies, and produces estimates of unknown variables or parameters. Unlike deterministic approaches, MHE requires an iterative approach that relies on linear programming or nonlinear programming solvers to find a solution. MHE reduces to the Kalman filter under certain simplifying conditions. A critical evaluation of the extended Kalman filter and the MHE found that the MHE improved performance at the cost of increased computational expense. Because of the computational expense, MHE has generally been applied to systems where there are greater computational resources and moderate to slow system dynamics. However, in the literature there are some methods to accelerate this method. Overview The application of MHE is generally to estimate measured or unmeasured states of dynamical systems. Initial conditions and paramet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfields: discrete optimization and continuous optimization. Optimization problems arise in all quantitative disciplines from computer science and engineering to operations research and economics, and the development of solution methods has been of interest in mathematics for centuries. In the more general approach, an optimization problem consists of maxima and minima, maximizing or minimizing a Function of a real variable, real function by systematically choosing Argument of a function, input values from within an allowed set and computing the Value (mathematics), value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations constitutes a large area of applied mathematics. Optimization problems Opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filtering Problem (stochastic Processes)
In the theory of stochastic processes, filtering describes the problem of determining the state of a system from an incomplete and potentially noisy set of observations. For example, in GPS navigation, filtering helps estimate a car’s true position (the state) from noisy satellite signals (the observations). While originally motivated by problems in engineering, filtering found applications in many fields from signal processing to finance. The problem of optimal non-linear filtering (even for the non-stationary case) was solved by Ruslan L. Stratonovich (1959, 1960), see also Harold J. Kushner's work and Moshe Zakai's, who introduced a simplified dynamics for the unnormalized conditional law of the filter known as the Zakai equation. The solution, however, is infinite-dimensional in the general case.Mireille Chaleyat-Maurel and Dominique Michel. Des resultats de non existence de filtre de dimension finie. Stochastics, 13(1+2):83-102, 1984. Certain approximations and special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Filters
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists since most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control Stability theory, stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of Optimal control, optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or Setpoint (control system), set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nob Hill Publishing, LLC
Nob may refer to: People * NoB (born 1964), Japanese singer Nobuo Yamada * Nob Yoshigahara (1936–2004), Japanese puzzle-maker Places * Nob, Israel, a place in the vicinity of Jerusalem * Nob Hill, San Francisco, a neighborhood in the California city Other uses * Nederlandse Onderwatersport Bond, the Dutch Underwater Federation * Newell's Old Boys, Argentine football team * Non-occluded baculovirus, a genus of virus * "One for his nob", a score in cribbage * A person of social standing (cf. nobility/nabob) * Derogatory term for a man's penis, typically used as an insult in the UK and Ireland See also * Knob (other) Knob or KNOB may refer to: Objects * A round handle ** Doorknob ** Control knob, controls a device ** Brodie knob, on a steering wheel * Tow ball or hitch ball * Dorset knob, a biscuit Landforms * A rounded hill or mountain, particularly ... * NOB (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiener Filter
In signal processing, the Wiener filter is a filter used to produce an estimate of a desired or target random process by linear time-invariant ( LTI) filtering of an observed noisy process, assuming known stationary signal and noise spectra, and additive noise. The Wiener filter minimizes the mean square error between the estimated random process and the desired process. Description The goal of the wiener filter is to compute a statistical estimate of an unknown signal using a related signal as an input and filtering it to produce the estimate. For example, the known signal might consist of an unknown signal of interest that has been corrupted by additive noise. The Wiener filter can be used to filter out the noise from the corrupted signal to provide an estimate of the underlying signal of interest. The Wiener filter is based on a statistical approach, and a more statistical account of the theory is given in the minimum mean square error (MMSE) estimator article. Typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sliding Mode Control
In control systems, sliding mode control (SMC) is a nonlinear control method that alters the dynamic system, dynamics of a nonlinear system by applying a discontinuous control signal (or more rigorously, a set-valued control signal) that forces the system to "slide" along a cross-section of the system's normal behavior. The state space (controls), state-feedback control law is not a continuous function of time. Instead, it can switch from one continuous structure to another based on the current position in the state space. Hence, sliding mode control is a variable structure control method. The multiple control structures are designed so that trajectories always move toward an adjacent region with a different control structure, and so the ultimate trajectory will not exist entirely within one control structure. Instead, it will ''slide'' along the boundaries of the control structures. The motion of the system as it slides along these boundaries is called a ''sliding mode'' and the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
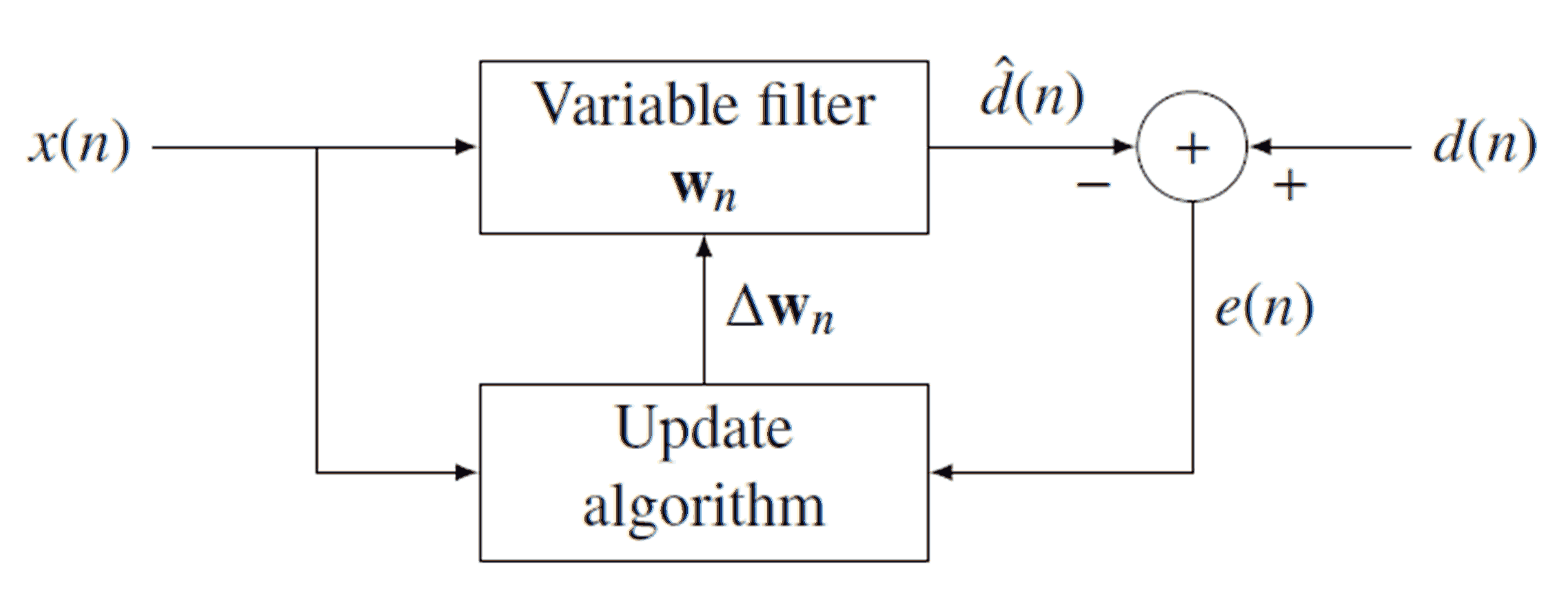
Recursive Least Squares
Recursive least squares (RLS) is an adaptive filter algorithm that recursively finds the coefficients that minimize a Weighted least squares, weighted linear least squares Loss function, cost function relating to the input signals. This approach is in contrast to other algorithms such as the least mean squares (LMS) that aim to reduce the mean square error. In the derivation of the RLS, the input signals are considered deterministic system (mathematics), deterministic, while for the LMS and similar algorithms they are considered stochastic. Compared to most of its competitors, the RLS exhibits extremely fast convergence. However, this benefit comes at the cost of high computational complexity. Motivation RLS was discovered by Carl Friedrich Gauss, Gauss but lay unused or ignored until 1950 when Plackett rediscovered the original work of Gauss from 1821. In general, the RLS can be used to solve any problem that can be solved by adaptive filters. For example, suppose that a signal d( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predictor Corrector
Predictor may refer to: * Branch predictor, a part of many modern processors * Kerrison Predictor, a military fire-control computer * Predictor variable, also known as an independent variable * A type of railway level crossing, circuit that tries to achieve a constant warning time by predicting the speed of the approaching train * Something which makes a prediction A prediction (Latin ''præ-'', "before," and ''dictum'', "something said") or forecast is a statement about a future event or about future data. Predictions are often, but not always, based upon experience or knowledge of forecasters. There ... See also * * * Prediction (other) * Predict (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Filter
Particle filters, also known as sequential Monte Carlo methods, are a set of Monte Carlo algorithms used to find approximate solutions for filtering problems for nonlinear state-space systems, such as signal processing and Bayesian statistical inference. The filtering problem consists of estimating the internal states in dynamical systems when partial observations are made and random perturbations are present in the sensors as well as in the dynamical system. The objective is to compute the posterior distributions of the states of a Markov process, given the noisy and partial observations. The term "particle filters" was first coined in 1996 by Pierre Del Moral about mean-field interacting particle methods used in fluid mechanics since the beginning of the 1960s. The term "Sequential Monte Carlo" was coined by Jun S. Liu and Rong Chen in 1998. Particle filtering uses a set of particles (also called samples) to represent the posterior distribution of a stochastic process giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-linear Filter
In signal processing, a nonlinear filter is a filter whose output is not a linear function of its input. That is, if the filter outputs signals and for two input signals and separately, but does not always output when the input is a linear combination . Both continuous-domain and discrete-domain filters may be nonlinear. A simple example of the former would be an electrical device whose output voltage at any moment is the square of the input voltage ; or which is the input clipped to a fixed range , namely . An important example of the latter is the running-median filter, such that every output sample is the median of the last three input samples . Like linear filters, nonlinear filters may be shift invariant or not. Non-linear filters have many applications, especially in the removal of certain types of noise that are not additive. For example, the median filter is widely used to remove spike noise — that affects only a small percentage of the samples, possibly b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |