|
Mountain View Oil Field
The Mountain View Oil Field is a large, mature, but still-productive oil field in Kern County, California, in the United States, in the extreme southern part of the San Joaquin Valley southeast of Bakersfield. It underlies the town of Arvin, as well as some smaller agricultural communities. The field is spread out across a large area, covering just under , with wells and storage facilities widely dispersed throughout the area, scattered among working agricultural fields of broccoli and carrots as well as citrus orchards. Discovered in 1933, it has produced over of oil in its lifetime, and although declining in production is one of the few inland California fields in which new oil is still being discovered. 239. As of the beginning of 2009, the field had numerous operators, unlike some of the larger, monolithic fields such as the Kern River field to the north, which is entirely owned by Chevron Corporation. Only independent oil companies operate on the Mountain View Field. Of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehachapi Mountains
The Tehachapi Mountains (; Kawaiisu: ''Tihachipia'', meaning "hard climb") are a mountain range in the Transverse Ranges system of California in the Western United States. The range extends for approximately in southern Kern County and northwestern Los Angeles County and form part of the boundary between the San Joaquin Valley and the Mojave Desert. Geography The Tehachapis form a geographic, watershed, habitat, and rain shadow divide separating the San Joaquin Valley to the northwest and the Mojave Desert to the southeast. The Tehachapis' crest varies in height from approximately . They are southeast of Bakersfield and the Central Valley, and west of Mojave and the Antelope Valley. The range runs southwest to northeast (SW-NE) connecting the Southern Sierra Nevada range on their northeast with the San Emigdio Mountains on the west and Sierra Pelona Mountains on the southwest. The Tehachapis are delineated from the San Emigdio Mountains by Tejon Pass at the range's weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Margarita Formation
The Santa Margarita Formation is a Neogene Period geologic formation in the San Joaquin Valley of central California. It preserves fossils dating back to the Miocene epoch. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in California * Paleontology in California Paleontology in California refers to paleontologist research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of California. California contains rocks of almost every age from the Precambrian to the Recent. Precambrian fossils are pres ... Fossils of Los Angeles References External links * * Geologic formations of California Miocene California Phosphorite formations Geography of the San Joaquin Valley Geology of Kern County, California {{California-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell Oil
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New York Stock Exchange. It is one of the oil and gas "supermajors" and by revenue and profits is consistently one of the largest companies in the world. Measured by both its own emissions, and the emissions of all the fossil fuels it sells, Shell was the ninth-largest corporate producer of greenhouse gas emissions in the period 1988–2015. Shell was formed in 1907 through the merger of Royal Dutch Petroleum Company of the Netherlands and The "Shell" Transport and Trading Company of the United Kingdom. The combined company rapidly became the leading competitor of the American Standard Oil and by 1920 Shell was the largest producer of oil in the world. Shell first entered the chemicals industry in 1929. Shell was one of the " Seven Sisters" which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes or plates. This texture (geology), texture reflects a high content of platy minerals, such as micas, talc, chlorite group, chlorite, or graphite. These are often interleaved with more granular minerals, such as feldspar or quartz. Schist typically forms during regional metamorphism accompanying the process of mountain building (orogeny) and usually reflects a medium Metamorphism#Metamorphic grades, grade of metamorphism. Schist can form from many different kinds of rocks, including sedimentary rocks such as mudstones and igneous rocks such as tuffs. Schist metamorphosed from mudstone is particularly common and is often very rich in mica (a ''mica schist''). Where the type of the original rock (the protolith) is discernible, the schist is us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fold (geology)
In structural geology, a fold is a stack of originally planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, that are bent or curved during permanent deformation. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to mountain-sized folds. They occur as single isolated folds or in periodic sets (known as ''fold trains''). Synsedimentary folds are those formed during sedimentary deposition. Folds form under varied conditions of stress, pore pressure, and temperature gradient, as evidenced by their presence in soft sediments, the full spectrum of metamorphic rocks, and even as primary flow structures in some igneous rocks. A set of folds distributed on a regional scale constitutes a fold belt, a common feature of orogenic zones. Folds are commonly formed by shortening of existing layers, but may also be formed as a result of displacement on a non-planar fault (''fault bend fold''), at the tip of a propagating fault (''fault propagation fold''), by differential compaction or due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homocline
In structural geology, a homocline or homoclinal structure (from old el, homo = same, cline = inclination), is a geological structure in which the layers of a sequence of rock strata, either sedimentary or igneous, dip uniformly in a single direction having the same general inclination in terms of direction and angle.Jackson, JA, J Mehl and K Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology.'' American Geological Institute, Alexandria, Virginia. 800 pp. Huggett, JR (2011) ''Fundamentals of Geomorphology,'' 3rd ed., Routledge, New York. 516 pp. A homocline can be associated with either one limb of a fold, the edges of a dome, , slice of thrust fault, or a tilted fault block. When the homoclinal strata consists of alternating layers of rock that vary hardness and resistance to erosion, their erosion produces either cuestas, homoclinal ridges, or hogbacks depending on the angle of dip of the strata.Thornbury, W. D., 1954, ''Principles of Geomorphology'' New York, John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edison Oil Field
The Edison Oil Field is a large oil field in Kern County, California, in the United States, in the southeastern part of the San Joaquin Valley and adjacent foothills east-southeast of Bakersfield. The field has a total productive area of over , most of which is intermingled with agricultural land uses; oil pumps and storage tanks are surrounded with row crops and orchards in much of the field's extent. Discovered in 1928, and with a cumulative production of of oil as of 2008, and having over in reserve, it is ranked 38th among California's oil fields by total ultimate recovery. p. 63. It is a mature field in decline, and is run entirely by small independent operators. As of 2008, there were 40 different oil companies active on the field, one of the most in the state for a single field. 914 wells remained active on the field, averaging only two barrels of oil per well per day from the dwindling reservoirs. Setting The field lies in the flat bottomlands of the lower San Joaquin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
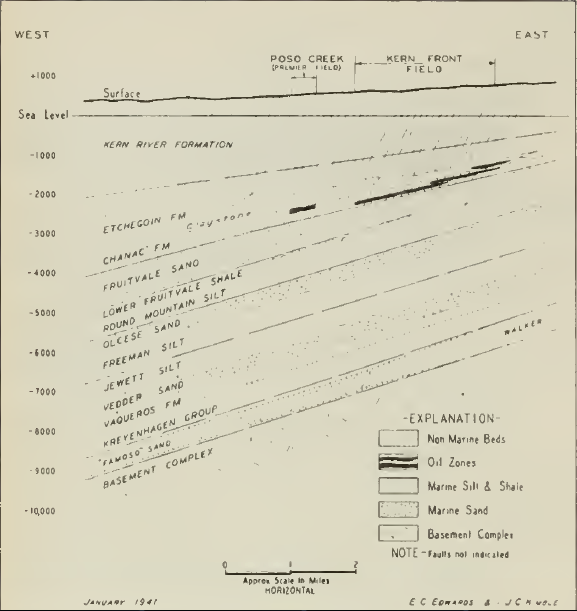
Kern Front Oil Field
The Kern Front Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in the lower Sierra Nevada foothills in Kern County, California. Discovered in 1912, and with a cumulative production of around of oil, it ranks 29th in size in the state, and is believed to retain approximately ten percent of its original oil (approximately ), according to the official estimates of the California Department of Oil, Gas, and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR). It is adjacent to the much larger Kern River Oil Field, which is to the southeast, and the Mount Poso Oil Field to the north. Setting The Kern Front Field is approximately due north of the city of Oildale, and north of Bakersfield, in the first gentle rise of the hills above the floor of the San Joaquin Valley. It is about long by , with the long axis being in the north-south direction, comprising a productive surface area of . Elevations vary from approximately above sea level. The field is spread out, especially compared to the exceedingly dense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odour is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetic. In standard conditions, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic temperatures to a dark blue liquid and finally a violet-black soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |