|
Mount Matutum
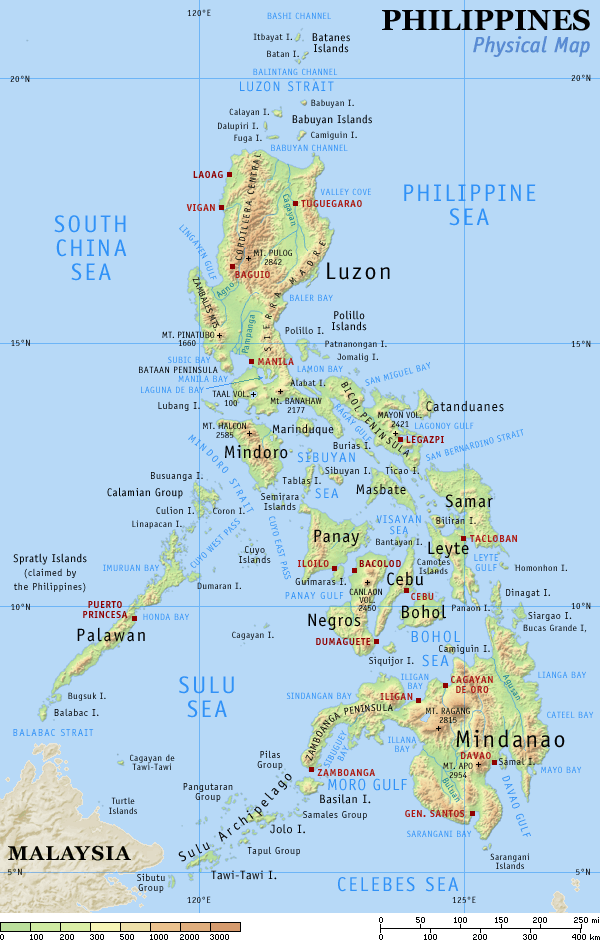
Mount Matutum is an active stratovolcano, is the highest point in the province of South Cotabato in the Philippines, with an elevation of 7,500 feet (2,286 metres) above sea level, approximately from Acmonan, Tupi, South Cotabato. Matutum and its foothills are predominantly inhabited by indigenous Blaan families. Its slopes are forested and host diverse species of plants and animals, including such endangered species as the Philippine eagle and the tarsier. Location Matutum is located in the province of South Cotabato, on the island of Mindanao, in the south of the Philippines, at geographical coordinates 6°22'N, 125°06.5'E. It is north of Polomolok, and about north-northwest of General Santos City. Physical features Matutum is a stratovolcano that rises asl with a base diameter of . It has 2 hot springs, called Acmonan and Linan, west-southwest of the volcano. Adjacent volcanic edifices are Landayao, Tampad, and Albulhek, which are all west of the volcano, and Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Active Volcanoes In The Philippines
This is a list of active volcanoes in the Philippines, as categorized by the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS). Volcanoes in the country have erupted within the last 600 years, with accounts of these eruptions documented by humans; or have erupted within the last 10,000 years (Holocene). As of 2018, PHIVOLCS has listed 24 volcanoes as Volcano#Active, active in the Philippines, 21 of which have had historical eruptions. The three exceptions are Cabalian, which is a strongly Fumarole, fumarolic volcano; Leonard Kniaseff, which was active 1,800 years ago (C14), and Mount Isarog, Isarog, which last erupted around 3500 BCE and 2374 BCE ± 87 based on radiocarbon dating There are 100 volcanoes in the Philippines listed by the Smithsonian Institution's Global Volcanism Program (GVP) at present, of which 20 are categorized as "historical" and 59 as "Holocene". The GVP lists volcanoes with historical, Holocene eruptions, or possibly older if strong signs of vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of The Philippines
In the Philippines, provinces ( fil, lalawigan) are one of its primary political and administrative divisions. There are 82 provinces at present, which are further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The local government units in the National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are independent of any provincial government. Each province is governed by an elected legislature called the Sangguniang Panlalawigan and an elected governor. The provinces are grouped into seventeen regions based on geographical, cultural, and ethnological characteristics. Thirteen of these regions are numerically designated from north to south, while the National Capital Region, the Cordillera Administrative Region, the Southwestern Tagalog Region, and the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao are only designated by acronyms. Each province is a member of the League of Provinces of the Philippines, an organization which aims to address issues affecting provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction Volcanoes
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcanoes Of The Philippines
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Potentially Active Volcanoes In The Philippines
This is a list of potentially active volcanoes in the Philippines, as classified by the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology. List See also * List of active volcanoes in the Philippines * List of inactive volcanoes in the Philippines * List of mountains in the Philippines References Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) Potentially Active Volcano list Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) Active Volcano list Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) Inactive Volcano list External links * {{Volcanoes of the Philippines Volcanoes A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ... Philippines, potentially active *potentially Volcanism of the Philippines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Protected Areas Of The Philippines
This is a list of protected areas of the Philippines administered by the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR)'s Biodiversity Management Bureau under the National Integrated Protected Areas System (NIPAS) Act of 1992. As of 2020, there are 244 protected areas in the Philippines covering a total area of about – 15.4% of the Philippines' total area. History The first important legislation that formed the basis of the current system of national parks and protected areas in the Philippines is Act No. 648, enacted in 1903 by the Philippine Commission. This act authorized the civil governor to "reserve for civil public purposes, and from sale or settlement, any part of the public domain not appropriated by law for special public purposes." A total of eight national reserves had been established on July 26, 1904, pursuant to this law. These are the Lamao Forest Reserve in Bataan, Mariquina Reserve in Rizal, Angat River Reserve in Bulacan, Caliraya Falls Reserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Inactive Volcanoes In The Philippines
This is a list of inactive volcanoes in the Philippines. Volcanoes with no record of eruptions are considered as extinct or inactive. Their physical form since their last activity has been altered by agents of weathering and erosion with the formation of deep and long gullies. Philippines Institute of Volcanology and Seismology. Retrieved on November 5, 2013. Inactive does not necessarily indicate the volcano will not erupt again. had no recorded historical eruption before its cataclysmic 1991 eruption [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ring Of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur. The Ring of Fire is a Horseshoe, horseshoe-shaped belt about long and up to about wide. The Ring of Fire includes the Pacific coasts of South America, North America and Kamchatka, and some islands in the western Pacific Ocean. Although there is consensus among geologists about almost all areas which are included in the Ring of Fire, they disagree about the inclusion or exclusion of a few areas, for example, the Antarctic Peninsula and western Indonesia. The Ring of Fire is a direct result of plate tectonics: specifically the movement, collision and destruction of lithosphere, lithospheric plates (e.g. the Pacific Plate) under and around the Pacific Ocean. The collisions have created a nearly continuous series of subdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phreatic Eruption
A phreatic eruption, also called a phreatic explosion, ultravulcanian eruption or steam-blast eruption, occurs when magma heats ground water or surface water. The extreme temperature of the magma (anywhere from ) causes near-instantaneous evaporation of water to steam, resulting in an explosion of steam, water, ash, rock, and volcanic bombs. At Mount St. Helens in Washington state, hundreds of steam explosions preceded the 1980 Plinian eruption of the volcano. A less intense geothermal event may result in a mud volcano. Phreatic eruptions typically include steam and rock fragments; the inclusion of liquid lava is unusual. The temperature of the fragments can range from cold to incandescent. If molten magma is included, volcanologists classify the event as a phreatomagmatic eruption. These eruptions occasionally create broad, low-relief craters called '' maars''. Phreatic explosions can be accompanied by carbon dioxide or hydrogen sulfide gas-emissions. Carbon dioxide c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanologists
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word ''vulcan''. Vulcan was the ancient Roman god of fire. A volcanologist is a geologist who studies the eruptive activity and formation of volcanoes and their current and historic eruptions. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, especially active ones, to observe volcanic eruptions, collect eruptive products including tephra (such as ash or pumice), rock and lava samples. One major focus of enquiry is the prediction of eruptions; there is currently no accurate way to do this, but predicting eruptions, like predicting earthquakes, could save many lives. Modern volcanology image:Icelandic tephra.JPG, Volcanologist examining tephra horizons in south-central Iceland. In 1841, the first volcanological observatory, the Vesuvius Observatory, was founded in the Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circulation through faults to hot rock deep in the Earth's crust. In either case, the ultimate source of the heat is radioactive decay of naturally occurring radioactive elements in the Earth's mantle, the layer beneath the crust. Hot spring water often contains large amounts of dissolved minerals. The chemistry of hot springs ranges from acid sulfate springs with a pH as low as 0.8, to alkaline chloride springs saturated with silica, to bicarbonate springs saturated with carbon dioxide and carbonate minerals. Some springs also contain abundant dissolved iron. The minerals brought to the surface in hot springs often feed communities of extremophiles, microorganisms adapted to extreme conditions, and it is possible that life on Earth had its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Above Mean Sea Level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''. The combination of unit of measurement and the physical quantity (height) is called "metres above mean sea level" in the metric system, while in United States customary and imperial units it would be called "feet above mean sea level". Mean sea levels are affected by climate change and other factors and change over time. For this and other reasons, recorded measurements of elevation above sea level at a reference time in history might differ from the actual elevation of a given location over sea level at a given moment. Uses Metres above sea level is the standard measurement of the elevation or altitude of: * Geographic locations such as towns, mountains and other landmarks. * The top of buildings and other structures. * Flying objects such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)