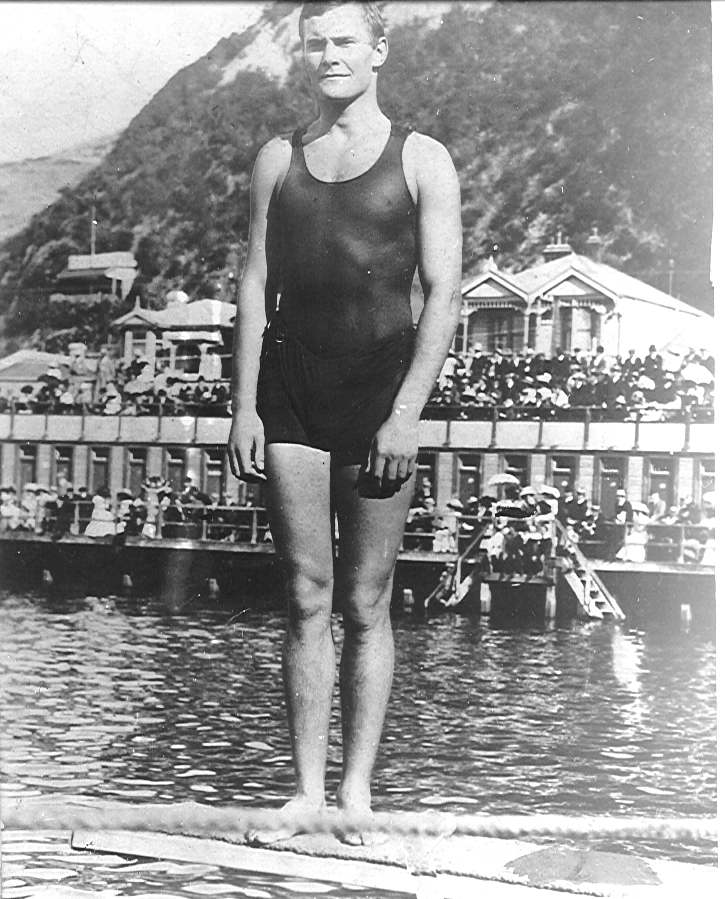|
Mount Massell
The Gallipoli Heights () are a group of peaks and ridges centered south-southeast of Monte Cassino, in the Freyberg Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica. They were named in association with Lord Freyberg and the nearby Freyberg Mountains by the Northern Party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1963–64. Location The Gallipoli Heights are in the south of the Freyberg Mountains, to the south of Monte Cassino, the Moawhango Névé and the Alamein Range. The Salamander Range is to the northeast, Evans Névé is to the southeast and south, and the Rennick Glacier is to the west. There are various isolated peaks and nunataks rising from the ice around the Gallipoli Heights. Features Saddle Hill . A small saddle-shaped table rising from the east end of the northern ridge of the Gallipoli Heights. The name is descriptive of the appearance of the hill when viewed from the north. Named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-AP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freyberg Mountains
The Freyberg Mountains () are a group of mountains in Victoria Land, Antarctica, bounded by Rennick Glacier, Bowers Mountains, Black Glacier, and Evans Neve. Named for New Zealand's most famous General, Lord Bernard Freyberg, by the Northern Party of New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1963-64. This mountain group includes the Alamein Range. These topographical features all lie situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare. Key mountains * Mount Baldwin () is a mountain 5 nautical miles (9 km) southeast of Smiths Bench, in the Freyberg Mountains. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for T.T. Baldwin, transport specialist, a member of the United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP) Victoria Land Traverse Party which surveyed this area in 1959-60. * Buttress Peak () is a peak at the east end of the central ridge of Gallipoli Heights. The descriptive name was suggested by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Freyberg
Lieutenant-General Bernard Cyril Freyberg, 1st Baron Freyberg, (21 March 1889 – 4 July 1963) was a British-born New Zealand soldier and Victoria Cross recipient, who served as the 7th Governor-General of New Zealand from 1946 to 1952. Freyberg served as an officer in the British Army during the First World War. He took part in the beach landings during the Gallipoli Campaign and was the youngest general in the British Army during the First World War, later serving on the Western Front, where he was decorated with the Victoria Cross and three Distinguished Service Orders, making him one of the most highly decorated British Empire soldiers of the First World War. He liked to be in the thick of the action: Winston Churchill called him "the Salamander" due to his ability to pass through fire unharmed. During the Second World War, he commanded the New Zealand Expeditionary Force in the Battle of Crete, the North African Campaign and the Italian Campaign. Freyberg was involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition
The New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) describes a series of scientific explorations of the continent Antarctica. The expeditions were notably active throughout the 1950s and 1960s. Features named by the expeditions 1957–1958 expedition The 1957–1958 expedition went to the Ross Dependency and named the Borchgrevink Glacier. Other features named include: * Carter Ridge * Felsite Island * Halfway Nunatak * Hedgehog Island * Moraine Ridge 1958–1959 expedition * Cadwalader Beach * Cape Hodgson * Carter Ridge * Isolation Point * Mountaineer Range * Mount Aurora * Mount Hayward * Mount Henderson (White Island) * Mount Bird. 1960–1961 expedition * Deverall Island * Lonewolf Nunataks 1961–1962 expedition * Aurora Heights * The Boil * Ford Spur * Graphite Peak * Half Century Nunatak * Half Dome Nunatak * Hump Passage * Last Cache Nunatak * Lookout Dome * Montgomerie Glacier * Mount Fyfe * Mount Macdonald * Snowshoe Pass * Turret Nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C72193s5 Ant
C7, C07 or C-7 may refer to: Vehicles (including military) * C-7 Caribou, a military transport aircraft * AEG C.VII, a World War I German armed reconnaissance aircraft * AGO C.VII, a World War I German reconnaissance aircraft * Albatros C.VII, a World War I German military reconnaissance aircraft * C-7, a United States Navy C class blimp and the first airship inflated with helium * Chevrolet Corvette (C7), the seventh generation of a sports car made by General Motors * Fokker C.VII, a 1928 Dutch reconnaissance seaplane * HMS C7, HMS ''C7'', a British Royal Navy C-class submarine * Sauber C7, a 1983 Group C prototype race car * USS Cincinnati (C-7), USS ''Cincinnati'' (C-7), a United States Navy protected cruiser Science * Caldwell 7 (NGC 2403), a spiral galaxy in Camelopardalis Technology * Nokia C7-00, a touch screen mobile from Nokia * VIA C7, an IA-32 central processing unit by VIA Technologies * C7, an incandescent light bulb of the size typically used in nightlights and Chris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moawhango Névé
Alamein Range () is a range lying west of Canham Glacier, in the Freyberg Mountains of Antarctica. It was named in association with Lord Bernard Freyberg and the Second New Zealand Expeditionary Force by the Northern Party of New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1963–64. Location The Alamein Range runs from northwest to southeast. It lies to the east of the Rennick Glacier and west of the Canham Glacier. The Salamander Range is parallel to it on the east side of the Canham Glaciier. In the north, the Canham Glacier joins the Rennick Glacier past the tip of the Alamein Range. Features, from north to south, include Takrouna Bluff, Benoit Peak and Mount Camelot. Features to the west, between the Alamein Range and Rennick Glacier, include Mount Strandmann, Smiths Bench, Mount Baldwin and the Moawhango Névé. Features Takrouna Bluff . A small but prominent bluff on the east side of Alamein Range, overlooking Canham Glacier from a position west-southw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamein Range
Alamein Range () is a range lying west of Canham Glacier, in the Freyberg Mountains of Antarctica. It was named in association with Lord Bernard Freyberg and the Second New Zealand Expeditionary Force by the Northern Party of New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1963–64. Location The Alamein Range runs from northwest to southeast. It lies to the east of the Rennick Glacier and west of the Canham Glacier. The Salamander Range is parallel to it on the east side of the Canham Glaciier. In the north, the Canham Glacier joins the Rennick Glacier past the tip of the Alamein Range. Features, from north to south, include Takrouna Bluff, Benoit Peak and Mount Camelot. Features to the west, between the Alamein Range and Rennick Glacier, include Mount Strandmann, Smiths Bench, Mount Baldwin and the Moawhango Névé. Features Takrouna Bluff . A small but prominent bluff on the east side of Alamein Range, overlooking Canham Glacier from a position west-sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander Range
Salamander Range () is a distinctive linear range between Canham Glacier and Black Glacier, in the Freyberg Mountains, Antarctica. The range was named by the Northern Party of New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1963–64, from the nickname given to Lord Freyberg by Sir Winston Churchill, for the lizard that is untouched by fire. Location The Salamander Range runs from northwest to southeast between the Canham Glacier to the west and the Black Glacier to the east. The Lanterman Range is to the north and the Leitch Massif to the northwest. The Alamein Range is west of the Canham Glacier and the Neall Massif and West Quartzite Range are east of the Black Glacier. The Evans Névé is to the south. Features of the range include, from north to south, Galatos Peak, Mount Pedersen, Mount Apolotok, Mount Hennessey, Mount Tukotok and Mount Staley. Mello Nunatak.and Symes Nunatak are to the south. Features Geographical features of Salamander Range include, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evans Névé
Evans Névé () is a large névé which nourishes Tucker Glacier, Mariner Glacier, Aviator Glacier, Rennick Glacier and Lillie Glacier in Victoria Land, Antarctica. The névé was named in honor for Edgar Evans of the ill-fated British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, by the Northern Party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1963–64. Evans, along with Edward Adrian Wilson, Lawrence Oates and Henry Robertson Bowers, accompanied Captain Robert F. Scott to the South Pole, Geographic South Pole, January 17, 1912. All five perished on the return journey after failing to beat Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen to the 90th parallel. This glaciological feature lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare. References Snow fields of the Ross Dependency Landforms of Victoria Land Pennell Coast Névés of Antarctica {{VictoriaLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rennick Glacier
Rennick Glacier is broad glacier, nearly long, which is one of the largest in Antarctica. It rises on the polar plateau westward of Mesa Range and is wide, narrowing to near the coast. It takes its name from Rennick Bay where the glacier reaches the sea. The seaward part of the glacier was photographed by U.S. Navy (USN) Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The upper reaches of the Rennick Glacier were discovered and explored by the U.S. Victoria Land Traverse (VLT) in February 1960, and the first ascent made of Welcome Mountain by John Weihaupt, Alfred Stuart, Claude Lorius and Arnold Heine of the VLT party. On February 10, 1960, Lieutenant Commander Robert L. Dale, pilot of U.S. Navy (USN) Squadron VX-6, evacuated the VLT from 7238S, 16132E, on this glacier, and then conducted an aerial photographic reconnaissance to Rennick Bay on the coast before returning the VLT team to McMurdo Station. Features * Illusion Hills, small hills on the glacier * Litell Rocks, an area of rock outcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit ''nunataq'') is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They are also called glacial islands. Examples are natural pyramidal peaks. When rounded by glacial action, smaller rock promontories may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the nunataks protrude above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some nunataks are isolated, sometimes they form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, which hampers the formation of glacial ice on their tops, although snow can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee
New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) is an adjudicating committee established to authorize the naming of features in the Ross Dependency on the Antarctic continent. It is composed of the members of the New Zealand Geographic Board plus selected specialists on Antarctica. This committee works in collaboration with similar place-naming authorities in Australia, Great Britain and the United States to reach concurrence on each decision. The NZ-APC committee was established in 1956. Names attributed by the committee * Alberich Glacier, named after Alberich, king of the elves and chief of the Nibelungen * Arena Saddle, named in conjunction with Arena Valley * Brawhm Pass, named after the six party members of the University of New South Wales expeditions of 1964–65 and 1966–67 * Caliper Cove, named for descriptive features * Canada Stream, named in conjunction with Canada Glacier * Cape Crossfire, named for descriptive features * Cuneiform Cliffs, named for des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |