|
Mount Hercules
Mount Hercules () is a large, flat-topped, elevated feature between Mount Aeolus and Mount Jason in the Olympus Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) for Hercules, a figure in Greek mythology. Marsh Cirque is a cirque on the southern slopes of Mount Hercules. The cirque is wide and in part occupied by a glacier. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 2004 after geologist Bruce D. Marsh, of the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland. Marsh investigated basement sill at McMurdo Dry Valleys sites in seven field seasons, 1995–2005, for the United States Antarctic Program. Mount Hercules is separated from Mount Jason Mount Jason () is a peak just west of Bull Pass in the Olympus Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) for Jason Jason ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Aeolus (Antarctica)
Mount Aeolus () is a prominent peak, over high, between Mount Boreas and Mount Hercules in the Olympus Range of Victoria Land. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) for Aeolus In Greek mythology, Aeolus or Aiolos (; grc, Αἴολος , ) is a name shared by three mythical characters. These three personages are often difficult to tell apart, and even the ancient mythographers appear to have been perplexed about which A ..., the Greek god of the winds. Mountains of Victoria Land Scott Coast {{ScottCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consistently ranks among the most prestigious universities in the United States and the world. The university was named for its first benefactor, the American entrepreneur and Quaker philanthropist Johns Hopkins. Hopkins' $7 million bequest to establish the university was the largest Philanthropy, philanthropic gift in U.S. history up to that time. Daniel Coit Gilman, who was inaugurated as :Presidents of Johns Hopkins University, Johns Hopkins's first president on February 22, 1876, led the university to revolutionize higher education in the U.S. by integrating teaching and research. In 1900, Johns Hopkins became a founding member of the American Association of Universities. The university has led all Higher education in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritsen Valley
Fritsen Valley is an upland valley to the north of the Mount Hercules summit area and west of Harris Ledge in the Olympus Range, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (2004) after Christian H. Fritsen, a microbiologist with the Division of Earth and Ecosystem Sciences, Desert Research Institute, Reno, Nevada, and a United States Antarctic Program The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has presence in the A ... investigator of pack ice and lake ice from about 1992. References Valleys of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harris Ledge
Harris Ledge () is a flat, ice-free ridge to the north of Mount Hercules in the Olympus Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1997 after Henry Harris of the Illinois State Geological Survey, who made hydrogeological studies with Keros Cartwright (after whom Cartwright Valley is named) in Victoria Valley, Wright Valley, and Taylor Valley Taylor Valley is the southernmost of the three large McMurdo Dry Valleys in the Transantarctic Mountains, Victoria Land, Antarctica, located west of McMurdo Sound at approximately . The valley extends from Taylor Glacier in the west to McMurdo So ... during the Dry Valley Drilling Project in the 1973–74, 1974–75, and 1975–76 seasons. References Ridges of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakai Snowfield
Nakai Snowfield () is a snowfield at about elevation that occupies the col between Mount Hercules and Mount Jason in Olympus Range, McMurdo Dry Valleys. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) (2004) after Nobuyuki Nakai, Department of Earth Sciences, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan; a participant in the McMurdo Dry Valleys Drilling Project Vice-Admiral Archibald McMurdo (24 September 1812 – 11 December 1875) was a Scottish naval officer and polar explorer after whom Antarctica's McMurdo Sound, McMurdo Station, McMurdo Ice Shelf, McMurdo Dry Valleys and McMurdo–South Pole High ..., 1973–76. Landforms of Victoria Land Snow fields of the Ross Dependency McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Program
The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean. United States Antarctic Program The United States established the U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) in 1959—the name was later changed to the U.S. Antarctic Program—immediately following the success of the International Geophysical Year (IGY). Today, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has a Presidential Mandate to manage the United States Antarctic Program, through which it operates three year-round research stations and two research vessels, coordinates all U.S. science on the southernmost continent, and works with other federal agencies, the U.S. military, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Dry Valleys
The McMurdo Dry Valleys are a row of largely snow-free valleys in Antarctica, located within Victoria Land west of McMurdo Sound. The Dry Valleys experience extremely low humidity and surrounding mountains prevent the flow of ice from nearby glaciers. The rocks here are granites and gneisses, and glacial tills dot this bedrock landscape, with loose gravel covering the ground. It is one of the driest places on Earth and has not seen rain for nearly two million years. The region is one of the world's most extreme deserts, and includes many features including Lake Vida, a saline lake, and the Onyx River, a meltwater stream and Antarctica's longest river. Although no living organisms have been found in the permafrost here, endolithic photosynthetic bacteria have been found living in the relatively moist interior of rocks, and anaerobic bacteria, with a metabolism based on iron and sulfur, live under the Taylor Glacier. The valleys are located within the McMurdo Valleys Antarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
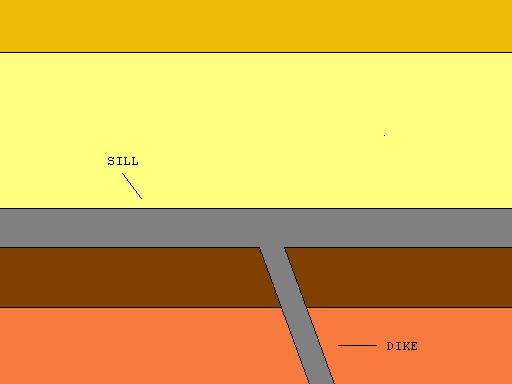
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A ''sill'' is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that a sill does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex . and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existing bedding pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was designated an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851, and today is the most populous independent city in the United States. As of 2021, the population of the Baltimore metropolitan area was estimated to be 2,838,327, making it the 20th largest metropolitan area in the country. Baltimore is located about north northeast of Washington, D.C., making it a principal city in the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area (CSA), the third-largest CSA in the nation, with a 2021 estimated population of 9,946,526. Prior to European colonization, the Baltimore region was used as hunting grounds by the Susquehannock Native Americans, who were primarily settled further northwest than where the city was later built. Colonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce D
The English language name Bruce arrived in Scotland with the Normans, from the place name Brix, Manche in Normandy, France, meaning "the willowlands". Initially promulgated via the descendants of king Robert the Bruce (1274−1329), it has been a Scottish surname since medieval times; it is now a common given name. The variant ''Lebrix'' and ''Le Brix'' are French variations of the surname. Actors * Bruce Bennett (1906–2007), American actor and athlete * Bruce Boxleitner (born 1950), American actor * Bruce Campbell (born 1958), American actor, director, writer, producer and author * Bruce Davison (born 1946), American actor and director * Bruce Dern (born 1936), American actor * Bruce Gray (1936–2017), American-Canadian actor * Bruce Greenwood Stuart Bruce Greenwood (born August 12, 1956) is a Canadian actor and producer. He is known for his role as the American president John F. Kennedy in '' Thirteen Days,'' for which he won the Satellite Award for Best Supporting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Jason
Mount Jason () is a peak just west of Bull Pass in the Olympus Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) for Jason Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He w ..., a figure in Greek mythology. References Mountains of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys Jason {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |