|
Mount Hannah
Mount Hannah is a mountain in the Mayacamas Mountains of the Northern California Coast Ranges. It is in Lake County, California. Location Mount Hannah is in Lake County, California. It is one of the mountains in the Cobb Mountain Area, many of which have volcanic origin. Others are Cobb Mountain, the most dominant, Seigler Mountain and Boggs Mountain. There are isolated small valleys and basins between the mountain peaks. Mount Hannah has an elevation of . Clean prominence is . Isolation is . The nearest higher neighbor is Cobb Mountain to the south. Geology Mount Hannah formed quite quickly during a polarity transition. It was built up by a number of closely-spaced eruptions. Three of the dacites in the Mount Hannah sequence have been dated to between 0.90 and 0.92 million years ago. There are indications that there may be a crustal magma chamber A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobb Mountain
Cobb Mountain is the tallest mountain in the Mayacamas Mountains of California. Location Cobb Mountain's main summit is located in Lake County, west of the town of Cobb. Like nearby Mount Saint Helena, Cobb Mountain is tall enough to receive winter snowfall. The mountain has a sub-peak referred to as Cobb Mountain – Southwest Peak with an elevation of about 4483+ feet, (1367+ m); Southwest Peak lies on the Sonoma-Lake county line and is the highest point in Sonoma County. Nearby taller peaks like Mount Saint Helena and Snow Mountain can be seen from this summit.Height and visual lines-of-sight are based on Google Earth images. Cobb Mountain is one of the mountains in the Cobb Mountain Area, many of which have volcanic origin. Others are Boggs Mountain, Mount Hannah and Seigler Mountain. There are isolated small valleys and basins between the mountain peaks. The east end of Cobb Mountain drains into the headwaters of Putah Creek, then into the Sacramento Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake County, California
Lake County is a county located in the north central portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 68,163. The county seat is Lakeport. The county takes its name from Clear Lake, the dominant geographic feature in the county and the largest non-extinct natural lake wholly within California. (Lake Tahoe is partially in Nevada; the Salton Sea was formed by flooding; Tulare Lake was drained by the agricultural industry.) Lake County forms the Clearlake, California micropolitan statistical area. It is directly north of the San Francisco Bay Area. Lake County is part of California's Wine Country, which also includes Napa, Sonoma, and Mendocino counties. It includes five American Viticultural Areas and over 35 wineries. History Lake County has been inhabited by Pomo Native Americans for over ten thousand years. Pomos had been fishermen and hunters, known especially for their intricate basketry made from lakeshore tules and other native plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayacamas Mountains
The Mayacamas Mountains are located in northwestern California in the United States. The mountain range is part of the Northern Inner Coast Ranges, of the California Coast Ranges System. Geography The Mayacamas Mountains are located south of the Mendocino Range, west of Clear Lake, and east of Ukiah in Mendocino and Lake Counties, and extend south into Napa and Sonoma Counties. The range stretches for in a northwest-southeasterly direction. Mountains in the range include: The range's highest point is Cobb Mountain, at in elevation, located in the central section. There are several other peaks over , including Mount Saint Helena and Hood Mountain. These peaks are sufficiently high to retain some snow cover in winter. Several streams rise in the Mayacamas Mountains including Mark West Creek, Sonoma Creek, Calabazas Creek, Arroyo Seco Creek, Putah Creek, and Santa Rosa Creek. ;Natural history Around ten million years ago, during pre-historic times (Miocene), the mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
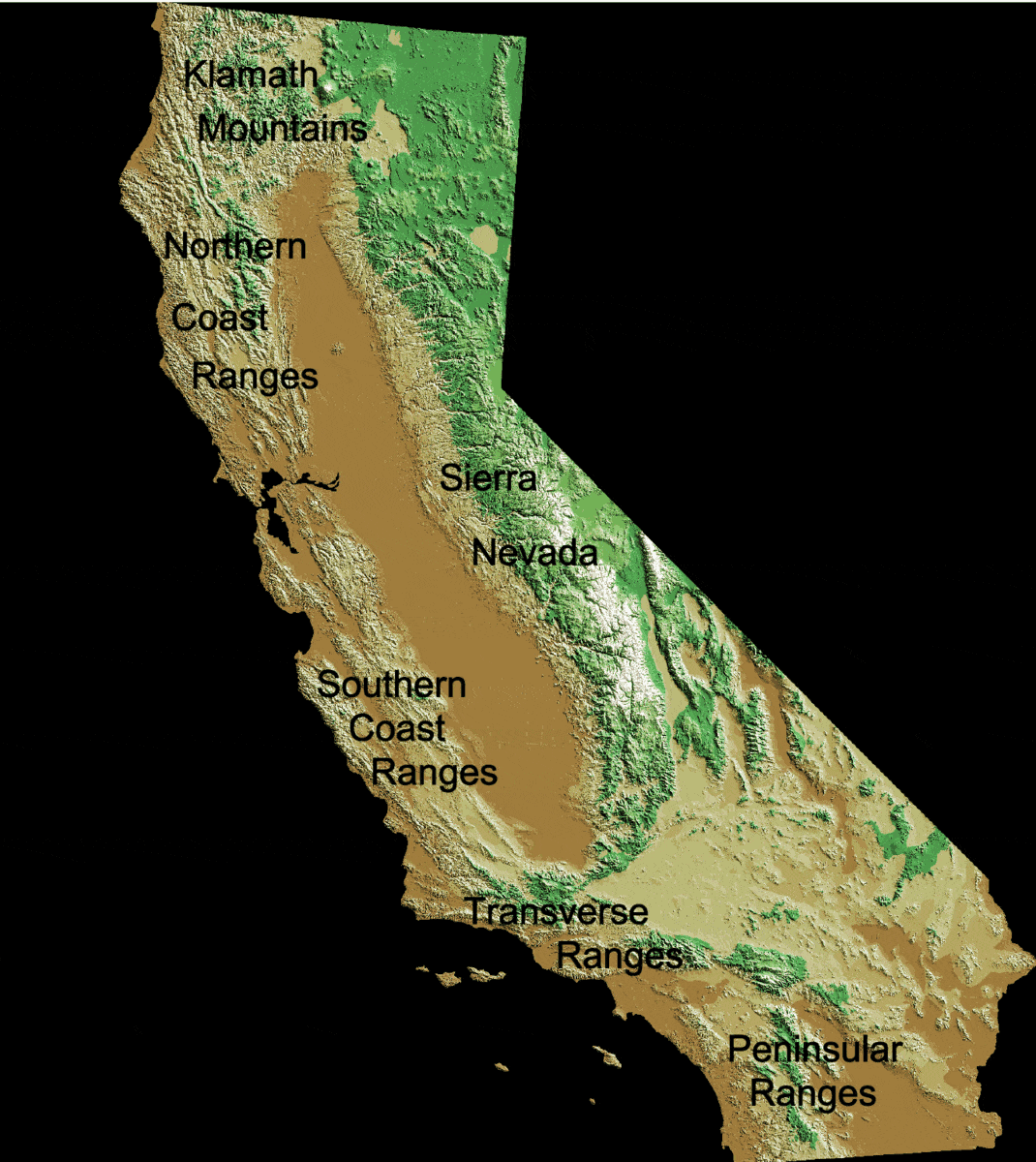
California Coast Ranges
The Coast Ranges of California span from Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains. Physiographically, they are a section of the larger Pacific Border province, which in turn is part of the larger Pacific Mountain System physiographic division. UNESCO has included the "California Coast Ranges Biosphere Reserve" in its Man and the Biosphere Programme of World Network of Biosphere Reserves since 1983. * Physiography The northern end of the California Coast Ranges overlap the southern end of the Klamath Mountains for approximately 80 miles on the west. They extend southward for more than 600 miles to where the coastline turns eastward along the Santa Barbara Channel, around the area of Point Conception. Here the southern end meets the Los Angeles Transverse Ranges, or ''Sierras de los Angeles''. The rocks themselves that com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seigler Mountain
Seigler Mountain is a mountain in the Mayacamas Mountains of the Northern California Coast Ranges. It is in Lake County, California. Name The mountain is named after Thomas Seigler, who discovered the Seigler Springs to the east of the mountain, where a resort grew up by the 1870s. Physical The mountain is in Lake County, California. It has an elevation of . Clean prominence is . Isolation is . The nearest higher neighbor is Mount Hannah to the WNW. Location Seigler Mountain is one of the mountains in the Cobb Mountain Area, which have a volcanic origin. Others are Cobb Mountain, the most dominant, Mount Hannah and Boggs Mountain. There are isolated small valleys and basins between the mountain peaks. Seigler Mountain is separated from Mount Hannah by Salminas Basin, a large mountain meadow with an unusual complex of wetlands that feeds Cole Creek. Flows of porphyritic lavas from Mount Hannah and Seigler Mountain cover about . The mountain was volcanically active 600,000 yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boggs Mountain
Boggs Mountain is a mountain the Mayacamas Mountains in Lake County, California. Part of the mountain holds the Boggs Mountain Demonstration State Forest. About 80% of the trees were burned in the September 2015 Valley Fire. Name In the early days of settlement of Lake County, the mountain was called Harbin Mountain after a settler named James M. Harbin who around 1856 took control of the land occupied by the Harbin Hot Springs, and gave his name to the springs and the mountain. An 1890 description by the State Mineralogist used this name to refer to the mountain. Later the mountain took the name Boggs Mountain. This name honors Henry C. Boggs (1820–1898), an early settler and entrepreneur in Lake County. The name Harbin Mountain survives, referring to a high point above Harbin Hot Springs on a ridge that comes down to the south from Boggs Mountain. Location Boogs Mountain is located in Lake County, California. It is high, in the heart of the Mayacamas Mountains, facing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarity Transition
A geomagnetic reversal is a change in a planet's magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged (not to be confused with geographic north and geographic south). The Earth's field has alternated between periods of ''normal'' polarity, in which the predominant direction of the field was the same as the present direction, and ''reverse'' polarity, in which it was the opposite. These periods are called '' chrons''. Reversal occurrences are statistically random. There have been at least 183 reversals over the last 83 million years (on average once every ~450,000 years). The latest, the Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, occurred 780,000 years ago, with widely varying estimates of how quickly it happened. Other sources estimate that the time that it takes for a reversal to complete is on average around 7,000 years for the four most recent reversals. Clement (2004) suggests that this duration is dependent on latitude, with shorter durations at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma Chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it upwards. If the magma finds a path to the surface, then the result will be a volcanic eruption; consequently, many volcanoes are situated over magma chambers. These chambers are hard to detect deep within the Earth, and therefore most of those known are close to the surface, commonly between 1 km and 10 km down. Dynamics of magma chambers Magma rises through cracks from beneath and across the crust because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. When the magma cannot find a path upwards it pools into a magma chamber. These chambers are commonly built up over time, by successive horizontal or vertical magma injections. Influx of new magma causes reaction of pre-existing crystals and the pressure in the chamber to increase. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Lake County, California
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |