|
Mount Gorongosa
Mount Gorongosa is an inselberg in Sofala Province of central Mozambique. Its highest peak, Gogogo, reaches an elevation of 1,863 meters (6,112 feet). It was created by Karoo Volcanism. The upper zone of the mountain (above 700 meters) was made part of Gorongosa National Park by the Mozambican government in 2010. The main part of the park lies at a lower elevation to the east of the mountain. Geography and geology Mount Gorongosa rises as an isolated massif from the surrounding lowlands. Mount Gorongosa is at the tip of a large, oval-shaped ring complex, some by . There are three main peaks, one in the north, one in the south, and Gogogo, the highest, in the southwest. Between them is a plateau that contains three valleys. The mountain is composed of granites of Late Jurassic age, ringed by gabbros on the western and southern slopes. Climate The mountain's climate is cooler and wetter than the surrounding lowlands. Moist oceanic air masses moving in from the southeast rise u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Language
Portuguese ( or, in full, ) is a western Romance language of the Indo-European language family, originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is an official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as " Lusophone" (). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology in its lexicon. With approximately 250 million native speakers and 24 million L2 (second language) speakers, Portuguese has approximately 274 million total speakers. It is usually listed as the sixth-most spoken language, the third-most sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
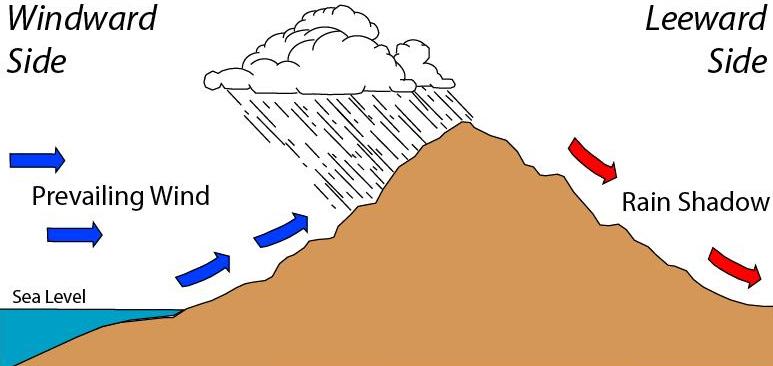
Windward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. along the direction towards which the wind is going. The side of a ship that is towards the leeward is its "lee side". If the vessel is heeling under the pressure of crosswind, the lee side will be the "lower side". During the Age of Sail, the term ''weather'' was used as a synonym for ''windward'' in some contexts, as in the ''weather gage''. Because it captures rain, the windward side of a mountain tends to be wet compared to the leeward it blocks. Origin The term "lee" comes from the middle-low German word // meaning "where the sea is not exposed to the wind" or "mild". The terms Luv and Lee (engl. Windward and Leeward) have been in use since the 17th century. Usage Windward and leeward directions (and the points o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afromontane
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands. Geography Afromontane communities occur above elevation near the equator, and as low as elevation in the Knysna-Amatole montane forests of South Africa. Afromontane forests are generally cooler and more humid than the surrounding lowlands. The Afromontane archipelago mostly follows the East African Rift from the Red Sea to Zimbabwe, with the largest areas in the Ethiopian Highlands, the Albertine Rift Mountains of Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Tanzania, and the Eastern Arc highlands of Kenya and Tanzan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Miombo Woodlands
The Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. It is one of four miombo woodlands ecoregions that span the African continent south of the Congo forests and East African savannas. Geography The Eastern miombo woodlands covers the hills and low plateaus in the watersheds of the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers, north and south of the Zambezi, and north and east of the Limpopo. The drier Zambezian and mopane woodlands occupy the lowlands along the Zambezi and its major tributaries, including the Shire and Lugenda, and the lowlands of the Limpopo. To the north and northwest, the Eastern miombo woodlands transition to the Central Zambezian miombo woodlands. To the southwest, they transition to the Southern Africa bushveld. The Southern Zanzibar-Inhambane coastal forest mosaic bounds the ecoregion on the southeast, along the Indian Ocean coast. Zambia's capital Lusaka and Zimbabwe's ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Highlands
:''"Eastern Highlands" also refers to Eastern Highlands Province in Papua New Guinea, and part of the Great Dividing Range, Australia.'' The Eastern Highlands, also known as the Manica Highlands, is a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The Eastern Highlands extend north and south for about through Zimbabwe's Manicaland Province and Mozambique's Manica Province. The Highlands are home to the Eastern Zimbabwe montane forest-grassland mosaic ecoregion. The ecoregion includes the portion of the highlands above 1000 meters elevation, including the Inyangani Mountains, Bvumba Mountains, Chimanimani Mountains, Chipinge Uplands, and the isolated Mount Gorongosa further east in Mozambique. The Southern miombo woodlands ecoregion lies at lower elevations east and west of the highlands. The highlands have a cooler, moister climate than the surrounding lowlands, which support distinct communities of plants and animals. The ecoregion is home to several plant commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic framework is optimal for all taxa. Ecoregions reflect the best compromise for as many taxa as possible. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Zimbabwe Montane Forest-grassland Mosaic
:''"Eastern Highlands" also refers to Eastern Highlands Province in Papua New Guinea, and part of the Great Dividing Range, Australia.'' The Eastern Highlands, also known as the Manica Highlands, is a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The Eastern Highlands extend north and south for about through Zimbabwe's Manicaland Province and Mozambique's Manica Province. The Highlands are home to the Eastern Zimbabwe montane forest-grassland mosaic ecoregion. The ecoregion includes the portion of the highlands above 1000 meters elevation, including the Inyangani Mountains, Bvumba Mountains, Chimanimani Mountains, Chipinge Uplands, and the isolated Mount Gorongosa further east in Mozambique. The Southern miombo woodlands ecoregion lies at lower elevations east and west of the highlands. The highlands have a cooler, moister climate than the surrounding lowlands, which support distinct communities of plants and animals. The ecoregion is home to several plant commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ericaceous Heathland
The Ericaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the heath or heather family, found most commonly in acidic and infertile growing conditions. The family is large, with c.4250 known species spread across 124 genera, making it the 14th most species-rich family of flowering plants. The many well known and economically important members of the Ericaceae include the cranberry, blueberry, huckleberry, rhododendron (including azaleas), and various common heaths and heathers (''Erica'', ''Cassiope'', ''Daboecia'', and ''Calluna'' for example). Description The Ericaceae contain a morphologically diverse range of taxa, including herbs, dwarf shrubs, shrubs, and trees. Their leaves are usually evergreen, alternate or whorled, simple and without stipules. Their flowers are hermaphrodite and show considerable variability. The petals are often fused (sympetalous) with shapes ranging from narrowly tubular to funnelform or widely urn-shaped. The corollas are usually radially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miombo Woodlands
The Miombo woodland is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome (in the World Wide Fund for Nature scheme) located primarily in Central Africa. It includes four woodland savanna ecoregions (listed below) characterized by the dominant presence of ''Brachystegia'' and ''Julbernardia'' species of trees, and has a range of climates ranging from humid to semi-arid, and tropical to subtropical or even temperate. The trees characteristically shed their leaves for a short period in the dry season to reduce water loss and produce a flush of new leaves just before the onset of the wet season with rich gold and red colours masking the underlying chlorophyll, reminiscent of autumn colours in the temperate zone. The woodland gets its name from ''miombo'' (plural, singular ''muombo''), the Bemba word for ''Brachystegia'' species. Other Bantu languages of the region, such as Swahili and Shona, have related if not identical words, such as Swahili ''miyombo'' (singu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submontane Zone
Altitudinal zonation (or elevational zonation) in mountainous regions describes the natural layering of ecosystems that occurs at distinct elevations due to varying environmental conditions. Temperature, humidity, soil composition, and solar radiation are important factors in determining altitudinal zones, which consequently support different vegetation and animal species. Altitudinal zonation was first hypothesized by geographer Alexander von Humboldt who noticed that temperature drops with increasing elevation. Zonation also occurs in intertidal and marine environments, as well as on shorelines and in wetlands. Scientist C. Hart Merriam observed that changes in vegetation and animals in altitudinal zones map onto changes expected with increased latitude in his concept of life zones. Today, altitudinal zonation represents a core concept in mountain research. Factors A variety of environmental factors determines the boundaries of altitudinal zones found on mountains, ranging f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montane Ecosystems
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands, shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply. Life zones As elevation increases, the climate becomes cooler, due to a decrease in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope towards the peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of dry climate region behind the mountain crests. This climate typically takes the form of shrub–steppe, xeric shrublands or even deserts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.png)