|
Mount Gharat
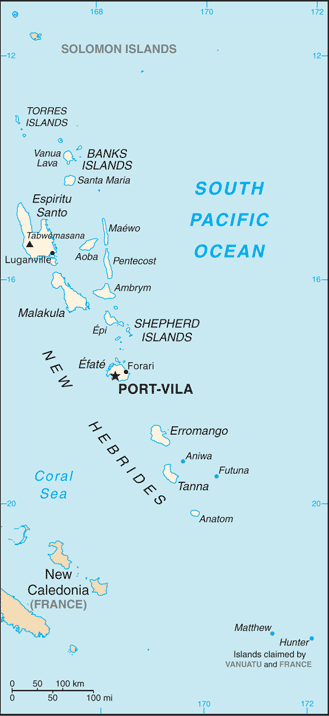
Mount Gharat or Mount Garet (797 m), a somma volcano, is the highest peak on the volcanic island of Gaua of the Banks Islands in northern Vanuatu. Geography The peak is located at the centre of the island, is volcanically active and is surrounded by Lake Letas on all sides except southwest. Name The volcano has slightly different names, depending on which of the local languages is being considered. It is known as ''Garet'' in Nume, ''Grāt'' in Dorig, ''Gerät'' in Koro, ''Gäräs'' in Lakon. The spelling ''Gharat'' found sometimes on maps is an attempt at transcribing Mota Mota, MOTA or variations thereof may refer to: Geography * Mota (island), Vanuatu * Mota, Ethiopia, a town * Mota, Gujarat, India, a town * Mota, Ljutomer, Slovenia, a village Music * ''M.O.T.A.'' (album), a 2005 album by Cultura Profética * "M ... ''Garat'' . All these names come from a Proto-Torres-Banks form *''ɣarati'', whose literal meaning is “itching, burning” ‒ perhaps in relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaua
Gaua (formerly known as ''Santa Maria Island'') is the largest and second most populous of the Banks Islands in Torba Province in northern Vanuatu. It covers 342 km². History Gaua was first sighted by Europeans during the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós, from 25 to 29 April 1606. The island’s name was then charted as ''Santa María''. Geography Gaua is subject to frequent earthquakes and cyclones. The climate is humid tropical; the average annual rainfall exceeds 3500 mm. It has rugged terrain, reaching up to Mount Gharat (797 m), the peak of the active stratovolcano which lies at the center of the island. Its most recent eruption was in 2013. The volcano has a 6 × 9 km caldera, within which lies a crater lake, known as Lake Letas, which is the largest lake in Vanuatu. To the east of the lake is Siri Waterfall (120 m drop). Natural history The upper slopes of the island have been recognised as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by Bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koro Language (Vanuatu)
Koro is an Oceanic language spoken on Gaua island in Vanuatu. Its 280 speakers live in the village of Koro, on the south coast of Gaua. Koro is a distinct language from its immediate neighbours, Dorig (300 sp.) and Olrat (4 sp.). Name The name ''Koro'', spelled natively as ''Kōrō'' , is an endonym referring to the village. Phonology Koro has 8 phonemic vowels. These include 7 monophthongs and one diphthong . The diphthong is spelled as . Grammar The system of personal pronouns in Koro contrasts clusivity, and distinguishes four numbers (singular, dual, trial, plural). Spatial reference in Koro is based on a system of geocentric (absolute) directionals, which is typical of Oceanic languages. François (2015). Notes and references References Bibliography * * . * * * * External links Linguistic map of north Vanuatu, showing range of Koro on Gaua Audio recordings in the Koro language in open access, by A. François (''Pangloss Collection The Pangloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Vanuatu
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calderas Of Oceania
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is gone. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur each century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times per century. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2016. More recently, a caldera collapse occurred at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018. Etymology The term ''caldera'' comes from Spanish ', and Latin ', meaning "co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Vanuatu
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where list of tectonic plates, tectonic plates are divergent boundary, diverging or convergent boundary, converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mota Language
Mota is an Oceanic language spoken by about 750 people on Mota island, in the Banks Islands of Vanuatu. The language (named after the island) is one of the most conservative Torres–Banks languages, and the only one to keep its inherited five-vowel system intact while also preserving most final vowels. History During the period 1840-1940, Mota was used as a missionary ''lingua franca'' throughout areas of Oceania included in the Melanesian Mission, an Anglican missionary agency. Mota was used on Norfolk Island, in religious education; on other islands with different vernacular languages, it served as the language of liturgical prayers, hymns, and some other religious purposes. Elizabeth Fairburn Colenso translated religious material into the language. Robert Henry Codrington compiled the first dictionary of Mota (1896), and worked with George Sarawia and others to produce a large number of early publications in this language. Phonology Phoneme inventory Mota phonemically con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakon Language
Lakon is an Oceanic language, spoken on the west coast of Gaua island in Vanuatu. Names The language name ''Lakon'' refers originally to the area where it is spoken ‒ namely Lakona Bay, corresponding to the west coast of Gaua. The alternative name ''Lakona'' is from the Mota language. These names are derived from a Proto-Torres-Banks form *''laᵑgona'', of unknown meaning. Lakon had four dialects, named Qatareu (''Qätärew'' ), Vure (''Vurē'' ), Toglatareu, and Togla. Phonology Consonants Lakon has 16 phonemic consonants. François (2022). The glottal stop only occurs before vowels in syllable-initial position. While non-phonemic, it is sometimes noted in the orthography, using a mark. Vowels Lakon has 16 phonemic vowels. These include 8 short /i ɪ ɛ æ a ɔ ʊ u/ and 8 long vowels /iː ɪː ɛː æː aː ɔː ʊː uː/. Historically, the phonemicisation of vowel length originates in the compensatory lengthening of short vowels when the alveolar trill w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorig Language
Dorig (formerly called ''Wetamut'') is an Oceanic language spoken on Gaua island in Vanuatu. The language’s 300 speakers live mostly in the village of Dorig (), on the south coast of Gaua. Smaller speaker communities can be found in the villages of Qteon (east coast) and Qtevut (west coast). Dorig's immediate neighbours are Koro and Mwerlap. Name The name ''Dorig'', spelled ''Dōrig'', is derived from the name of the village where it is spoken. The term is related to ''Dōlav'' (the Dorig name of a village that is called in Lakon as ''Jōlap'' ), with the ''-rig'' and ''-lav'' parts meaning "small" and "big" respectively. The element ''dō'' is obscure; hence the only term that can be reconstructed for Proto-Torres-Banks is ''*-riɣi''. Phonology Dorig has 8 phonemic vowels. These include 7 short monophthongs and one long vowel . Dorig has 15 consonant phonemes. The phonotactic template for a syllable in Dorig is: — e.g. ‘woman’; ‘poor’; ‘octopus’. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banks Islands
The Banks Islands (in Bislama ''Bankis'') are a group of islands in northern Vanuatu. Together with the Torres Islands to their northwest, they make up the northernmost province of Torba. The island group lies about north of Maewo, and includes Gaua and Vanua Lava, two of the 13 largest islands in Vanuatu. In 2009, the islands had a population of 8,533. The island group's combined land area is 780 km2. Geography The largest island is Gaua (formerly called Santa Maria), which has a rugged terrain, rising to Mount Gharat, an active volcano at the centre of the island, at . Gaua's freshwater Lake Letas, in its volcanic crater, is the largest lake in Vanuatu. A slightly smaller island in the group, Vanua Lava, is higher, at ; it too has an active volcano: Mount Suretamate (also spelled Süretimiat or Sere'ama, ). To the east of Vanua Lava are two islets in the groupo, Ravenga and Kwakea (also spelled Qakea). Sola, the provincial capital, is on Vanua Lava. The third largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nume Language
Nume (also called ''Gog'' and ''Tarasag'') is an Oceanic language spoken on Gaua island in Vanuatu. Its 700 speakers live on the northeast coast of Gaua. Nume is a distinct language from its immediate southern neighbors, Mwerlap and Dorig. Names The name ''Nume'' originates in the name of a village, now abandoned. ''Tarasag'' is currently the community's main village. The alternate name ''Gog'' refers to the broader area, and by extension, to the island. Phonology Nume has 7 phonemic vowels, which are all short monophthongs. : Grammar The system of personal pronouns in Nume contrasts clusivity, and distinguishes four numbers (singular, dual, trial, plural). Spatial reference in Nume is based on a system of geocentric (absolute) directionals, which is typical of Oceanic languages. François (2015). References Bibliography * * . * * * External links Linguistic map of north Vanuatu, showing range of Nume on Gaua Audio recordings in the Nume language in open access, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |