|
Mount Field (Antarctica)
The Churchill Mountains are a mountain range group of the Transantarctic Mountains System, located in the Ross Dependency region of Antarctica. They border on the western side of the Ross Ice Shelf, between Byrd Glacier and Nimrod Glacier. Several of the range's highest summits, including Mounts Egerton, Field, Nares, Wharton, and Albert Markham were first seen and named by the Discovery Expedition of 1901–1904 (aka: British National Antarctic Expedition), under Robert Falcon Scott The mountains were mapped in detail by the USGS from Tellurometer surveys during 1960–61, and by United States Navy air photos in 1960. They were named by the US-ACAN for Sir Winston Churchill. Mountains and peaks ;Mount Albert Markham Mount Albert Markham is a striking flat-topped mountain, standing midway between Mount Nares and Pyramid Mountain. Discovered by the Discovery Expedition and named for Admiral Sir Albert Hastings Markham, a member of the Ship Committee for the expedition. ;Moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Dependency
The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160° east to 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60° south. It is claimed by New Zealand, a claim accepted only by the other six countries with territorial claims in Antarctica. Under the 1961 Antarctic Treaty, of which all territorial claimants are signatories, including New Zealand, all claims are held in abeyance. Article IV states: "No acts or activities taking place while the present Treaty is in force shall constitute a basis for asserting, supporting or denying a claim to territorial sovereignty in Antarctica or create any rights of sovereignty in Antarctica". The Dependency takes its name from Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered the Ross Sea, and includes part of Victoria Land, and most of the Ross Ice Shelf. Ross, Balleny, Scott and Roosevelt Islands also form part of the Dependency. History of claim Following his discovery of Victo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Wharton (hydrographer)
Admiral Sir William James Lloyd Wharton (2 March 1843, in London – 29 September 1905, in Cape Town) :wikisource:Wharton, William James Lloyd (DNB12) was a British admiral and Hydrographer of the Navy. Early life He was born in London, the second son of Robert Wharton, County Court Judge of York. He was educated at Barney's Academy, Gosport and the Royal Naval Academy. Royal Navy service He joined the Royal Navy in August 1857 and was promoted to lieutenant in 1863. His first surveying work was in HMS Gannet, including work in the Bay of Fundy, where some of the highest tides in the world make surveying challenging. In 1870 he was part of an expedition in HMS Urgent to observe a total eclipse of the sun in Gibraltar. He was promoted to commander in 1872. As captain of ''Shearwater'' he carried out extensive surveying the Sea of Marmora and the Bosphorus, as well as in the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean. In the Bosphorus he designed ingenious methods to measure the flow at dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-130 Hercules
The Lockheed C-130 Hercules is an American four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). Capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, the C-130 was originally designed as a troop, Medical evacuation, medevac, and Cargo aircraft, cargo transport aircraft. The versatile airframe has found uses in other roles, including as a gunship (AC-130), for airborne infantry, airborne assault, search and rescue, scientific research support, weather reconnaissance, aerial refueling, maritime patrol, and aerial firefighting. It is now the main tactical airlifter for many military forces worldwide. More than 40 variants of the Hercules, including civilian versions marketed as the Lockheed L-100, operate in more than 60 nations. The C-130 entered service with the U.S. in 1956, followed by Australia and many other nations. During its years of service, the Hercules has participated in numerous milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troop Carrier Squadron
A troop is a military sub-subunit, originally a small formation of cavalry, subordinate to a squadron. In many armies a troop is the equivalent element to the infantry section or platoon. Exceptions are the US Cavalry and the King's Troop Royal Horse Artillery where a troop is a subunit comparable to an infantry company or artillery battery. Historically the remainder of the Royal Horse Artillery used the term Troop in the same manner however they are now aligned with the rest of the Royal Regiment of Artillery in referring to Troops as subordinate to artillery batteries. Troops is often used to refer to the other members of one's company or cause, but because of its military connotations, it conveys a particularly altruistic type of dedicated worker. Traditionally, troops refers to the soldiers in a military. A cavalry soldier of private rank is called a trooper in many Commonwealth armies (abbreviated "Tpr", not to be confused with "trouper"). A related sense of the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
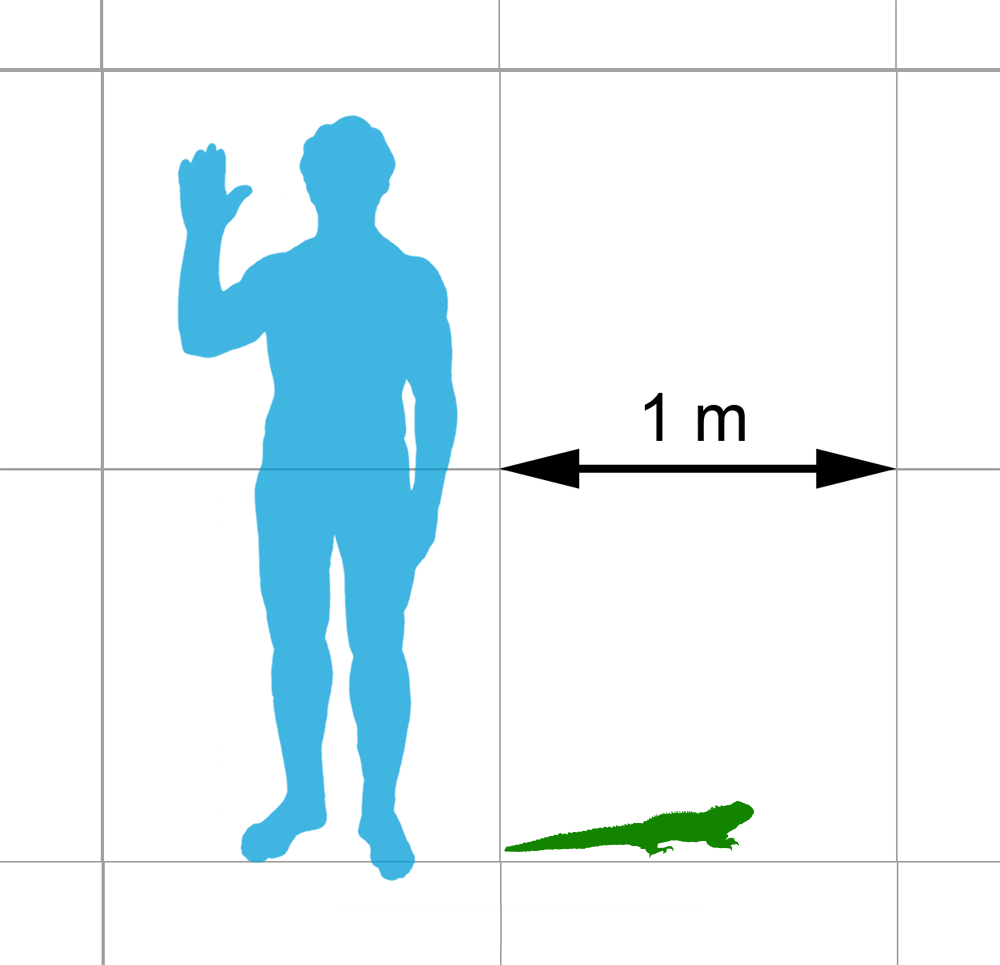
Tuatara
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to from head to tail-tip and wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George S
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-year-old pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
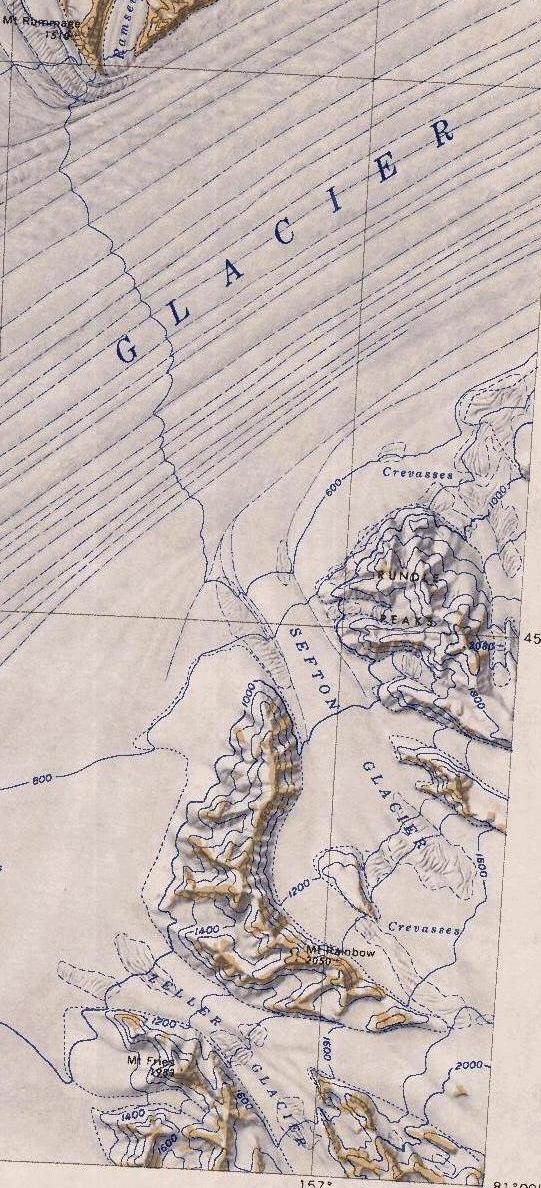
Flynn Glacier
Flynn Glacier () is a glacier about long, draining eastward from Mount Nares in the Churchill Mountains of Antarctica, and entering Starshot Glacier south of Kelly Plateau. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander William F. Flynn (CEC), U.S. Navy, commanding officer Mobile Construction Battalion, Special Detachment Bravo, at McMurdo Sound McMurdo Sound is a sound in Antarctica. It is the southernmost navigable body of water in the world, and is about from the South Pole. Captain James Clark Ross discovered the sound in February 1841, and named it after Lt. Archibald McMurdo o ..., winter 1957. References Glaciers of Oates Land {{OatesLand-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Committee
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Vesey Hamilton
Sir Richard Vesey Hamilton (28 May 1829 – 17 September 1912) was a Royal Navy officer. As a junior officer he twice volunteered to take part in missions to search for Sir John Franklin's ill-fated expedition to find the Northwest Passage. He also took part in the Battle of Fatshan Creek in June 1857 during the Second Opium War. Later in his career he became commander-in-chief at China Station and took his fleet into Vladivostok harbour in 1886, which surprised the Russians. He became First Naval Lord in July 1889 and in that role he was primarily concerned with implementing the recommendations contained in a report on the disposition of the ships of the Royal Navy many of which were unarmoured and together incapable of meeting the combined threat from any two of the other naval powers ("the Two-power Standard"): these recommendations had been enshrined in the Naval Defence Act 1889. He finished his career as President of the Royal Naval College at Greenwich. Early car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent Plateau
The Kent Plateau () is an ice-covered plateau in the northern extreme of the Churchill Mountains of Antarctica. Name Kent Plateau was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander Donald F. Kent, U.S. Navy, logistics officer to Admiral Dufek at the outset of U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze I, 1955–56. Location The Kent Plateau is an ice-covered plateau, long and wide, extending northward from Mount Egerton and Kiwi Pass to the vicinity of Mount Hamilton. The plateau is on the west of a ridge of mountains that runs north from Mount Durnford, dips at Kiwi Pass, then continues north from Mount Moa to Mount Hamilton along the east edge of the plateau. To the west of the plateau along the southeast edge of the Byrd Glacier there is a chain of mountains broken by glaciers that flow down from the plateau region to Byrd Glacier. Glaciers Several short glaciers run down from the plateau into Byrd Glacier. From southwest to northeast they are: Zeller Glacier . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-124 Globemaster
The Douglas C-124 Globemaster II, nicknamed "Old Shaky", is an American heavy-lift cargo aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company in Long Beach, California. The C-124 was the primary heavy-lift transport for United States Air Force (USAF) Military Air Transport Service (MATS) during the 1950s and early 1960s, until the Lockheed C-141 Starlifter entered service. It served in MATS, later Military Airlift Command (MAC), units of the Air Force Reserve and Air National Guard until retired in 1974. Design and development Douglas Aircraft developed the C-124 from 1947 to 1949, from a prototype they created from a World War II–design Douglas C-74 Globemaster, and based on lessons learned during the Berlin Airlift. The aircraft was powered by four large Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major piston engines producing each. The C-124's design featured two large clamshell doors and a hydraulically actuated ramp in the nose as well as a cargo elevator under the aft fuselage. The C-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)