|
Mount Dover
Mount Dover () is a mountain in Antarctica, high, surmounting the southeast end of Gale Ridge where the ridge abuts the Washington Escarpment, in the Neptune Range, Pensacola Mountains. Exploration and name Mount Dover was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photographs in 1956–66- It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for James H. Dover, a geologist with the Patuxent Range field party in 1962–63. Location Mount Dover is towards the south of the Washington Escarpment, west of the Iroquois Plateau and east of the Roderick Valley. It is north of Mount Hawkes, Bennett Spires and the Barnes Icefalls, and south of the Nelson Peak. The Gale Ridge extends northwest from Mount Dover, and includes Mount Cowart and Kinsella Peak. Nearby features Barnes Icefalls . The icefalls along Washington Escarpment between Mount Dover and Bennett Spires Mount Hawkes is, at , the highest mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pensacola Mountains
The Pensacola Mountains are a large group of mountain ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains System, located in the Queen Elizabeth Land region of Antarctica. Geography They extend 450 km (280 mi) in a NE-SW direction. Subranges of the Pensacola Mountains include: Argentina Range, Forrestal Range, Dufek Massif, Cordiner Peaks, Neptune Range, Patuxent Range, Rambo Nunataks and Pecora Escarpment. These mountain units lie astride the extensive Foundation Ice Stream and Support Force Glacier which drain northward to the Ronne Ice Shelf. ;Naming Discovered and photographed on 13 January 1956 in the course of a transcontinental nonstop plane flight by personnel of United States Navy Operation Deep Freeze I from McMurdo Sound to Weddell Sea and return. Named by US-ACAN for the U.S. Naval Air Station, Pensacola, Florida, in commemoration of the historic role of that establishment in training aviators of the U.S. Navy. The mountains were mapped in detail by USGS from surveys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
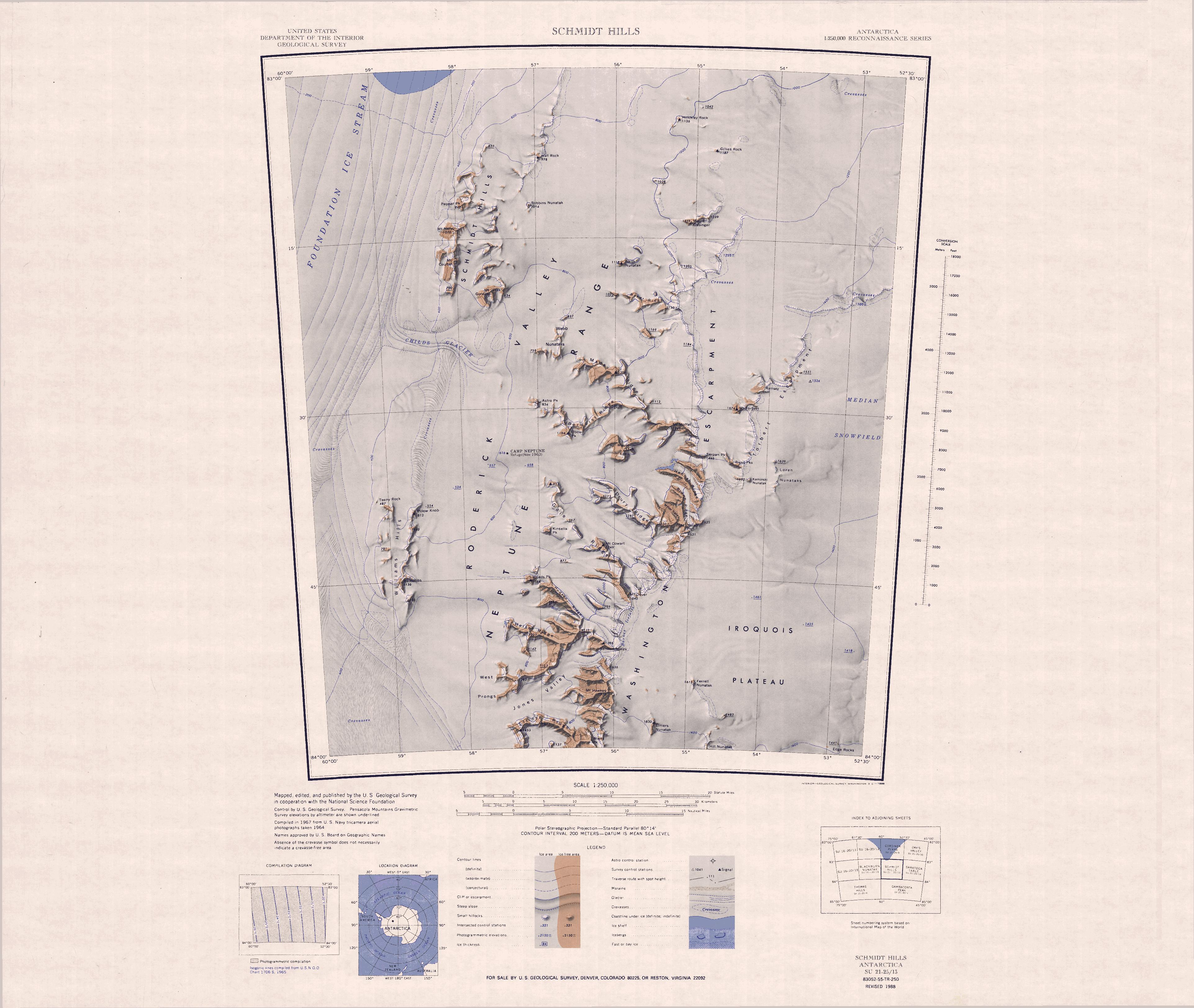
Neptune Range
The Neptune Range is a mountain range, long, lying WSW of Forrestal Range in the central part of the Pensacola Mountains in Antarctica. The range is composed of Washington Escarpment with its associated ridges, valleys and peaks, the Iroquois Plateau, and the Schmidt and Williams Hills. It was discovered and photographed on 13 January 1956 on a US Navy transcontinental plane flight from McMurdo Sound to Weddell Sea and return. Named by US-ACAN after the Navy 2V-2N Neptune aircraft with which this flight was made. The entire Pensacola Mountains were mapped by USGS in 1967 and 1968 from ground surveys and United States Navy tricamera aerial photographs taken in 1964. Key mountains * Astro Peak () is a peak, 835 m, standing 1 mile (1.6 km) off the west end of Berquist Ridge. So named by US-ACAN because the USGS established an astro control station on this peak during the 1965-66 season. * Mount Dasinger () is a mountain, 1,360 m, standing 6 nautical miles (11&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Escarpment
Washington Escarpment () is the major west-facing escarpment of the Neptune Range, Pensacola Mountains in Antarctica, extending some 50 miles (80 km) and being the point of origin of a number of west-trending rock ridges. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1956–66. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for the University of Washington The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington. Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seattle a ... at Seattle. Several members of the Neptune Range field party of 1963-64 attended this university. References Escarpments of Queen Elizabeth Land University of Washington Escarpments of Antarctica {{QueenElizabethLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patuxent Range
The Patuxent Range or macizo Armada Argentina is a major range of the Pensacola Mountains, comprising the Thomas Hills, Anderson Hills, Mackin Table and various nunataks and ridges bounded by the Foundation Ice Stream, Academy Glacier and the Patuxent Ice Stream. Discovered and partially photographed on January 13, 1956 in the course of a transcontinental nonstop plane flight by personnel of U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze I from McMurdo Sound to Weddell Sea and return. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for the Naval Air Station Patuxent River (at Cedar Point, Maryland) located on the south side of the mouth of the Patuxent River. The range was mapped in detail by USGS from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1956-66. Key geographic features * O'Connell Nunatak () is a peaked rock nunatak, , standing 6 nautical miles (11 km) south-southeast of Mount Murch in the southern Anderson Hills. Named by US-ACAN for Richard V. O'Connell, seismologist at Amundse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C83052s5 Schmidt Hills
C83 may refer to: *Byron Airport, a public airport serving Contra Costa County, California, USA. * ''Corydoras loxozonus'', a freshwater catfish. * Ruy Lopez The Ruy Lopez (; ), also called the Spanish Opening or Spanish Game, is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. e4 e5 :2. Nf3 Nc6 :3. Bb5 The Ruy Lopez is named after 16th-century Spanish priest Ruy López de Segura. It is one o ... chess openings ECO code * Diffuse non-Hodgkin's lymphoma ICD-10 code * HMS Southampton (C83), a 1934 British Royal Navy cruiser * Labour Standards (Non-Metropolitan Territories) Convention, 1947 code * Caldwell 83 ( NGC 4945), a spiral galaxy in the constellation Centaurus C-83 may refer to : * C-83 Coupe, an aircraft {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquois Plateau
Iroquois Plateau () is a large, mainly ice-covered plateau situated east of the southern part of the Washington Escarpment in the Pensacola Mountains of Edith Ronne Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1956–66, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after the Bell UH-1 Iroquois The Bell UH-1 Iroquois (nicknamed "Huey") is a utility military helicopter designed and produced by the American aerospace company Bell Helicopter. It is the first member of the prolific Huey family, as well as the first turbine-powered helic ... helicopter which has greatly facilitated field operations in Antarctica. References Plateaus of Antarctica Landforms of Queen Elizabeth Land {{QueenElizabethLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roderick Valley
Schmidt Hills () is a group of rock hills, long, lying north of Childs Glacier and west of Roderick Valley in the Neptune Range of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. Mapping and name The Schmidt Hills were mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos and 1956–1966. They were named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Dwight L. Schmidt, USGS geologist to the Pensacola Mountains in 1962–63, 1963–64 and 1965–66. Location The Schmidt Hills are in the northwest of the Neptune Range on the east side of the Foundation Ice Stream near the point where it joins the Ronne Ice Shelf. They are north of the Williams Hills and west of the northern end of the Washington Escarpment, from which they are separated by the Roderick Valley. Features include, from south to north, Mount Gorecki, Mount Coulter, Mount Nervo, Pepper Peak, Robbins Nunatak and Wall Rock. Features Mount Gorecki . A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Hawkes
Mount Hawkes is, at , the highest mountain along the Washington Escarpment, standing at the east side of Jones Valley in the Neptune Range of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. It was discovered and photographed on January 13, 1956, in the course of the trans-Antarctic nonstop plane flight by personnel of U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze I from McMurdo Sound to the Weddell Sea and return. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander William M. Hawkes of the U.S. Navy, who was the co-pilot of the P2V-2N Neptune aircraft making this flight. The Hawkes Heights are also named for Hawkes, who was assigned to Air Development Squadron Six (VX-6 Air Development Squadron Six (VX-6 or AIRDEVRON SIX, commonly referred to by its nickname, "puckered penguins") was a United States Navy Air Development Squadron based at McMurdo Station, Antarctica. Established at Naval Air Station Patuxent River, ...) in 1955–56. References Mountains of Queen Elizabeth Land Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bennett Spires
Mount Hawkes is, at , the highest mountain along the Washington Escarpment, standing at the east side of Jones Valley Jones Valley () is a snow-covered valley between West Prongs and Elliott Ridge in the southern Neptune Range of the Pensacola Mountains in Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photo ... in the Neptune Range of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. It was discovered and photographed on January 13, 1956, in the course of the trans-Antarctic nonstop plane flight by personnel of U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze I from McMurdo Sound to the Weddell Sea and return. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander William M. Hawkes of the U.S. Navy, who was the co-pilot of the P2V-2N Neptune aircraft making this flight. The Hawkes Heights are also named for Hawkes, who was assigned to Air Development Squadron Six (VX-6) in 1955–56. References Mountains of Queen Elizabeth Land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |