|
Mount Cameroon And Bioko Montane Forests
The Mount Cameroon and Bioko montane forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in central Africa. It occupies the upper slopes of coastal Mount Cameroon in Cameroon, and the mountains of nearby Bioko island in Equatorial Guinea. Geography The ecoregion includes the distinct montane forests on the higher elevations of two volcanic peaks, Mount Cameroon, which lies in Cameroon near the coast, and Bioko, a volcanic island to the southwest in Equatorial Guinea. The montane forests occur as low as 500 meters elevation on Mount Cameroon. They also occur above 1500 meters elevation on three peaks on Bioko, Pico Basilé (3,011 meters elevation), Gran Caldera de Luba (2,261 m), and Pico Biao (2,009 m). The montane forests are surrounded at lower elevations by the Cross-Sanaga-Bioko coastal forests ecoregion. Both Bioko and Mount Cameroon are part of the Cameroon Volcanic Line, a line of volcanoes that runs northeast-southwest across the Cameroon Highlands and extending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luba Crater Scientific Reserve
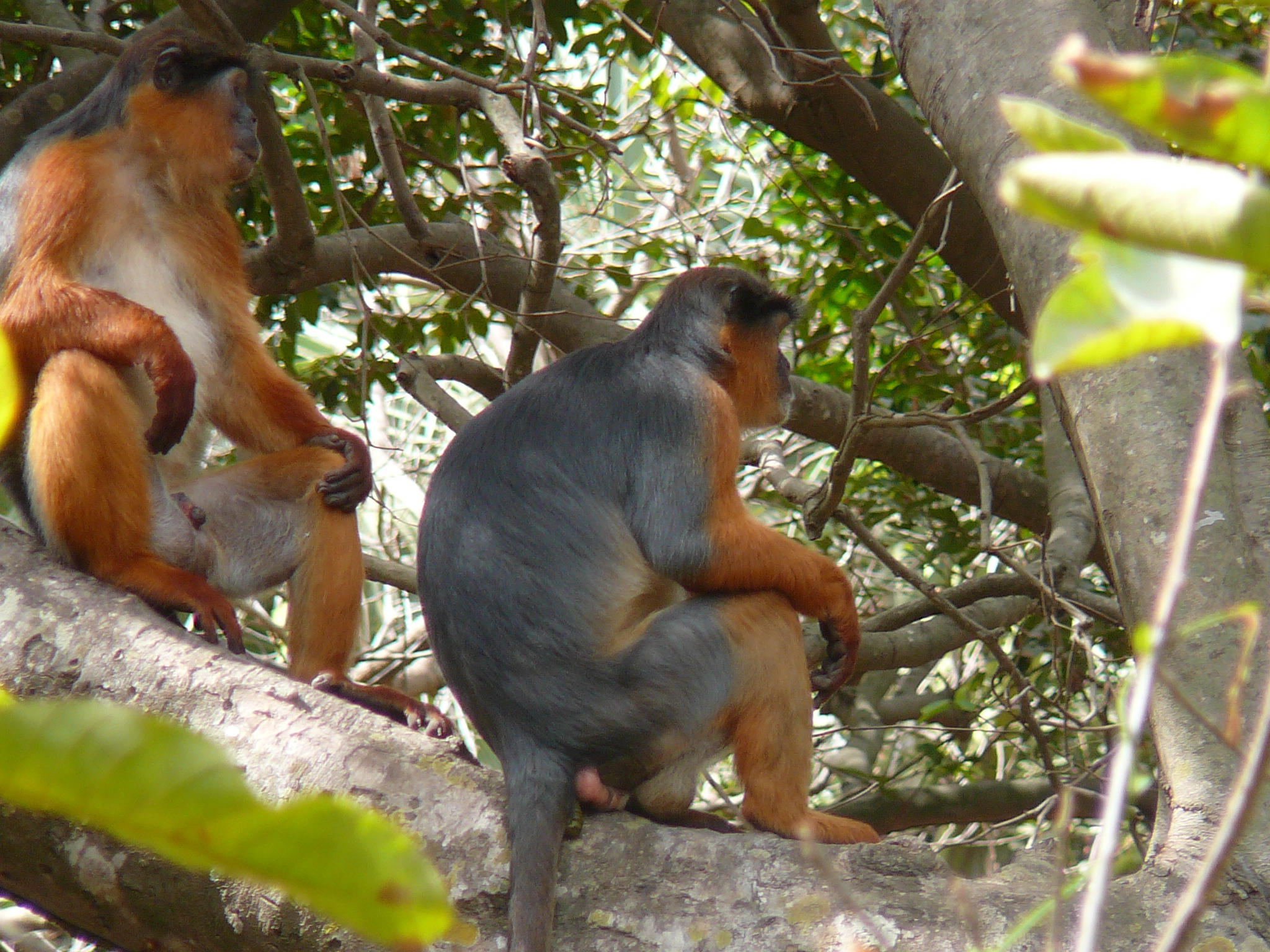
The Gran Caldera de Luba Scientific Reserve ( es, Reserva Científica de la Gran Caldera de Luba) is a protected area of on the volcanic island of Bioko (formerly called Fernando Pó), a part of Equatorial Guinea. The dense rainforest is rich in plant and animal species including a high population of primates, some endemic to the reserve. Much of the reserve consists of pristine forest. However, the primate population is under threat due to growing demand for bushmeat coupled with lack of enforcement of the ban on hunting in the reserve. Location The Gran Caldera de Luba Crater Scientific Reserve is in the island of Bioko, which is part of the small country of Equatorial Guinea. Before the country gained independence from Spain in 1968 the main cash crop was cocoa. Since then agriculture has been neglected and many of the cocoa plantations have returned to the forest. Until recently a poor country, exploitation of large offshore reserves of oil and gas has dramatically increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
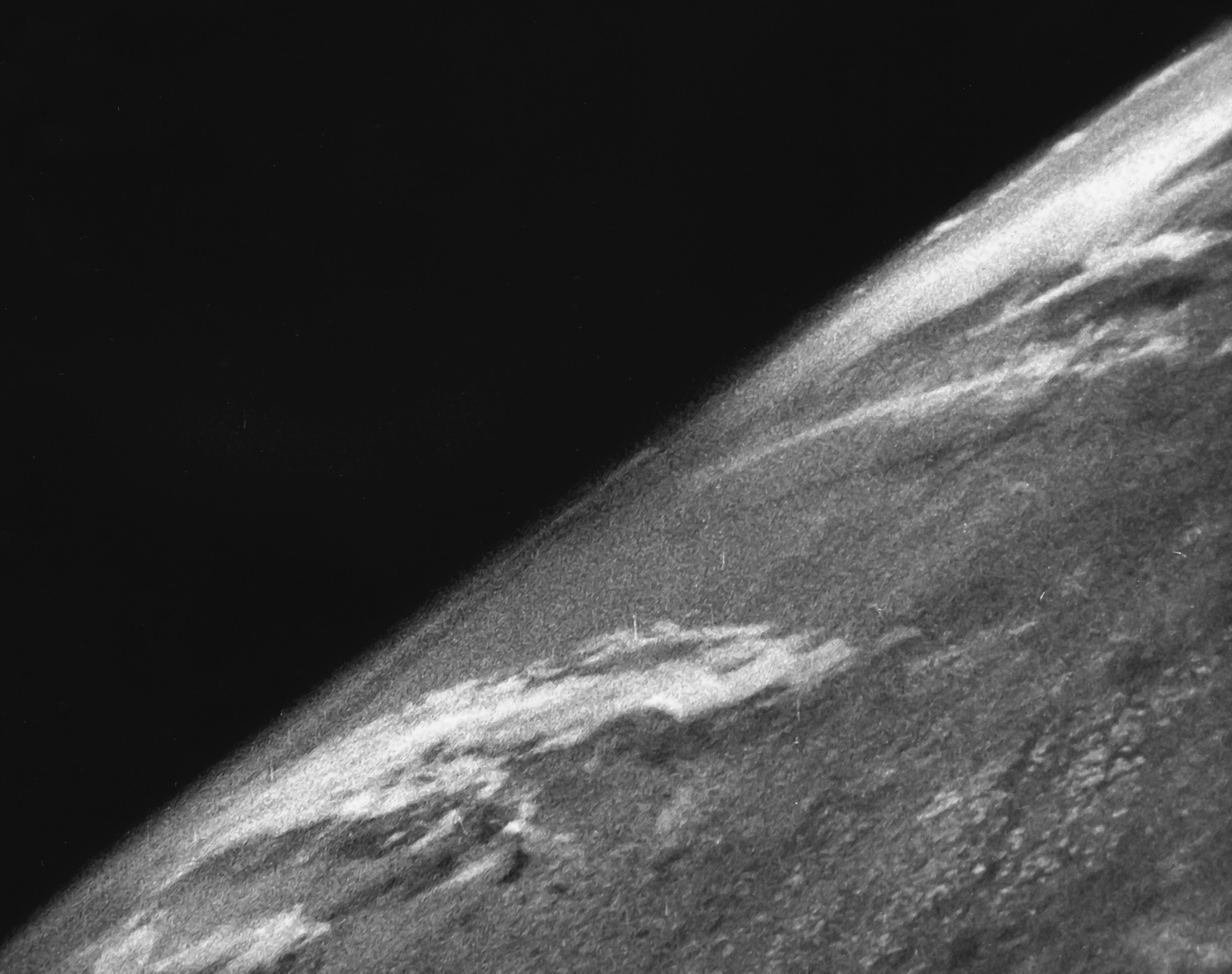
Satellite Imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell images by licensing them to governments and businesses such as Apple Maps and Google Maps. History The first images from space were taken on Sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital flights. The U.S-launched V-2 flight on October 24, 1946, took one image every 1.5 seconds. With an Apsis, apogee of 65 miles (105 km), these photos were from five times higher than the previous record, the 13.7 miles (22 km) by the Explorer II balloon mission in 1935. The first satellite (orbital) photographs of Earth were made on August 14, 1959, by the U.S. Explorer 6. The first satellite photographs of the Moon might have been made on October 6, 1959, by the Soviet satellite Luna 3, on a mission to photograph the far side of the Moon. The Blue Marble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrotropical Ecoregions
The Afrotropical realm is one of Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the majority of the Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, southern Iran and extreme southwestern Pakistan, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region. Major ecological regions Most of the Afrotropic, with the exception of Africa's southern tip, has a tropical climate. A broad belt of deserts, including the Atlantic and Sahara deserts of northern Africa and the Arabian Desert of the Arabian Peninsula, separate the Afrotropic from the Palearctic realm, which includes northern Africa and temperate Eurasia. Sahel and Sudan South of the Sahara, two belts of tropical grassland and savanna run east and west across the continent, from the Atlantic Ocean to the Ethiopian Highlands. Immediately south of the Sahara lies the Sahel belt, a transitional zone of semi-arid short grassland and vachellia sav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afromontane Forests
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands. Geography Afromontane communities occur above elevation near the equator, and as low as elevation in the Knysna-Amatole montane forests of South Africa. Afromontane forests are generally cooler and more humid than the surrounding lowlands. The Afromontane archipelago mostly follows the East African Rift from the Red Sea to Zimbabwe, with the largest areas in the Ethiopian Highlands, the Albertine Rift Mountains of Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Tanzania, and the Eastern Arc highlands of Kenya and Tanzania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afromontane Ecoregions
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands. Geography Afromontane communities occur above elevation near the equator, and as low as elevation in the Knysna-Amatole montane forests of South Africa. Afromontane forests are generally cooler and more humid than the surrounding lowlands. The Afromontane archipelago mostly follows the East African Rift from the Red Sea to Zimbabwe, with the largest areas in the Ethiopian Highlands, the Albertine Rift Mountains of Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Tanzania, and the Eastern Arc highlands of Kenya and Tanzania. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Guinean Forests
The Lower Guinean forests is region of coastal tropical moist broadleaf forest in West Africa, extending along the eastern coast of the Gulf of Guinea from eastern Benin through Nigeria and Cameroon. The Dahomey Gap, a region of savanna and dry forest in Togo and Benin, divides the Lower Guinean forests from the Upper Guinean forests to the west, which extend along the western coast of the Gulf of Guinea from Togo to Liberia and north to Guinea. To the north and northeast, the Lower Guinean forests transition to the drier inland Guinean forest–savanna mosaic and Northern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic and to the southeast by the Congolian Coastal forests, whose boundary is the Sanaga River in Cameroon.Linder, H. Peter, Helen M. de Klerk Julia Born et al. (2012). "The partitioning of Africa: statistically defined biogeographical regions in sub‐Saharan Africa". ''Journal of Biogeography'' Volume 39, Issue 7 May 2012/ref> The Lower Guinean forests share many biotic affinities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pico Basilé National Park
The Pico Basilé National Park ( es, Parque nacional del Pico Basilé) is a protected area with the status of national park on the island of Bioko in the northern part of the African country of Equatorial Guinea, near the Gulf of Guinea, in the Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe .... It stands out for its diversity of landscapes and vegetation and especially for its population of primates, that are threatened by the illegal hunting. Although in 2007 the government of that country prohibited the hunting of diverse species, international organizations have shown concern for the noncompliance of the decree. The park is named after the Basilé peak, the highest in Equatorial Guinea, with 3011 m (9878 feet). Administratively it is included within the jurisdic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Cameroon National Park
Mount Cameroon is an active volcano in the South West region of Cameroon next to the city of Buea near the Gulf of Guinea. Mount Cameroon is also known as Cameroon Mountain or Fako (the name of the higher of its two peaks) or by its indigenous name ''Mongo ma Ndemi'' ("Mountain of Greatness"). It is the highest point in sub-Saharan western and central Africa, the fourth-most prominent peak in Africa, and the 31st-most prominent in the world. The mountain is part of the area of volcanic activity known as the Cameroon Volcanic Line, which also includes Lake Nyos, the site of a disaster in 1986. The most recent eruption occurred on February 3, 2012. Description Mount Cameroon is one of Africa's largest volcanoes, rising to above the coast of west Cameroon. It rises from the coast through tropical rainforest to a bare summit, which is cold, windy, and occasionally dusted with snow. The massive steep-sided volcano of dominantly basaltic-to-trachybasaltic composition forms a vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werneria Preussi
''Werneria preussi'' is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in southwestern Cameroon Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ... and—highly disjunctly and based on a more than 100 years old record—in Togo. Some sources also mention Equatorial Guinea. Its natural habitats are rocky streams and waterfalls in submontane forests, but it also occurs in degraded secondary habitats. It lives exclusively in and around water and breeds in streams. It is locally common but probably threatened by habitat loss, loss of its forest caused by agricultural encroachment and human settlement. References Werneria, preussi Amphibians of Cameroon Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Amphibians described in 1893 {{Bufonidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
