|
Mount Boppy Gold Mine
Mount Boppy Gold Mine was a gold mine at Canbelego, New South Wales, Australia. The original Mount Boppy Gold Mine operated from 1901 to 1922. It was, at the time, regarded as being the largest gold producer in New South Wales. The gold-bearing deposit that became the Mount Boppy Gold Mine was discovered, in September 1896. The discoverer of the gold-bearing lode, a prospector, Michael Delaney O'Grady, lived near the Boppy Mount railway station, on the Cobar railway line. It was while walking back to his home, in September 1896, that he recognised the lode, where it was exposed in a watercourse. After dollying a sample of the rock, he found it was rich in gold. The lode initially was worked by O'Grady and his partner Thomas Reid, under a mining claim known as 'Hidden Treasure'. In November 1897, the claim, and another 10 acres of mining claim land owned by other prospectors, were sold to the Anglo-Australian Exploration Company, for £1,000. The new owners sank four shafts, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canbelego
Canbelego is a village in the Orana region of New South Wales, Australia. It is now virtually a ghost town but was once a much larger settlement associated with the Mount Boppy Gold Mine. At the 2016 census, the population of Canbelego, including its surrounding area, was 39, but the village itself had only four residents in early 2020. In 1905, the population had been around 1,500, with around 300 of these being employees of the mine. Between 1907 and 1917, the population was around 2,000. Location It is located approximately 640 km north-west of Sydney, 50 km east of Cobar and 5km south of the nearest point on the Barrier Highway. History Aboriginal and early settler history The area now known as Canbelego is part of the traditional lands of the Wangaaypuwan dialect speakers (also known as Wangaibon) of the Ngiyampaa people. The Surveyor-General Thomas Mitchell and his expedition had camped and obtained water, in early 1845, at a place that he called "Canbelego" but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Cyanidation
Gold cyanidation (also known as the cyanide process or the MacArthur-Forrest process) is a hydrometallurgical technique for extracting gold from low-grade ore by converting the gold to a water-soluble coordination complex. It is the most commonly used leaching process for gold extraction. Cyanidation is also widely used in the extraction of silver, usually after froth flotation. Production of reagents for mineral processing to recover gold represents more than 70% of cyanide consumption globally. Other metals are recovered from the process include copper, zinc, and silver, but gold is the main driver of this technology. Due to the highly poisonous nature of cyanide, the process is controversial and its use is even banned in some parts of the world. Cyanide can be safely used in the gold mining industry. A key feature for safe use of cyanide is to ensure adequate pH control at an alkaline pH level above 10.5. At industrial scale, pH control is mainly achieved using lime, as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrightville, New South Wales
Wrightville was a mining village in the Orana region of New South Wales, Australia. Once it was a significant settlement, with its own municipal government, public school, convent school, post office, police station, four hotels, and railway connection. At its peak, around 1907, its population probably reached 2,000 people. Its site and that of the adjacent former village of Dapville are now an uninhabited part of Cobar. Location Wrightville was located on the road to Hillston, about four kilometers south-east of Cobar. This road is now known as Kidman Way. The northernmost part of the village straddled the main road to Hillston, but the bulk of Wrightville lay to the south and west of that main road. The branch railway, after it turned south from the road to Hillston, ran just outside the eastern edge of the village. On the eastern edge of the village, toward its southern end, was the Occidental Gold Mine (later the New Occidental Gold Mine), and just to the village's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
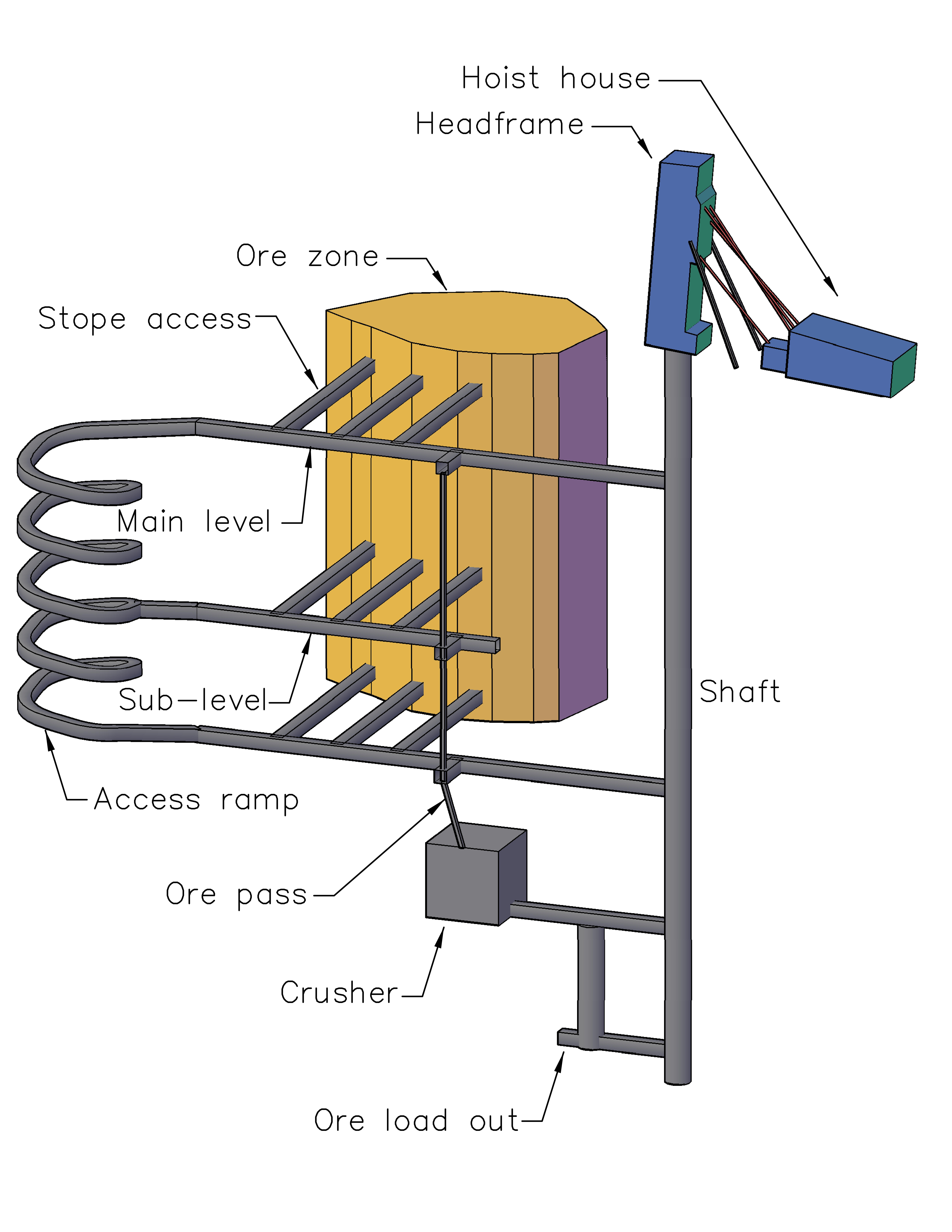
Hard Rock Mining
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the same techniques used to excavate ores of gems, such as diamonds and rubies. Soft-rock mining refers to the excavation of softer minerals, such as salt, coal, and oil sands. Mine access Underground access Accessing underground ore can be achieved via a decline (ramp), inclined vertical shaft or adit. *Declines can be a spiral tunnel which circles either the flank of the deposit or circles around the deposit. The decline begins with a box cut, which is the portal to the surface. Depending on the amount of overburden and quality of bedrock, a galvanized steel culvert may be required for safety purposes. They may also be started into the wall of an open cut mine. *Shafts are vertical excavations sunk adjacent to an ore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailings
In mining, tailings are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different to overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that overlies an ore or mineral body and is displaced during mining without being processed. The extraction of minerals from ore can be done two ways: placer mining, which uses water and gravity to concentrate the valuable minerals, or hard rock mining, which pulverizes the rock containing the ore and then relies on chemical reactions to concentrate the sought-after material. In the latter, the extraction of minerals from ore requires comminution, i.e., grinding the ore into fine particles to facilitate extraction of the target element(s). Because of this comminution, tailings consist of a slurry of fine particles, ranging from the size of a grain of sand to a few micrometres. Mine tailings are usually produced from the mill in slurry form, which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish Water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '' brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more often expressed as 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (‰), which is a specific gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Mill
A stamp mill (or stamp battery or stamping mill) is a type of mill machine that crushes material by pounding rather than grinding, either for further processing or for extraction of metallic ores. Breaking material down is a type of unit operation. Description A stamp mill consists of a set of heavy steel (iron-shod wood in some cases) stamps, loosely held vertically in a frame, in which the stamps can slide up and down. They are lifted by cams on a horizontal rotating shaft. As the cam moves from under the stamp, the stamp falls onto the ore below, crushing the rock, and the lifting process is repeated at the next pass of the cam. Each one frame and stamp set is sometimes called a "battery" or, confusingly, a "stamp" and mills are sometimes categorised by how many stamps they have, i.e. a "10 stamp mill" has 10 sets. They usually are arranged linearly, but when a mill is enlarged, a new line of them may be constructed rather than extending the line. Abandoned mill sites (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfide Mineral
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the arsenides, the antimonides, the bismuthinides, the sulfarsenides and the sulfosalts.http://www.minerals.net/mineral/sort-met.hod/group/sulfgrp.htm Minerals.net Dana Classification, SulfidesKlein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, Jr., 1986, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', Wiley, 20th ed., pp 269-293 Sulfide minerals are inorganic compounds. Minerals Common or important examples include: * Acanthite *Chalcocite *Bornite * Galena * Sphalerite *Chalcopyrite *Pyrrhotite *Millerite *Pentlandite *Covellite *Cinnabar *Realgar *Orpiment *Stibnite *Pyrite *Marcasite *Molybdenite Sulfarsenides: *Cobaltite *Arsenopyrite *Gersdorffite Sulfosalts: *Pyrargyrite *Proustite *Tetrahedrite *Tennantite *Enargite *Bournonite * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daily Telegraph (Sydney)
''The Daily Telegraph'', also nicknamed ''The Tele'', is an Australian tabloid newspaper published by Nationwide News Pty Limited, a subsidiary of News Corp Australia, itself a subsidiary of News Corp. It is published Monday through Saturday and is available throughout Sydney, across most of regional and remote New South Wales, the Australian Capital Territory and South East Queensland. A 2013 poll conducted by Essential Research found that the ''Telegraph'' was Australia's least-trusted major newspaper, with 49% of respondents citing "a lot of" or "some" trust in the paper. Amongst those ranked by Nielsen, the ''Telegraph'' website is the sixth most popular Australian news website with a unique monthly audience of 2,841,381 readers. History ''The Daily Telegraph'' was founded in 1879, by John Mooyart Lynch, a former printer, editor and journalist who had once worked on the ''Melbourne Daily Telegraph''. Lynch had failed in an attempt to become a politician and was lookin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobar Railway Line
The Cobar railway line is a railway line in New South Wales, Australia. It branches west towards Cobar from the Main West Line at Nyngan. The Main West once continued northwest to Bourke but is now closed beyond Nyngan. However, copper concentrates from mines near Hermidale and Cobar are still railed on this line to ports on the New South Wales coast. The Cobar line opened on 1 July 1892, and continues to carry wheat and ore. Passenger services ceased on 22 September 1975. Cobar railway station has been redeveloped into a community facility. History The early development of Cobar was directly associated with the discovery of copper in the area. Aborigine guides showed a low hill, with outcrops of reddish oxide of ochre, to a party of tank-sinkers in 1870. These three men noticed that the rocks had been streaked green and blue. Samples collected were found to contain carbonate of copper. An area of 16.2ha was secured under a Mineral Conditional Purchase. In the middle of 1871, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)