|
Morrow Field
Norton Air Force Base (1942–1994) was a United States Air Force facility east of downtown San Bernardino in San Bernardino County, California. Overview For the majority of its operational lifetime, Norton was a logistics depot and heavy-lift transport facility for a variety of military aircraft, equipment and supplies as part of Air Materiel/Air Force Logistics Command (1946–1966), then as part of Military Airlift/Air Mobility Command (1966–1994). Major secondary missions of Norton Air Force Base was as Headquarters Air Defense Command for Southern California, during the 1950s and 1960s. The Air Force Audio-Visual Center produced air force films for training and public relations. The ''Air Force Now'' film, shown at monthly commander's calls at air force bases around the world was produced at Norton. Norton hosted numerous Air Force Reserve transport units. The Office of the Inspector General was located at Norton, as was the Directorate of Aerospace Safety and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Mobility Command
Air Mobility Command (AMC) is a major command (MAJCOM) of the U.S. Air Force. It is headquartered at Scott Air Force Base, Illinois, east of St. Louis, Missouri. Air Mobility Command was established on 1 June 1992, and was formed from elements of the inactivated Military Airlift Command (MAC) and Strategic Air Command (SAC). AMC melded MAC's worldwide airlift system of primarily C-5 Galaxy, C-141 Starlifter (later replaced by C-17 Globemaster III beginning in 1995), and C-130 Hercules airlift aircraft with SAC's tanker force of KC-135 Stratotanker and KC-10 Extender aerial refueling aircraft, the latter air refueling aircraft having been freed from their strategic nuclear strike commitment to SAC's B-52 Stratofortress and B-1 Lancer bomber fleet by the end of the Cold War and the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Overview Air Mobility Command's mission is to provide global air mobility. The command also plays a crucial role in providing humanitarian support at home and arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
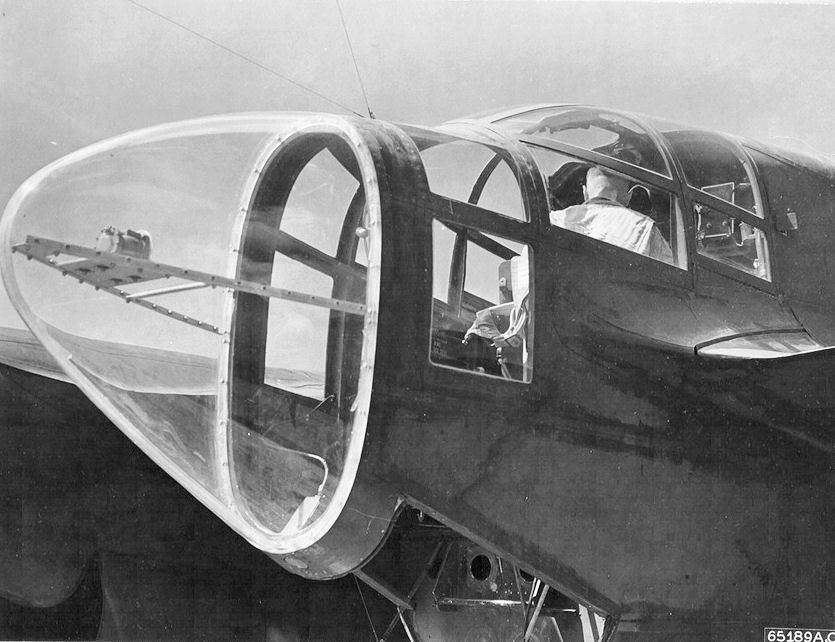
Boeing B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the B-17 Flying Fortress, the Superfortress was designed for high-altitude strategic bombing, but also excelled in low-altitude night incendiary bombing, and in dropping naval mines to blockade Japan. B-29s dropped the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the only aircraft ever to drop nuclear weapons in combat. One of the largest aircraft of World War II, the B-29 was designed with state-of-the-art technology, which included a pressurized cabin, dual-wheeled tricycle landing gear, and an analog computer-controlled fire-control system that allowed one gunner and a fire-control officer to direct four remote machine gun turrets. The $3 billion cost of design and production (equivalent to $ billion today), far exceeding the $1.9 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas C-47 Skytrain
The Douglas C-47 Skytrain or Dakota (RAF, RAAF, RCAF, RNZAF, and SAAF designation) is a military transport aircraft developed from the civilian Douglas DC-3 airliner. It was used extensively by the Allies during World War II and remained in front-line service with various military operators for many years.Parker 2013, pp. 13, 35, 37, 39, 45-47. Design and development The C-47 differed from the civilian DC-3 by way of numerous modifications, including being fitted with a cargo door, hoist attachment and strengthened floor - along with a shortened tail cone for glider-towing shackles, and an astrodome in the cabin roof.Wilson, Stewart. ''Aircraft of WWII''. Fyshwick, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd., 1998. . During World War II, the armed forces of many countries used the C-47 and modified DC-3s for the transport of troops, cargo, and wounded. The U.S. naval designation was R4D. More than 10,000 aircraft were produced in Long Beach and Santa Monica, California, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop P-61 Black Widow
The Northrop P-61 Black Widow is a twin-engine United States Army Air Forces fighter aircraft of World War II. It was the first operational U.S. warplane designed as a night fighter, and the first aircraft designed specifically as a night fighter. Named for the North American spider ''Latrodectus mactans'', it was an all-metal, twin-engine, twin-boom design armed with four forward-firing 20 mm (.79 in) Hispano M2 autocannon in the lower fuselage, and four M2 Browning machine guns in a dorsal gun turret. Developed during the war, the first test flight was made on May 26, 1942, with the first production aircraft rolling off the assembly line in October 1943. Although not produced in the large numbers of its contemporaries, the Black Widow was operated effectively as a night fighter by United States Army Air Forces squadrons in the European Theater, Pacific Theater, China Burma India Theater, and Mediterranean Theater during World War II. It replaced earlier British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic P-47 Thunderbolt
The Republic P-47 Thunderbolt is a World War II-era fighter aircraft produced by the American company Republic Aviation from 1941 through 1945. It was a successful high-altitude fighter and it also served as the foremost American fighter-bomber in the ground-attack role. Its primary armament was eight .50-caliber machine guns, and it could carry 5-inch rockets or a bomb load of . When fully loaded, the P-47 weighed up to 8 tons, making it one of the heaviest fighters of the war. The Thunderbolt was effective as a short-to medium-range escort fighter in high-altitude air-to-air combat and ground attack in both the European and Pacific theaters. The P-47 was designed around the powerful Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp 18-cylinder radial engine, which also powered two U.S. Navy/U.S. Marine Corps fighters, the Grumman F6F Hellcat and the Vought F4U Corsair. An advanced turbosupercharger system ensured the aircraft's eventual dominance at high altitudes, while also influencing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive twin-boom design with a central nacelle containing the cockpit and armament. Along with its use as a general fighter, the P-38 was used in various aerial combat roles, including as a highly effective fighter-bomber, a night fighter, and a long-range escort fighter when equipped with drop tanks. The P-38 was also used as a bomber-pathfinder, guiding streams of medium and heavy bombers, or even other P-38s equipped with bombs, to their targets."P-38 Lightning" National Museum of the United States Air Force. Retrieved 21 January ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American P-51 Mustang
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter aircraft, fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in April 1940 by a team headed by James H. Kindelberger of North American Aviation (NAA) in response to a requirement of the British Purchasing Commission. The Purchasing Commission approached North American Aviation to build Curtiss P-40 Warhawk, Curtiss P-40 fighters under license for the Royal Air Force (RAF). Rather than build an old design from another company, North American Aviation proposed the design and production of a more modern fighter. The prototype NA-73X airframe was rolled out on 9 September 1940, 102 days after the contract was signed, and first flew on 26 October. The Mustang was designed to use the Allison V-1710 engine, which had limited high-altitude performance in its earlier variants. The aircraft was first flown operationally by the RAF a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Public Utilities Commission
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC or PUC) is a regulatory agency that regulates privately owned public utilities in the state of California, including electric power, telecommunications, natural gas and water companies. In addition, the CPUC regulates common carriers, including household goods movers, passenger transportation companies such as limousine services, and rail crossing safety. The CPUC has headquarters in the Civic Center district of San Francisco, and field offices in Los Angeles and Sacramento. History On April 1, 1878, the California Office of the Commissioner of Transportation was created. During the 19th century, public concerns over the unbridled power of the Southern Pacific Railroad grew to the point that a three-member Railroad Commission was established, primarily to approve transportation prices. However, the Southern Pacific quickly dominated this commission to its advantage, and public outrage re-ignited. As experience with public regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Bernardino Daily Sun
''The San Bernardino Sun'' is a paid daily newspaper in San Bernardino County. Founded in 1894, it has significant circulation in neighboring Riverside County, and serves most of the Inland Empire in Southern California, with a circulation area spanning from the border of Los Angeles and Orange counties to the west, east to Yucaipa, north to the San Bernardino Mountain range and south to the Riverside County line. Its local competitor is ''The Press-Enterprise'' in Riverside. It publishes the annual PrepXtra high school football magazine with capsules and schedules for all schools in Pomona Valley and San Bernardino Counties. Times Mirror, owner of the ''Los Angeles Times'', bought the paper in 1964, but was ordered to sell it due to antitrust concerns. Gannett purchased it in 1968, and MediaNews Group took control of it in 1999, making it a sister newspaper to the ''Times rival, the ''Los Angeles Daily News''. It is a member of the Southern California News Group The Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colton, California
Colton is a city in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Nicknamed "Hub City", Colton is located in the Inland Empire region of the state and is a suburb of San Bernardino, California, San Bernardino, approximately south of the city's Downtown San Bernardino, downtown. The population of Colton is 52,154 according to the 2010 census, up from 47,662 at the 2000 census. Colton is the site of Colton Crossing, which was one of the busiest at-grade rail transport, railroad crossings in the United States. The crossing was installed in 1882 by the California Southern Railroad to cross the Southern Pacific Railroad tracks while building northward from San Diego. As a result of railroad acquisitions and mergers, this became the point at which the Burlington Northern Santa Fe's "Southern Transcontinental Route" crossed the Union Pacific's "Sunset Route". As traffic on each line began to soar in the mid-1990s, fueled largely by the vast increase in imports passing through the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Air Lines
Western Airlines was a major airline based in California, operating in the Western United States including Alaska and Hawaii, and western Canada, as well as to New York City, Boston, Washington, D.C., and Miami and to Mexico City, London and Nassau. Western had hubs at Los Angeles International Airport, Salt Lake City International Airport, and the former Stapleton International Airport in Denver. Before it merged with Delta Air Lines in 1987 it was headquartered at Los Angeles International Airport (LAX). Throughout the company's history, their slogan was "Western Airlines...The Only Way to Fly!" History Western Air Express In 1925, the United States Postal Service began to give airline contracts to carry airmail throughout the country. Western Airlines first incorporated in 1925 as ''Western Air Express'' by Harris Hanshue. It applied for, and was awarded, the 650-mile long Contract Air Mail Route #4 (CAM-4) from Salt Lake City, Utah, to Los Angeles. On 17 April 1926, Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |