|
Morningness–eveningness Questionnaire
The morningness–eveningness questionnaire (MEQ) is a self-assessment questionnaire developed by researchers James A. Horne and Olov Östberg in 1976. Its main purpose is to measure whether a person's circadian rhythm (biological clock) produces peak alertness in the morning, in the evening, or in between. The original study showed that the subjective time of peak alertness correlates with the time of Thermoregulation#Variations due to circadian rhythms, peak body temperature; morning types (Lark (person), early birds) have an earlier temperature peak than evening types (Night owl (person), night owls), with intermediate types having temperature peaks between the morning and evening chronotype groups. The MEQ is widely used in psychological and medical research and has been professionally cited more than 4,000 times. MEQ questions The standard MEQ consists of 19 multiple-choice questions, each having four or five response options. Some example questions are: Responses to the q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Questionnaire
A questionnaire is a research Research is "creativity, creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular att ... instrument that consists of a set of questions (or other types of prompts) for the purpose of gathering information from respondents through survey or statistical study. A research questionnaire is typically a mix of close-ended questions and open-ended questions. Open-ended, long-term questions offer the respondent the ability to elaborate on their thoughts. The Research questionnaire was developed by the Statistical Society of London in 1838. Although questionnaires are often designed for statistics, statistical analysis of the responses, this is not always the case. Questionnaires have advantages over some other types of statistical survey, surveys in that they are cheap, do not require as much eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the environment (Entrainment (chronobiology), entrained by the environment). These 24-hour rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and they have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ''wikt:circa#Latin, circa'', meaning "approximately", and ''dies'', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous, they are adjusted to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers (German for "time givers"), which include light, temperature and redox cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature as its own body temperature, thus avoiding the need for internal thermoregulation. The internal thermoregulation process is one aspect of homeostasis: a state of dynamic stability in an organism's internal conditions, maintained far from thermal equilibrium with its environment (the study of such processes in zoology has been called physiological ecology). If the body is unable to maintain a normal temperature and it increases significantly above normal, a condition known as hyperthermia occurs. Humans may also experience lethal hyperthermia when the wet bulb temperature is sustained above for six hours. The opposite condition, when body temperature decreases below normal levels, is known as hypothermia. It results when the homeostatic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lark (person)
A lark, early bird, morning person, or (in Scandinavian countries) an A-person, is a person who usually gets up early in the morning and goes to bed early in the evening. The term relates to the birds known as larks, which are known to sing before dawn. Human "larks" may sleep from around 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. (or earlier), and tend to feel most energetic just after they get up in the morning. They are thus well-suited for working the day shift. The opposite of the lark is the owl, often awake at night. A person called a ''night owl'' is someone who usually stays up late and may feel most awake in the evening and at night. Researchers have traditionally used the terms morningness and ''eveningness'' to describe these two chronotypes. Charting chronotypes Till Roenneberg, a chronobiologist in Munich, has mapped the circadian rhythms of more than 200,000 people. Biological processes, including sleep-wake patterns, that display an oscillation of about 24 hours are called circadian rhyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Owl (person)
A night owl, evening person or simply owl, is a person who tends to stay up until late at night, or to the very early hours of the morning. Night owls who are involuntarily unable to fall asleep for several hours after a normal time may have delayed sleep phase disorder. The opposite of a night owl is an early bird – a lark as opposed to an owl – which is someone who tends to begin sleeping at a time that is considered early and also wakes early. Researchers traditionally use the terms ''morningness'' and eveningness for the two chronotypes or diurnality and nocturnality in animal behavior. In several countries, especially in Scandinavia, early birds are called ''A-people'' and a night owl is called a B-person. History While staying up after dark was considered a negative trait, this changed in 17th and 18th century Europe (and subsequently spread beyond) due to the development and implementation of artificial lighting: more domestic lights, added street lighting, and adap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronotype
A chronotype is the behavioral manifestation of underlying circadian rhythm's myriad of physical processes. A person's chronotype is the propensity for the individual to sleep at a particular time during a 24-hour period. ''Eveningness'' (delayed sleep period; most active and alert in the evening) and ''morningness'' (advanced sleep period; most active and alert in the morning) are the two extremes with most individuals having some flexibility in the timing of their sleep period. However, across development there are changes in the propensity of the sleep period with pre-pubescent children preferring an advanced sleep period, adolescents preferring a delayed sleep period and many elderly preferring an advanced sleep period. The causes and regulation of chronotypes, including developmental change, individual propensity for a specific chronotype, and flexible versus fixed chronotypes have yet to be determined. However, research is beginning to shed light on these questions, such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two embryos, or ''dizygotic'' ('non-identical' or 'fraternal'), meaning that each twin develops from a separate egg and each egg is fertilized by its own sperm cell. Since identical twins develop from one zygote, they will share the same sex, while fraternal twins may or may not. In rare cases twins can have the same mother and different fathers (heteropaternal superfecundation). In contrast, a fetus that develops alone in the womb (the much more common case, in humans) is called a ''singleton'', and the general term for one offspring of a multiple birth is a ''multiple''. Unrelated look-alikes whose resemblance parallels that of twins are referred to as doppelgängers. Statistics The human twin birth rate in the United States rose 76% from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Ability
Cognitive skills, also called cognitive functions, cognitive abilities or cognitive capacities, are brain-based skills which are needed in acquisition of knowledge, manipulation of information and reasoning. They have more to do with the mechanisms of how people learn, remember, solve problems and pay attention, rather than with actual knowledge. Cognitive skills or functions encompass the domains of perception, attention, memory, learning, decision making, and language abilities. Specialisation of functions Cognitive science has provided theories of how the brain works, and these have been of great interest to researchers who work in the empirical fields of brain science. A fundamental question is whether cognitive functions, for example visual processing and language, are autonomous modules, or to what extent the functions depend on each other. Research evidence points towards a middle position, and it is now generally accepted that there is ''a degree'' of modularity in aspects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat whereas the latter is defined as the emotional response to a real threat. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, somatic complaints, and rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight or flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of future threat including dread. People facing anxiety may withdraw fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melatonin
Melatonin is a natural product found in plants and animals. It is primarily known in animals as a hormone released by the pineal gland in the brain at night, and has long been associated with control of the sleep–wake cycle. In vertebrates, melatonin is involved in synchronizing circadian rhythms, including sleep–wake timing and blood pressure regulation, and in control of seasonal rhythmicity including reproduction, fattening, moulting and hibernation. Many of its effects are through activation of the melatonin receptors, while others are due to its role as an antioxidant. In plants, it functions to defend against oxidative stress. It is also present in various foods. Melatonin was discovered in 1958. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, melatonin is used as a dietary supplement and medication in the treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia and circadian rhythm sleep disorders; for information on melatonin as a supplement and medication, see the melatoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Routine Protocol
A constant routine protocol is a common method used in human circadian rhythm research to study internally generated, or endogenous, circadian rhythms without the effect of external, or exogenous, influences. In the method, subjects are kept in constant conditions for at least 24 hours. These include constant light and temperature, as well as constant semi-recumbent posture. In addition, subjects' food intake is evenly distributed throughout the protocol, and subjects are typically not allowed to sleep for the duration. While in these conditions, subjects are often assessed for a number of variables of interest. Two of the most common and best understood of these variables are core body temperature and melatonin. History The term was first coined by in 1978 after it was used in an experiment to determine the effects of jet lag independent of an individual's behavioral cycle - though the methods involved in a constant routine date back to at least 1947. The protocol arose from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
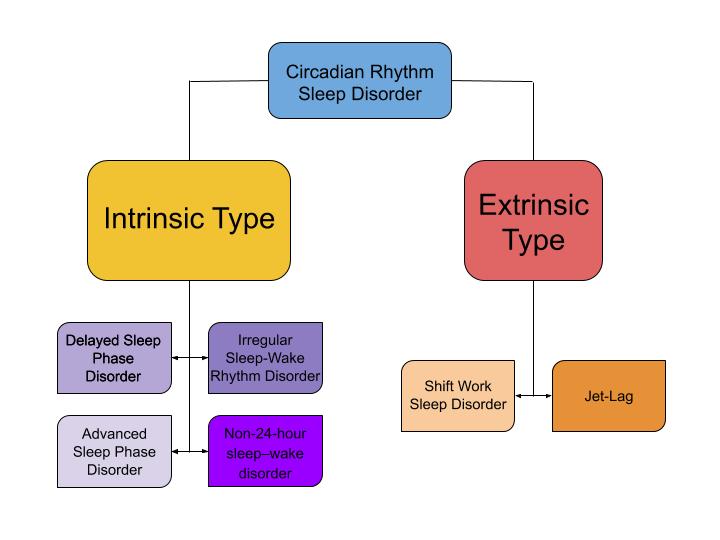
Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorder
Circadian rhythm sleep disorders (CRSD), also known as circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders (CRSWD), are a family of sleep disorders which affect the timing of sleep. CRSDs arise from a persistent pattern of sleep/wake disturbances that can be caused either by dysfunction in one's biological clock system, or by misalignment between one's endogenous oscillator and externally imposed cues. As a result of this mismatch, those affected by circadian rhythm sleep disorders have a tendency to fall asleep at unconventional time points in the day. These occurrences often lead to recurring instances of disturbed rest, where individuals affected by the disorder are unable to go to sleep and awaken at "normal" times for work, school, and other social obligations. Delayed sleep phase disorder, advanced sleep phase disorder, non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder and irregular sleep–wake rhythm disorder represents the four main types of CRSD. Overview Humans, like most living organisms, have v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |